Overview
The fundamental differences between DC and PWM modes stem from their operational mechanisms and their suitability for specific applications.
- PWM mode provides enhanced precision in control and energy efficiency, making it a superior choice for many scenarios.
- This article illustrates how PWM’s pulse width modulation enables quieter operation and dynamic speed adjustments, rendering it ideal for noise-sensitive environments.
- In contrast, DC mode, characterized by its constant voltage operation, offers simpler and more cost-effective solutions, albeit with limitations in adaptability and efficiency.
Introduction
The choice between PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and DC (Direct Current) fans represents a pivotal decision for electronics engineers, significantly influencing factors such as energy efficiency and noise levels across various applications.
- PWM fans deliver sophisticated control and versatility, enabling precise speed adjustments that enhance performance in noise-sensitive environments.
- In contrast, DC fans offer a more straightforward, cost-effective solution, albeit often at the expense of efficiency and adaptability.
As engineers delve into the intricacies of fan technology, a pressing question emerges: which fan type genuinely meets the demands of contemporary applications, and in what ways do their operational mechanisms dictate their suitability for specific tasks?
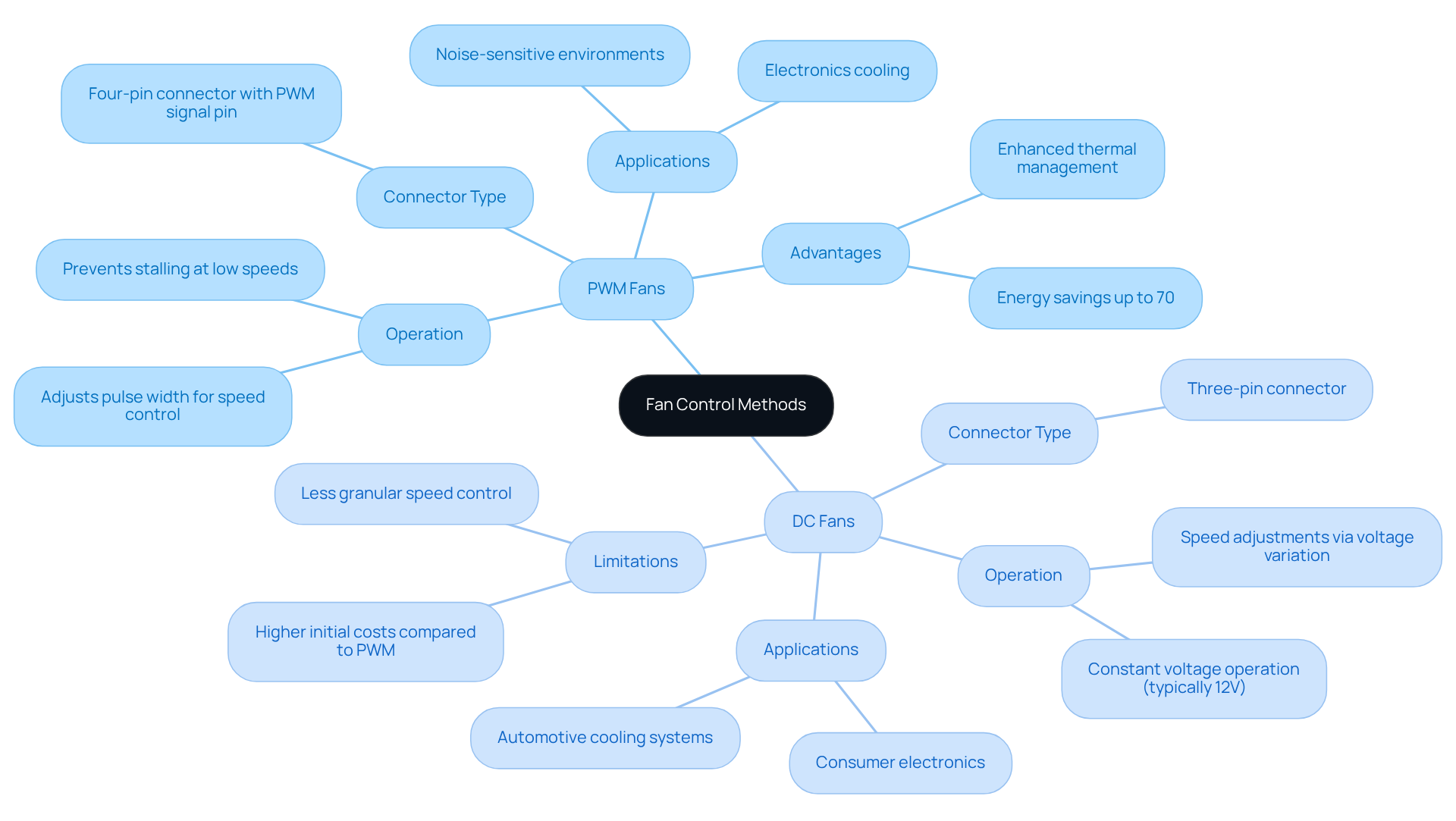
Define PWM and DC Fans: Core Principles and Functionality
