Introduction
The debate between PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and DC (Direct Current) fans stands as a pivotal consideration for electronics engineers navigating the complexities of cooling solutions. As the demand for energy efficiency and noise reduction escalates, grasping the operational mechanisms and advantages of each fan type becomes imperative. The challenge, however, lies in discerning which fan technology – PWM or DC – will most effectively meet specific application needs while balancing performance and cost.
Understanding these distinctions not only aids in making informed decisions but also enhances the overall effectiveness of cooling systems in various applications. By delving into the intricacies of both technologies, engineers can better align their choices with project requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Define PWM and DC Fans: Core Principles and Functionality
In electronic systems, the choice between PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) units and DC (Direct Current) devices is often discussed in terms of dc vs pwm fan mode as two prevalent cooling solutions. Gagner-Toomey Associates emerges as a leading provider of innovative cooling solutions tailored for these applications. PWM blowers utilize a control method that adjusts the width of electrical pulses delivered to the motor, facilitating variable rate control. This capability allows the fan to operate at reduced speeds without compromising performance, making it ideal for applications that require quiet operation and energy efficiency.
Conversely, DC devices function by varying the voltage supplied to the motor, which directly influences the rotation rate. Typically, DC devices feature a simpler design, often comprising three pins for power, ground, and velocity control. While effective for basic cooling needs, their control in the dc vs pwm fan mode lacks the precision of PWM devices, potentially leading to less efficient operation in dynamic environments. Gagner-Toomey’s extensive portfolio includes a diverse range of DC input Tube Axial units and Centrifugal Blowers, optimized for performance and efficiency, catering to a wide array of applications in electronics and beyond.
