Introduction
Understanding the complexities of fan performance is crucial for engineers aiming to optimize cooling systems in today’s fast-paced technological environment. Mastering fan performance curves enables them to make informed decisions that not only enhance system efficiency but also extend the lifespan of electronic components. Yet, the challenge arises in accurately interpreting these curves under varying operational conditions and metrics. What critical insights can engineers extract from these graphs to ensure their designs meet both performance and energy efficiency standards?
Understand Fan Performance Curves
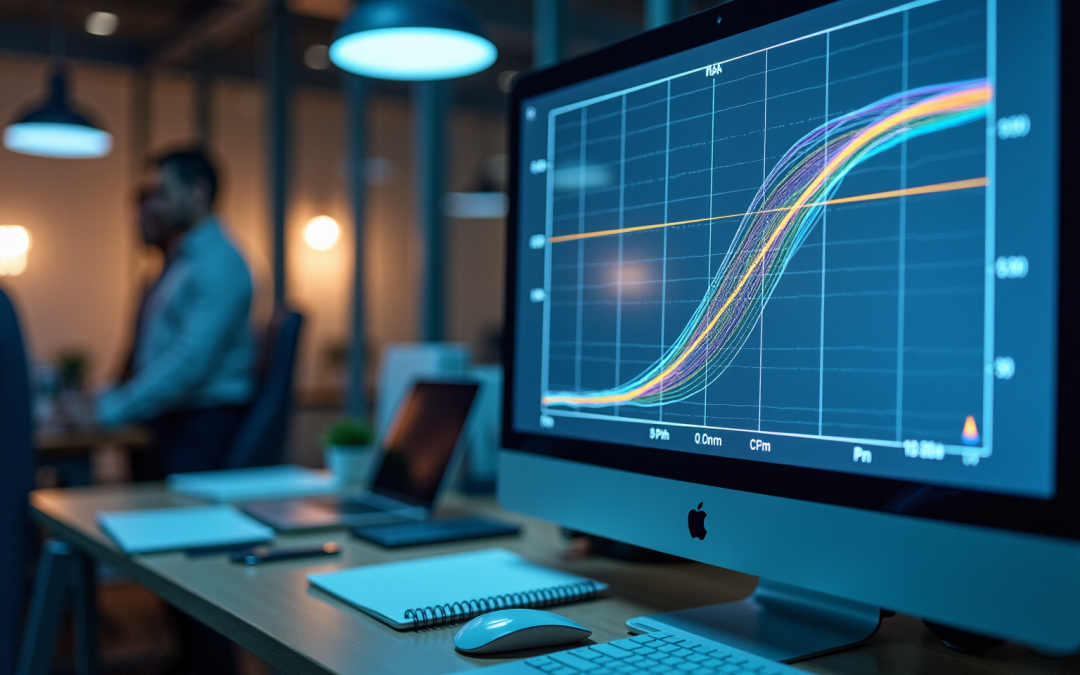
Graphs illustrating fan performance visually depict the relationship between airflow (measured in CFM), static pressure (SP), and power consumption (BHP) for specific fan models. These graphs are essential for engineers, demonstrating how a fan operates under varying conditions. Understanding these shapes enables informed decisions regarding fan performance and system design.
- X-Axis (Airflow): This axis represents the volume of air the fan can move, typically quantified in cubic feet per minute (CFM).
- Y-Axis (Static Pressure): This axis indicates the resistance the fan must overcome to move air, measured in inches of water gauge (in. wg).
- Lines: Each line on the graph corresponds to a specific fan speed (RPM), illustrating how airflow and static pressure fluctuate with changing conditions.
The significance of airflow and static pressure in fan operation is paramount. Engineers emphasize that a comprehensive understanding of fan performance and operation graphs is crucial for enhancing system efficiency. For example, selecting a fan that operates near the peak of its efficiency curve can greatly enhance fan performance while minimizing energy consumption.
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a diverse range of DC input Tube Axial devices and Centrifugal Blowers, optimized for effectiveness, efficiency, and low noise—key factors for various applications in electronics cooling. Notable features include sizes ranging from 15 to 280mm for Tube Axial fans and 15 to 225mm for Centrifugal Blowers, with IP protection available upon request, further aiding engineers in their selection process.