units utilize an advanced control method that adjusts the width of electrical pulses, which is crucial for understanding in managing rotation rates precisely. This technique allows for exact control, permitting the fan to operate at reduced speeds without the risk of stalling, which is particularly beneficial in . Conversely, in the context of DC vs PWM mode, DC (Direct Current) devices function on a constant voltage, typically 12V, with speed adjustments made by varying the voltage supplied to the unit. While this results in simpler operation, it restricts the granularity of speed control.
PWM units are distinguished by a four-pin connector that includes a dedicated PWM signal pin, whereas DC devices generally feature a three-pin connector. This distinction between DC vs PWM mode is crucial for engineers when selecting devices for specific applications, especially in scenarios where are paramount.
Gagner-Toomey Associates, the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers for temperature regulation, offers an extensive range of and , available in sizes ranging from 15 to 280mm and 15 to 225mm, respectively, with IP protection options available upon request. Recent advancements in ventilation technology, particularly in DC vs PWM mode, have demonstrated compared to conventional AC units, highlighting their growing importance in modern . Furthermore, case studies indicate that the integration of can significantly improve thermal management, ensuring optimal performance across various electronic applications, including those within the Electronics, Automotive, and Telecom sectors.
Compare Operational Mechanisms: PWM vs. DC Fans
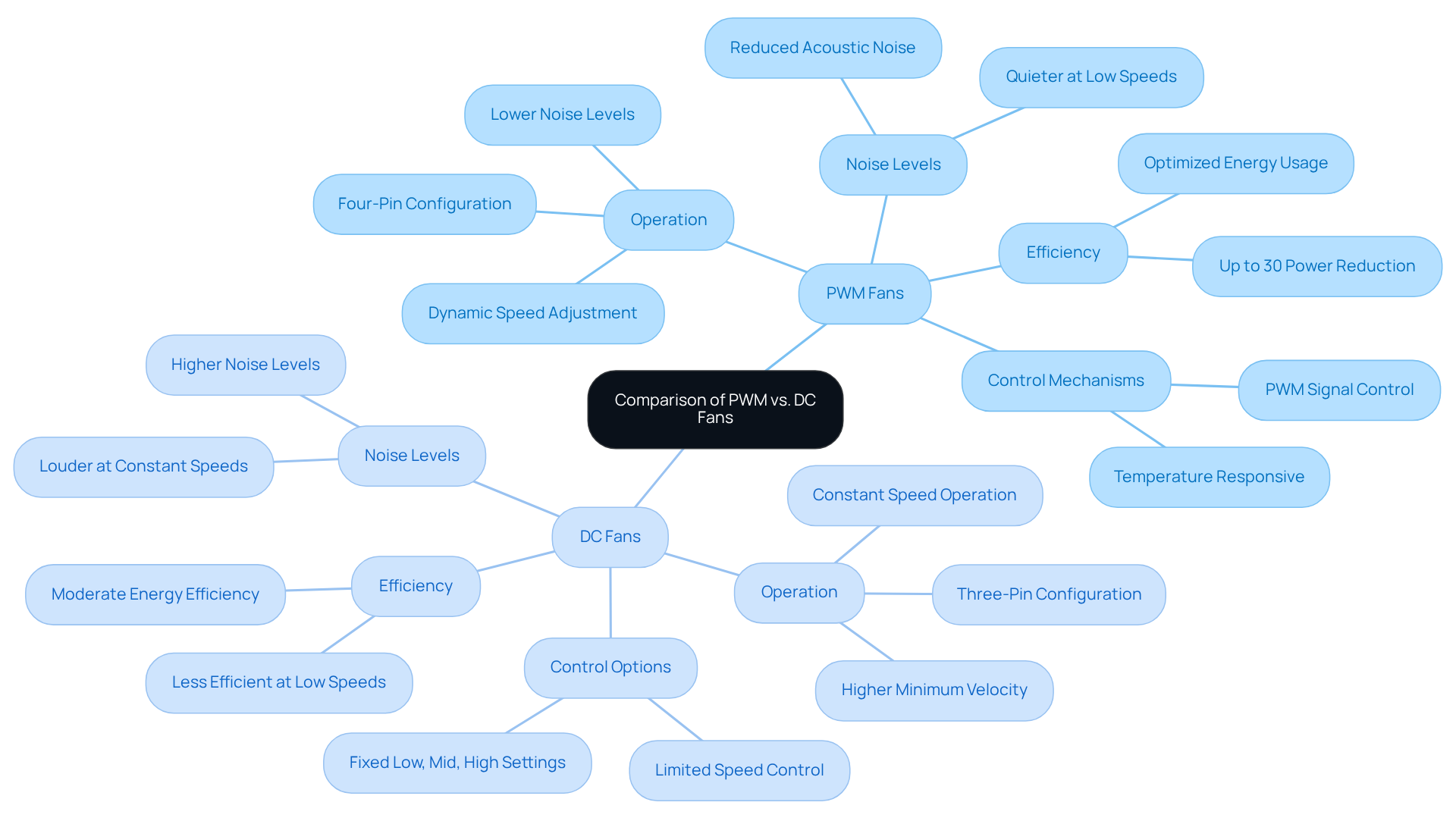
PWM motors operate in to leverage pulse width modulation, delivering rapid electrical pulses to the device and facilitating , including exceptionally low RPMs. This capability is particularly advantageous in environments where noise reduction is paramount, as can operate effectively at levels as low as 20% of their maximum capacity.
Conversely, those interested in the dc vs pwm mode adjust their motor speed by modifying the voltage supplied, which can lead to inefficiencies, especially at lower speeds. This often results in DC devices maintaining a , making them less suitable for applications requiring meticulous .
Furthermore, when discussing dc vs pwm mode, DC enthusiasts typically encounter , operating at fixed low, mid, or high settings, which restricts their adaptability to varying temperature demands. Additionally, the continuous rapid movements of DC motors in terms of dc vs pwm mode often result in increased noise levels.
Consequently, PWM devices are increasingly favored in high-performance systems where precise temperature regulation is essential. Notably, PWM units can dynamically adjust their speeds in response to temperature sensor signals, .
Moreover, , whereas DC variants generally feature three pins—an important distinction for engineers tasked with selecting the appropriate type.