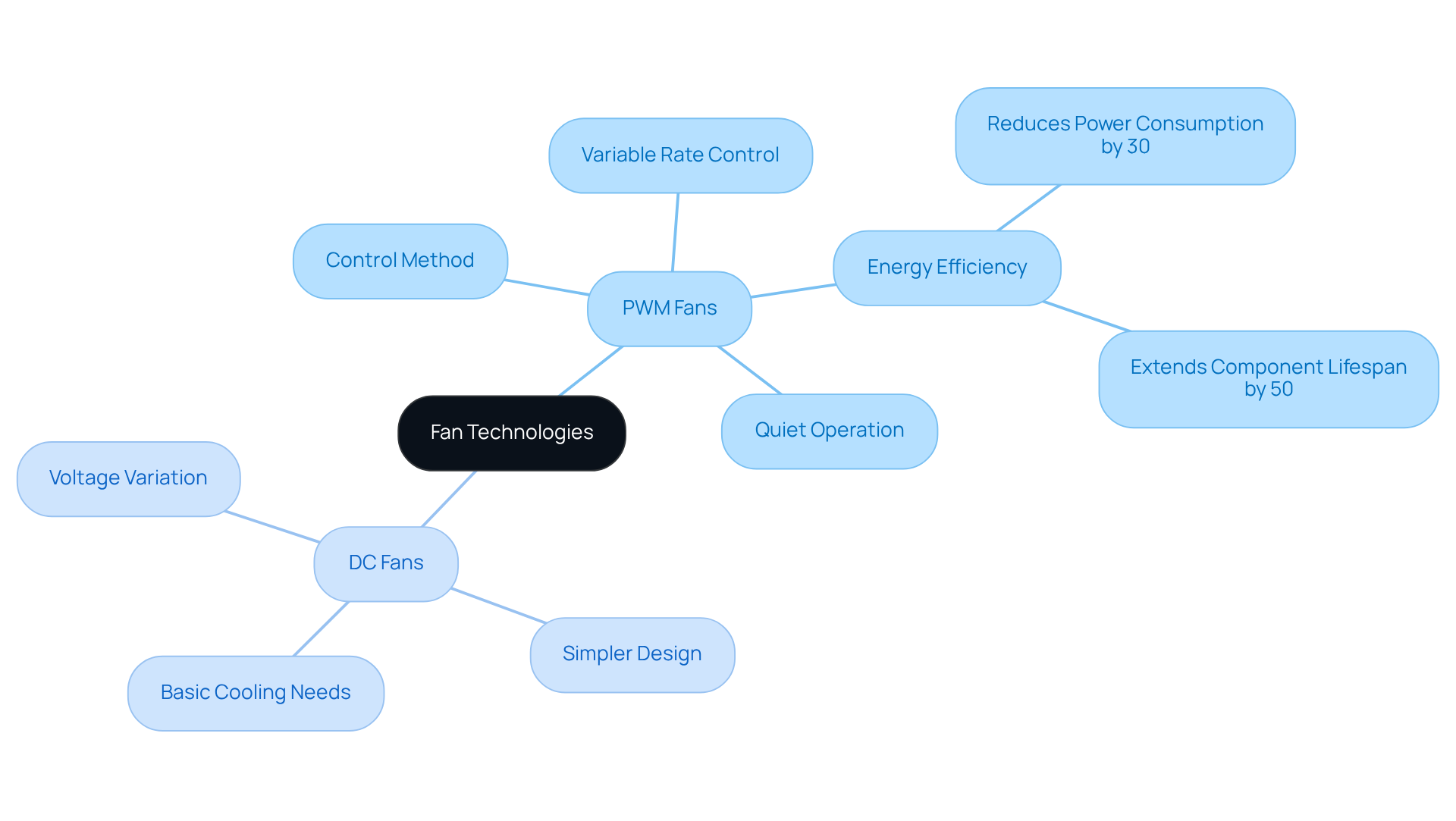
Compare Operational Mechanisms: PWM vs. DC Fans
The operational mechanisms of PWM and DC units differ significantly in their velocity control methods, highlighting the importance of understanding DC vs PWM fan mode for performance optimization. PWM cooling devices utilize a four-pin connector, where the fourth pin transmits a PWM signal that rapidly alternates the power supplied to the motor. This high-frequency switching enables precise speed adjustments, allowing PWM devices to operate efficiently at speeds as low as 20% of their maximum RPM. Such capability is particularly advantageous in applications that require dynamic cooling adjustments, enhancing energy efficiency and minimizing noise levels. Studies have shown that PWM devices can achieve a remarkable 60% reduction in power consumption and a noise decrease of approximately 6 dB compared to conventional models, making them an ideal choice for high-performance systems.
In contrast, DC units typically operate with a three-pin connector, where speed is regulated by adjusting the voltage supplied to the device, highlighting the differences in DC vs PWM fan mode. This method can lead to diminished operational efficiency, as DC devices often struggle to reach the same low speeds as their PWM counterparts. Furthermore, the steady voltage source in DC motors can result in increased noise levels at reduced speeds, causing vibrations and less smooth operation. As noted by David Hanrahan, advancements in fan speed control techniques are essential for effectively managing thermal conditions. While DC units are simpler and more cost-effective, they may not deliver the same level of performance and efficiency as PWM models, particularly when evaluating the DC vs PWM fan mode in high-demand environments. Implementing PWM technology not only enhances cooling efficiency but also provides significant economic advantages, reinforcing its value in modern electronic applications.