Real-world examples underscore the practical application of these concepts. In a specific case study, engineers analyzed fan operation graphs to pinpoint the ideal functioning point for a cooling mechanism, ensuring that the selected fan performance maintained both efficiency and reliability throughout its lifespan. This analysis highlighted the critical role of static pressure in HVAC systems, where increased resistance can lead to diminished airflow, ultimately affecting system efficiency.
In the electronics sector, understanding fan characteristics is vital. As technology evolves, the demand for effective cooling solutions escalates, making it essential for engineers to leverage fan performance for successful design and implementation. By mastering graphs of fan performance, engineers can ensure their systems operate at optimal effectiveness, extending the lifespan of electronic components and enhancing overall reliability. Additionally, engineers are encouraged to participate in upcoming webinars, such as the one on Multimotor Plenum Fan Architecture, to deepen their understanding of Gagner-Toomey’s innovative cooling solutions.
Identify Key Metrics on the Curve
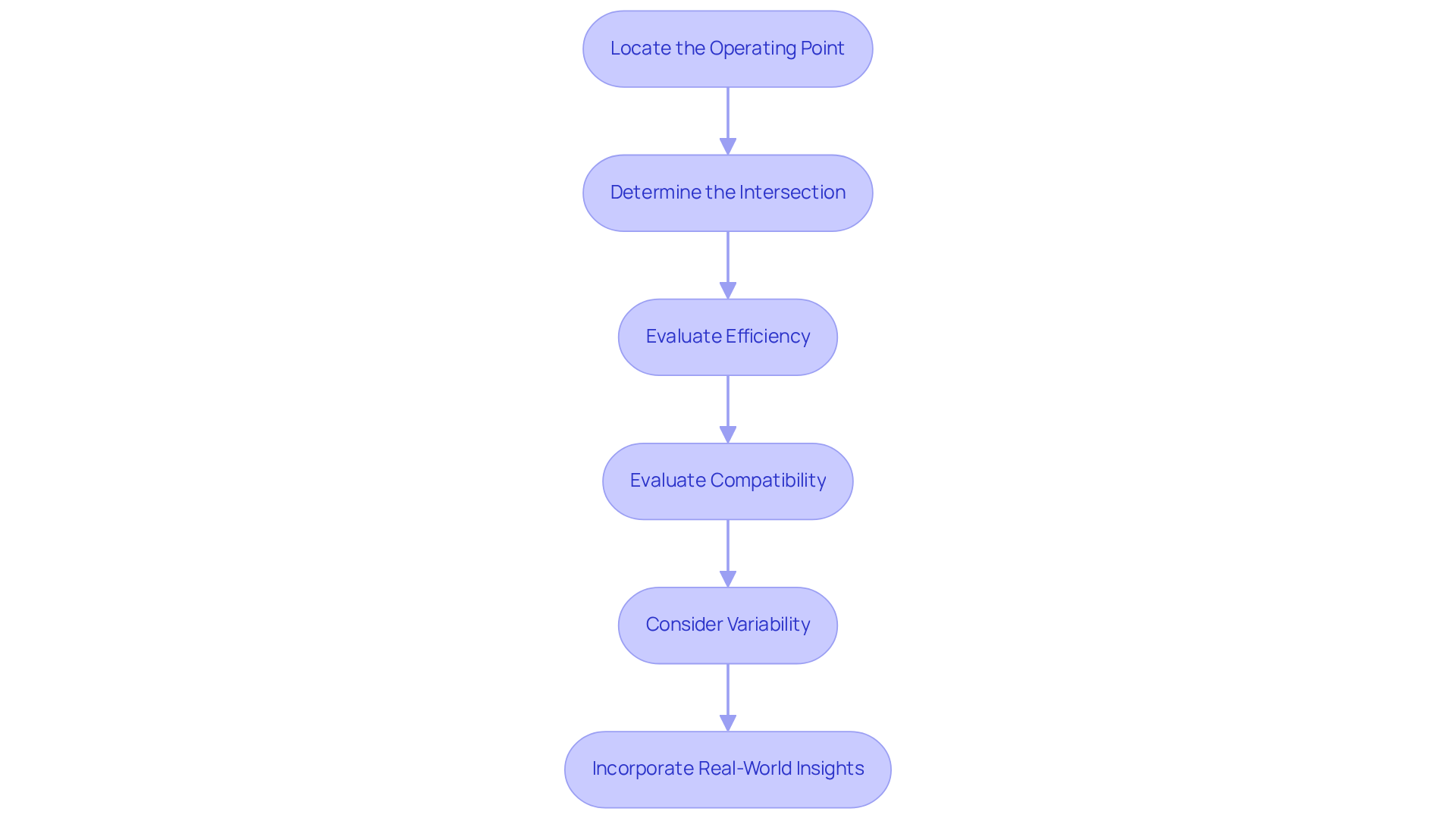
When analyzing a fan performance curve, engineers must focus on several critical metrics that directly impact system efficiency and effectiveness:
-
Maximum Airflow (CFM): This metric indicates the highest volume of air a fan can deliver at a specific static pressure, which is essential for meeting cooling requirements across various applications. For example, at sea level, approximately 40 CFM is necessary to remove 340W of heat, while larger systems may demand airflow rates as high as 17,000 m³/h. Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a comprehensive range of DC input Tube Axial devices and Centrifugal Blowers, optimized for performance and efficiency, enabling engineers to find the right airflow solutions tailored to their specific needs.