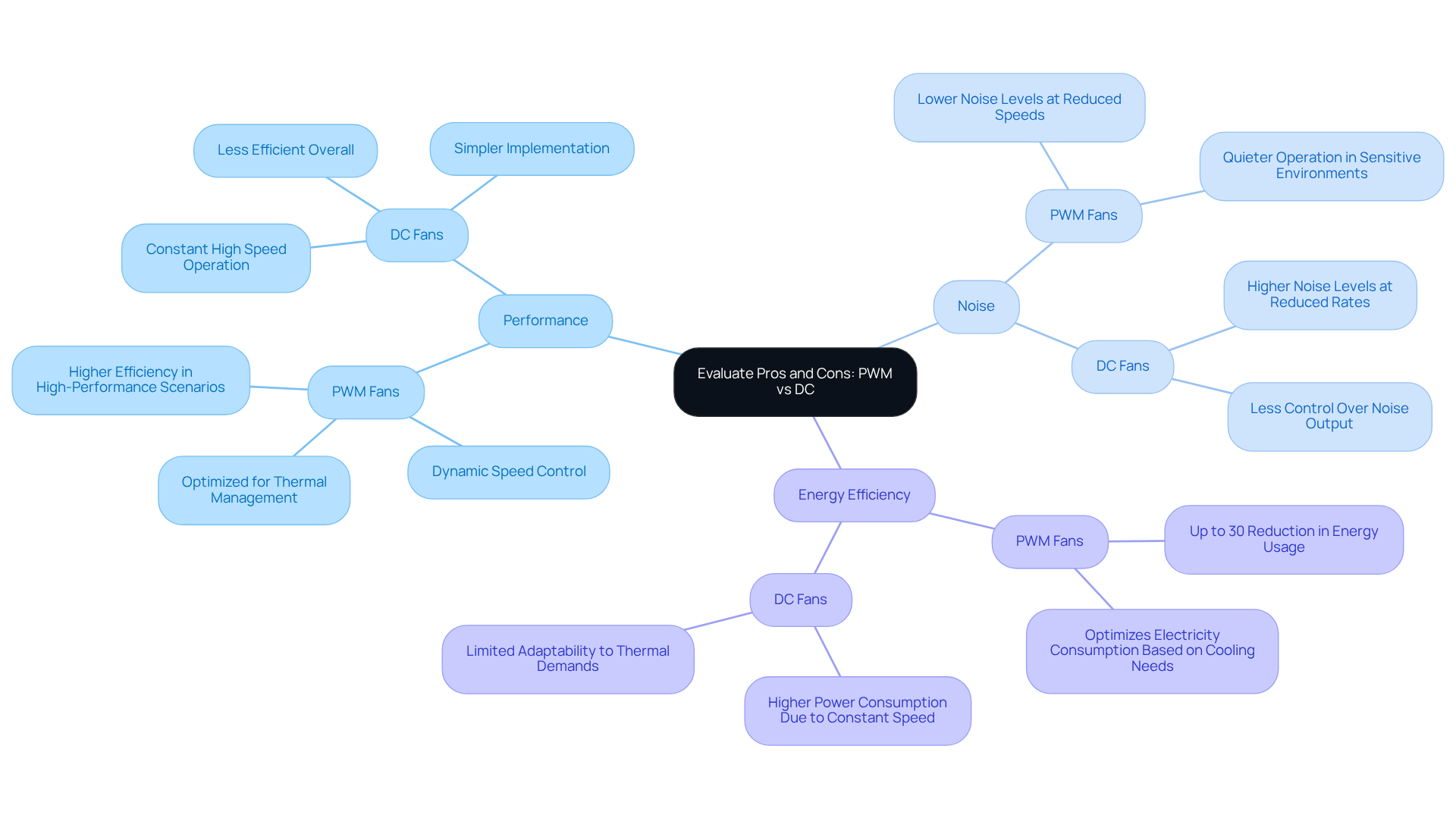
Evaluate Pros and Cons: Performance, Noise, and Energy Efficiency
PWM units excel in and , functioning effectively at reduced levels to minimize both sound and power usage. This capability makes them particularly suitable for environments where , such as data centers and high-performance computing systems. according to cooling needs, minimizing waste in large systems or data centers. In contrast, DC enthusiasts, while typically simpler and more economical, often generate higher noise levels, particularly at reduced rates, and can be less efficient overall. They usually operate at constant high rates, resulting in excessive power usage and restricted airflow management.