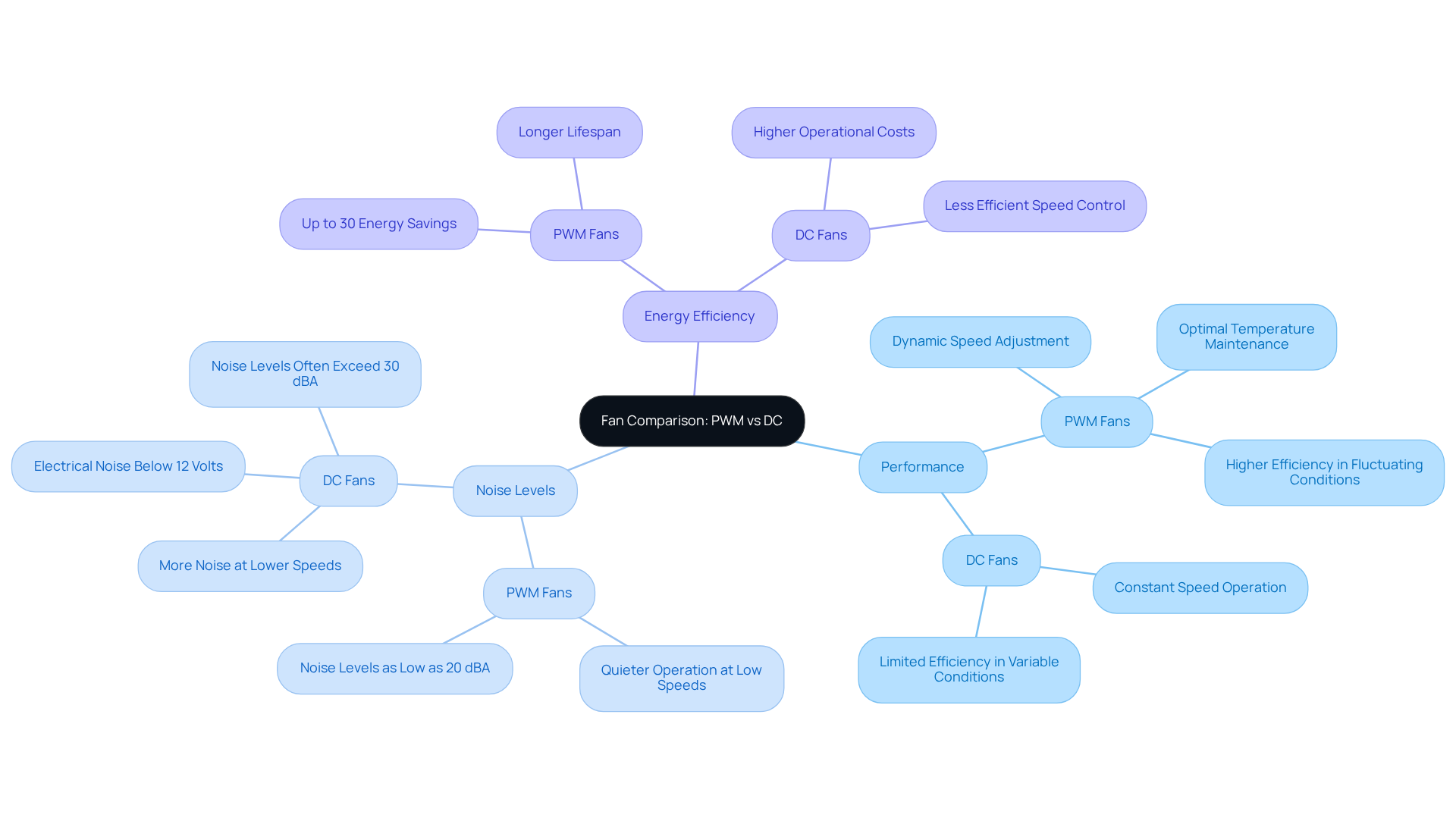
Evaluate Pros and Cons: Performance, Noise, and Energy Efficiency
Evaluating PWM and DC Fans: Key Factors to Consider
When it comes to selecting between PWM and DC fans, several critical factors demand your attention:
Performance
- PWM fans stand out in performance, thanks to their dynamic speed adjustment capabilities.
- This feature allows them to respond effectively to varying cooling needs, ensuring optimal temperature maintenance while minimizing noise levels.
- In contrast, DC devices typically operate at a constant rate unless connected to a controller, which can limit their efficiency in fluctuating thermal conditions.
- Moreover, PWM units can adjust their speeds based on real-time temperature measurements, significantly enhancing their effectiveness in regulating thermal situations.
Noise Levels
- When it comes to noise, PWM units generally operate more quietly, particularly at lower speeds.
- They can run at reduced RPMs without generating significant noise.
- On the other hand, DC fans may produce more noise at lower speeds due to their voltage control method, which can lead to vibrations and increased sound output.
- For example, PWM units can achieve noise levels as low as 20 dBA, while DC models often exceed 30 dBA under similar conditions.
- Additionally, DC fans can generate electrical noise when operating below 12 volts, which can be problematic in sensitive applications.
Energy Efficiency
- Energy efficiency is another area where PWM devices excel.
- They significantly reduce power consumption during low-load conditions.