-
Peak Static Pressure: This metric reflects the maximum resistance a fan can overcome, crucial for applications that encounter high back pressure, such as those with complex ductwork or filters. A solid understanding of static pressure is vital, as it directly influences energy efficiency and operational costs. Gagner-Toomey’s supporters are designed to handle various static pressure scenarios, allowing engineers to select devices that match the required static pressure and avoid unnecessary energy consumption.
-
Efficiency Point: This point on the graph represents where the fan operates most efficiently, characterized by the highest airflow at the lowest power usage. Choosing a fan that operates near this point can significantly enhance fan performance, leading to substantial energy savings, potentially up to 20% in cooling applications. Gagner-Toomey’s innovative cooling solutions, including EC fans and blowers, are engineered to maximize efficiency, making them ideal for electronics cooling applications.
-
Operating Range: This area on the curve defines where the fan can operate effectively without generating excessive noise or vibration. Engineers must ensure that the selected fan operates within this range to maintain reliability and efficacy. Gagner-Toomey’s extensive portfolio includes miniature blower and fan solutions that cater to tight spaces, ensuring optimal functionality across various applications.
By mastering these metrics and leveraging Gagner-Toomey’s extensive assortment of cooling solutions, engineers can make informed decisions about fan performance when selecting fans for specific cooling or ventilation requirements. This ultimately enhances system efficiency and longevity.