A 25% reduction in fan speed can lead to a noise decrease of approximately 6 dB, demonstrating the potential for quieter operation without sacrificing performance. Although in the DC vs PWM mode discussion, to implement and more budget-friendly, they lack the precision and adaptability that , which feature four wires (power, ground, tachometer, PWM signal) compared to the three wires (power, ground, tachometer) of DC variants. In the context of DC vs PWM mode, for projects where noise reduction and energy efficiency are priorities, PWM devices are the superior choice, capable of achieving up to a 30% reduction in energy usage compared to their DC counterparts.
Additionally, allows for dynamic speed adjustments via based on thermal demands, further enhancing operational efficiency and significantly reducing noise levels. This makes them ideal for sensitive applications, where maintaining optimal performance while is crucial.
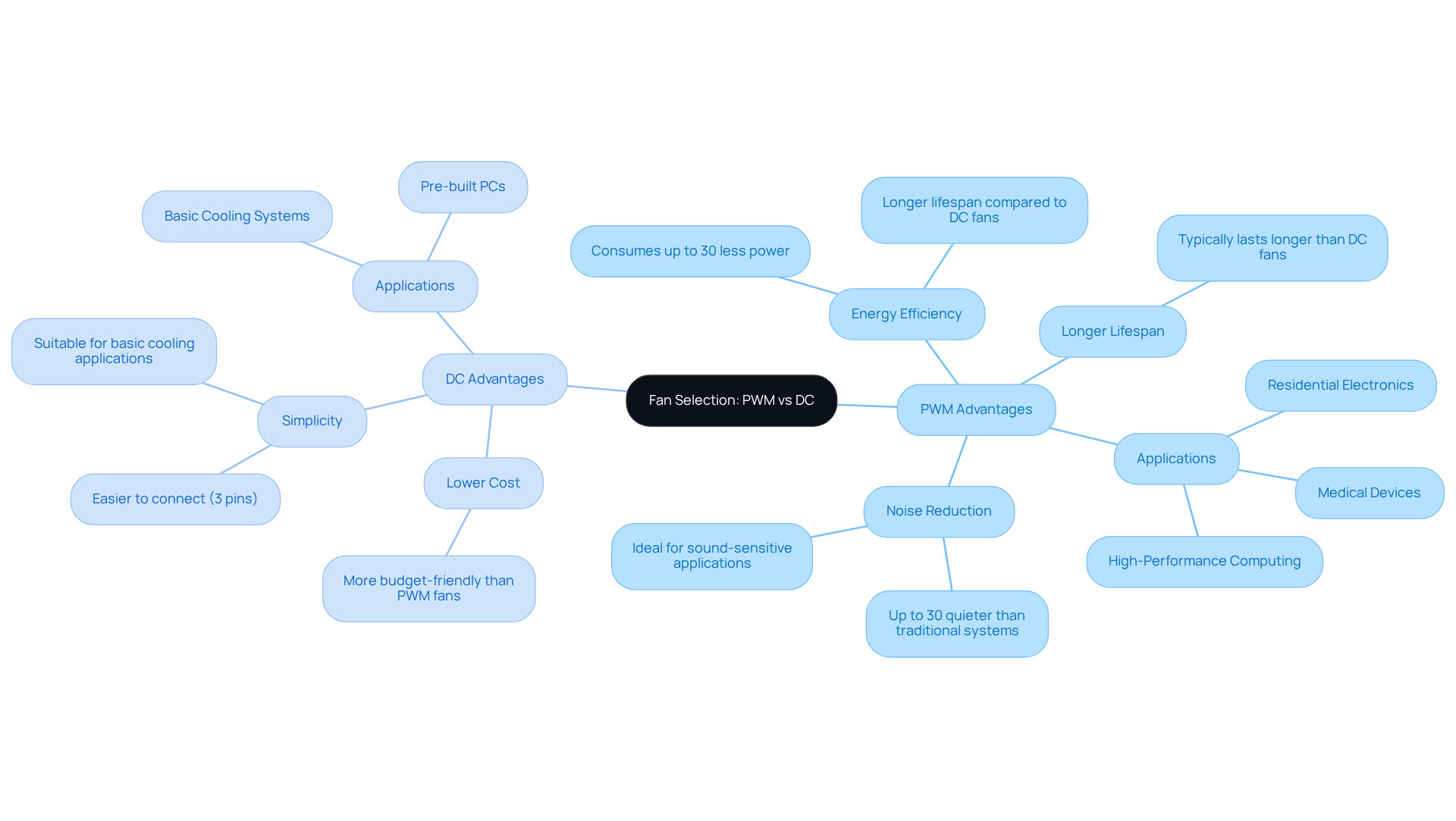
Assess Application Suitability: Choosing Between PWM and DC Fans
When selecting between , engineers must carefully evaluate the specific requirements of their applications. PWM units are particularly advantageous in environments where noise reduction and . This makes them ideal for , medical devices, and residential electronics. Their capacity to operate silently at reduced rates facilitates without disturbing sound-sensitive settings, as they can rotate at lower speeds compared to direct current motors.