- Research indicates that when considering DC vs PWM fan mode, PWM devices can achieve energy savings of up to 30% compared to traditional DC models, making them a more sustainable choice for long-term use.
- While DC fans may be less expensive initially, they often incur higher operational costs due to their less efficient speed control mechanisms, especially when operating below their optimal voltage.
- Furthermore, PWM units typically have a longer lifespan than DC units, contributing to their overall efficiency and durability.
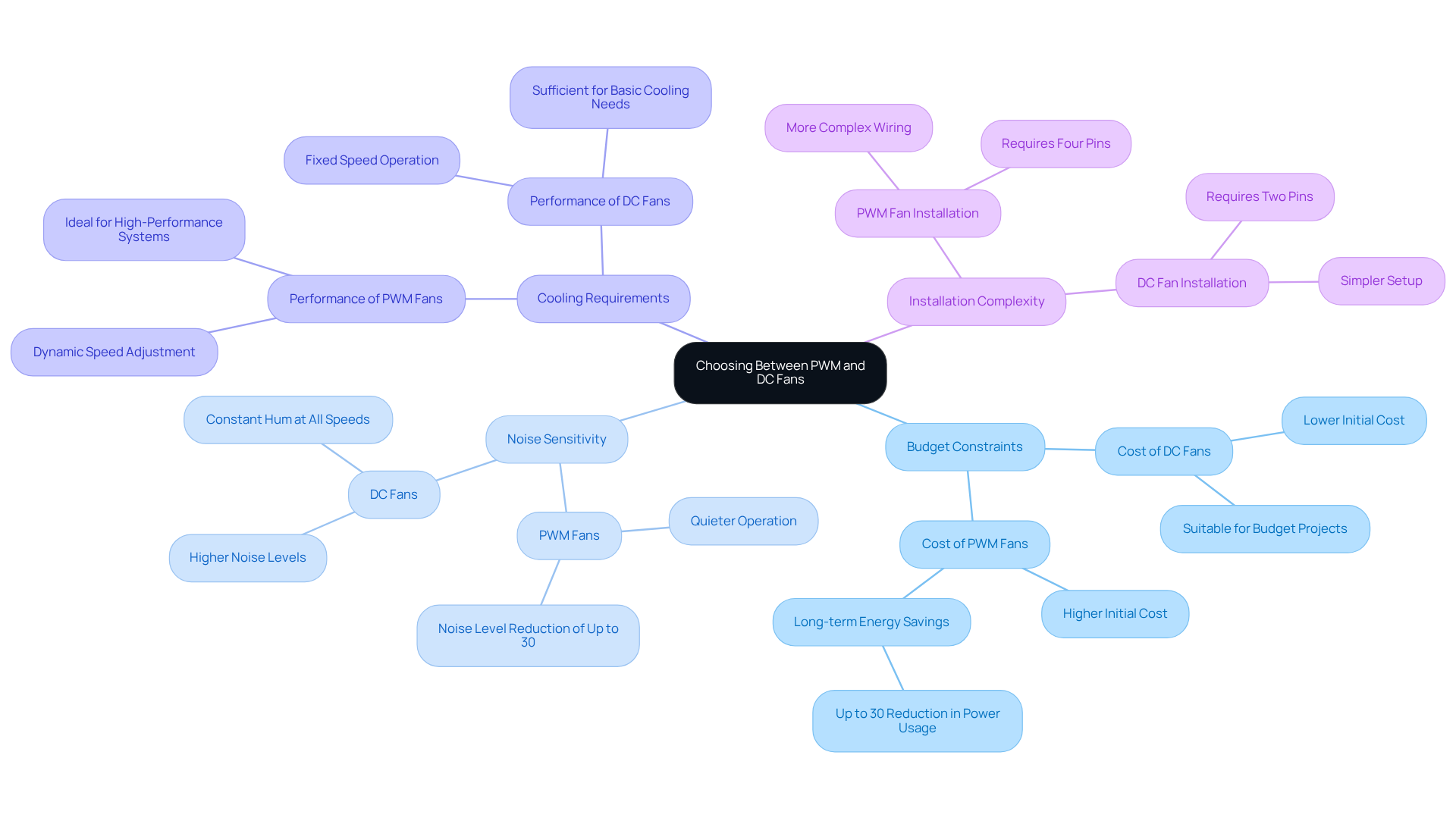
Assess Application Suitability: Choosing Between PWM and DC Fans
When choosing between PWM and DC fans, engineers must consider several critical factors:
-
Budget Constraints: For projects with limited budgets or older hardware, DC fans often provide a more economical solution. Their lower cost makes them suitable for less demanding applications while still delivering adequate cooling performance. However, it’s essential to recognize that PWM units can reduce power usage by up to 30% compared to conventional DC devices, potentially leading to long-term savings that offset their higher initial cost.
-
Noise Sensitivity: In environments where noise levels are paramount, such as audio equipment or medical devices, PWM cooling solutions emerge as the preferred option. They operate more quietly at reduced speeds, significantly lowering sound output and enhancing user comfort. Research shows that PWM technology can achieve noise level reductions of up to 30% in sensitive settings, making them ideal for applications where acoustic comfort is crucial.
-
Cooling Requirements: High-performance systems that demand precise temperature control benefit from PWM cooling devices. Their ability to dynamically adjust speeds enables optimal thermal management in scenarios like gaming PCs, servers, and industrial devices, where maintaining specific temperatures is vital. Data centers utilizing PWM devices have reported a decrease in Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) from 1.55 to 1.42, underscoring the effectiveness of PWM technology in challenging environments.
-
Installation Complexity: While DC devices are easier to install and may suffice for basic setups, PWM units offer advanced functionality through variable speed control. This added complexity is justified in systems that require enhanced cooling performance and efficiency. Engineers should also consider wiring configurations, as PWM models typically necessitate four pins for connection, compared to the two pins needed for DC devices.
In practical applications, engineers often grapple with the challenge of balancing budget constraints against performance needs. For instance, a project requiring significant thermal management may lean towards PWM devices when considering the DC vs PWM fan mode, despite their higher initial cost, as the long-term energy savings and superior cooling performance can justify the investment. Conversely, for budget-sensitive projects, DC motors may be the preferred option, delivering reliable performance without the need for advanced features. A case study highlights that while PWM fans are favored for their performance and efficiency, DC fans remain viable for budget-conscious projects, illustrating the narrowing price gap between these two technologies.
Conclusion
Choosing between PWM and DC fans is a pivotal decision for optimizing cooling solutions in electronic systems. Engineers must grasp the distinct functionalities and operational mechanisms of these two fan types to make informed choices that enhance performance, energy efficiency, and noise control.
Key comparisons throughout this discussion underscore the advantages of PWM fans. Their ability to dynamically adjust speeds leads to significant energy savings and quieter operation, making them ideal for high-performance applications. In contrast, while DC fans are simpler and more cost-effective, they often fall short in precision and efficiency. By evaluating performance, noise levels, and application suitability, engineers can identify the best fan type tailored to their specific needs.
Ultimately, the choice between PWM and DC fans should be dictated by the unique requirements of each project. For applications that demand precise thermal management and minimal noise, PWM fans stand out as the superior option. Conversely, in budget-constrained scenarios, DC fans may still deliver adequate performance. As technology evolves, understanding these distinctions will be crucial for engineers striving to enhance system efficiency and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PWM in the context of fans?
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a control method used in PWM blowers that adjusts the width of electrical pulses delivered to the motor, allowing for variable rate control and enabling the fan to operate at reduced speeds without compromising performance.
How do DC fans operate?
DC (Direct Current) fans operate by varying the voltage supplied to the motor, which directly influences the rotation rate. They typically have a simpler design with three pins for power, ground, and velocity control.
What are the advantages of using PWM fans over DC fans?
PWM fans provide more precise control over speed, allowing for quieter operation and energy efficiency, especially in applications that require variable speed settings.
What are the limitations of DC fans compared to PWM fans?
DC fans lack the precision of PWM devices in speed control, which can lead to less efficient operation in dynamic environments.
What types of products does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a diverse range of DC input Tube Axial units and Centrifugal Blowers, optimized for performance and efficiency in various applications in electronics and beyond.