Conversely, proponents of often find them to be the preferable choice for simpler systems or projects constrained by budget, as they typically come at a lower cost than . DC units are frequently employed in basic cooling applications where and generally connect using three pins.
Notably, statistics reveal that PWM devices can diminish compared to traditional systems, and they also tend to exhibit a longer lifespan than their DC counterparts. Ultimately, the choice of fans in should be guided by the specific operational requirements and limitations of the project, including the necessary pin configurations—PWM fans necessitate four pins for connection.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between PWM and DC fans is essential for engineers navigating the complexities of electronic cooling solutions. This article has outlined the fundamental differences in their operational mechanisms, emphasizing how PWM technology offers superior control, energy efficiency, and noise reduction compared to traditional DC fans. The choice between these two types of fans hinges on specific application needs, making it crucial to grasp their unique functionalities.
Key insights discussed include:
- The advanced pulse width modulation technique employed by PWM fans, which allows for precise speed adjustments and lower operational noise.
- In contrast, DC fans, while simpler and more cost-effective, often fall short in terms of efficiency and adaptability, particularly in noise-sensitive environments.
- The importance of considering factors such as application requirements, budget constraints, and desired performance when selecting between PWM and DC fans.
Ultimately, the decision to use PWM or DC fans should be informed by the specific demands of each project. By prioritizing energy efficiency and noise reduction, PWM fans emerge as the optimal choice for high-performance applications. Engineers are encouraged to evaluate their cooling needs carefully, as the right fan technology can significantly enhance system performance and longevity, ensuring that electronic devices operate smoothly and quietly in any environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PWM in the context of fans?
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is an advanced control method that adjusts the width of electrical pulses to manage the rotation rates of fans precisely, allowing for reduced speeds without the risk of stalling.
How do DC fans operate?
DC (Direct Current) fans operate on a constant voltage, typically 12V, with speed adjustments made by varying the voltage supplied to the fan, resulting in simpler operation but less precise speed control compared to PWM fans.
What are the main differences between PWM and DC fans?
PWM fans use a four-pin connector that includes a dedicated PWM signal pin, while DC fans generally have a three-pin connector. This difference is crucial for engineers when selecting devices for applications requiring energy efficiency and noise reduction.
What advantages do PWM fans have over traditional AC units?
PWM fans can demonstrate energy savings of up to 70% compared to conventional AC units and can significantly improve thermal management in various electronic applications.
What types of fans does Gagner-Toomey Associates produce?
Gagner-Toomey Associates produces a wide range of standard and custom air-movers, including DC input Tube Axial units and Centrifugal Blowers, available in sizes from 15 to 280mm and 15 to 225mm, respectively.
In what sectors is PWM technology particularly beneficial?
PWM technology is particularly beneficial in the Electronics, Automotive, and Telecom sectors, where optimal performance and thermal management are critical.