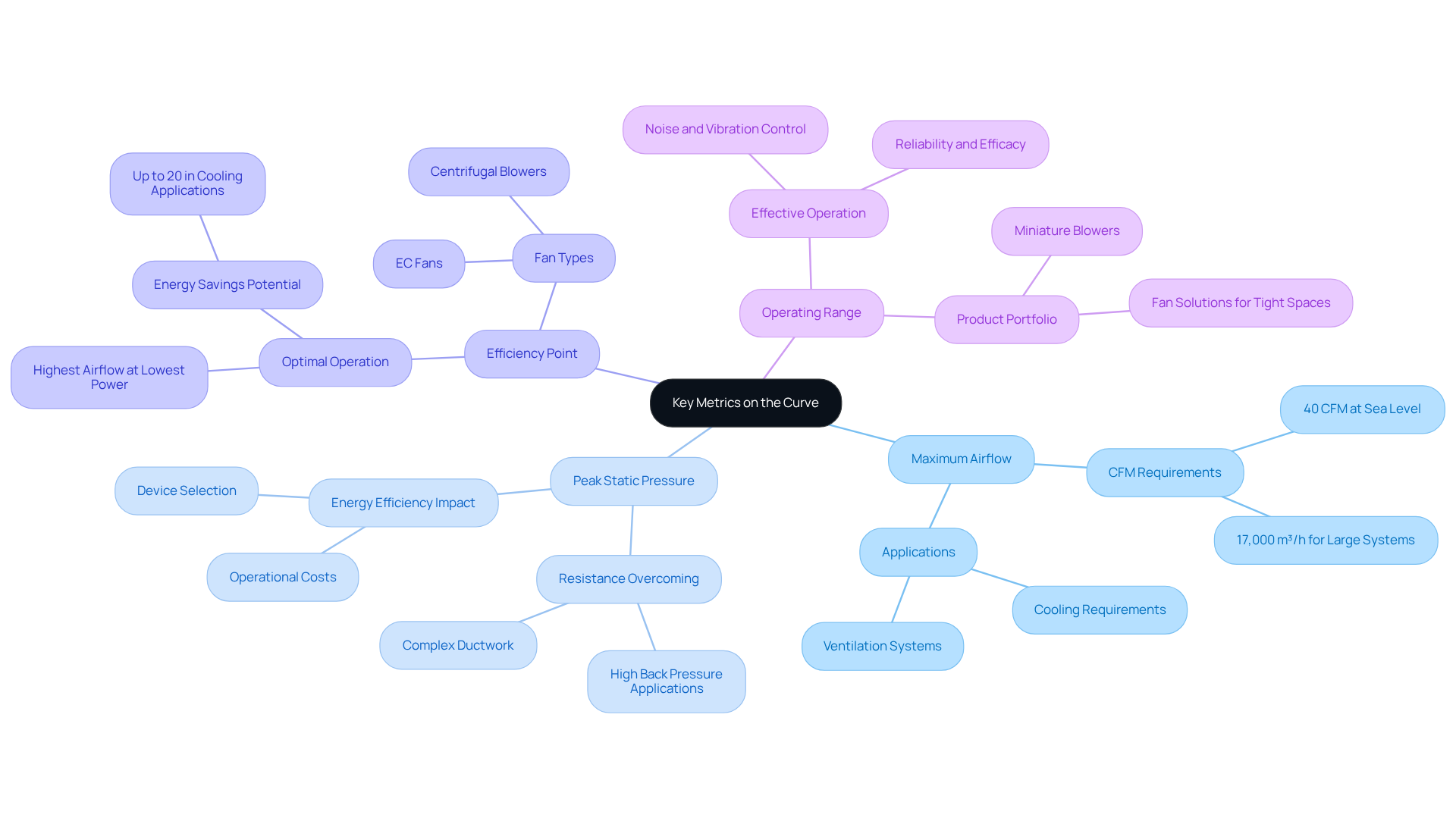
Analyze the Performance Curve Step-by-Step
To effectively analyze a fan performance curve, follow these steps:
-
Locate the Operating Point: Start by identifying the desired airflow (CFM) and static pressure (SP) for your application on the graph. Tube axial fans are the most common type in electronic cooling systems, so keep this in mind when selecting your fan.
-
Determine the Intersection: Next, find where your operating point intersects with the fan curve. This intersection reveals the fan performance under those specific conditions, providing crucial insights into its operation.
-
Evaluate Efficiency: Check the efficiency at the intersection point. An FEI of 1.00 indicates efficiency equal to the baseline fan setup, while values above suggest enhanced energy efficiency. Conversely, values below 1.00 in FEI do not meet the efficiency target, so ensure this aligns with your energy consumption needs.
-
Evaluate Compatibility: Compare the fan’s efficacy with the network’s resistance curve to ensure compatibility. The fan must be capable of overcoming the system’s pressure requirements, which is essential for maintaining optimal airflow.
-
Consider Variability: Finally, account for potential changes in operating conditions, such as temperature or altitude, which can significantly influence fan efficiency. Adjust your analysis to reflect these variables, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of the fan’s operational capabilities.
Incorporating insights from real-world applications can further illustrate the importance of accurately determining operating points. For instance, consider a case study where a factory’s air volume demand decreased from 50,000 CFM to 25,000 CFM after decommissioning five machines. This example underscores the necessity of precise analysis in optimizing fan performance.
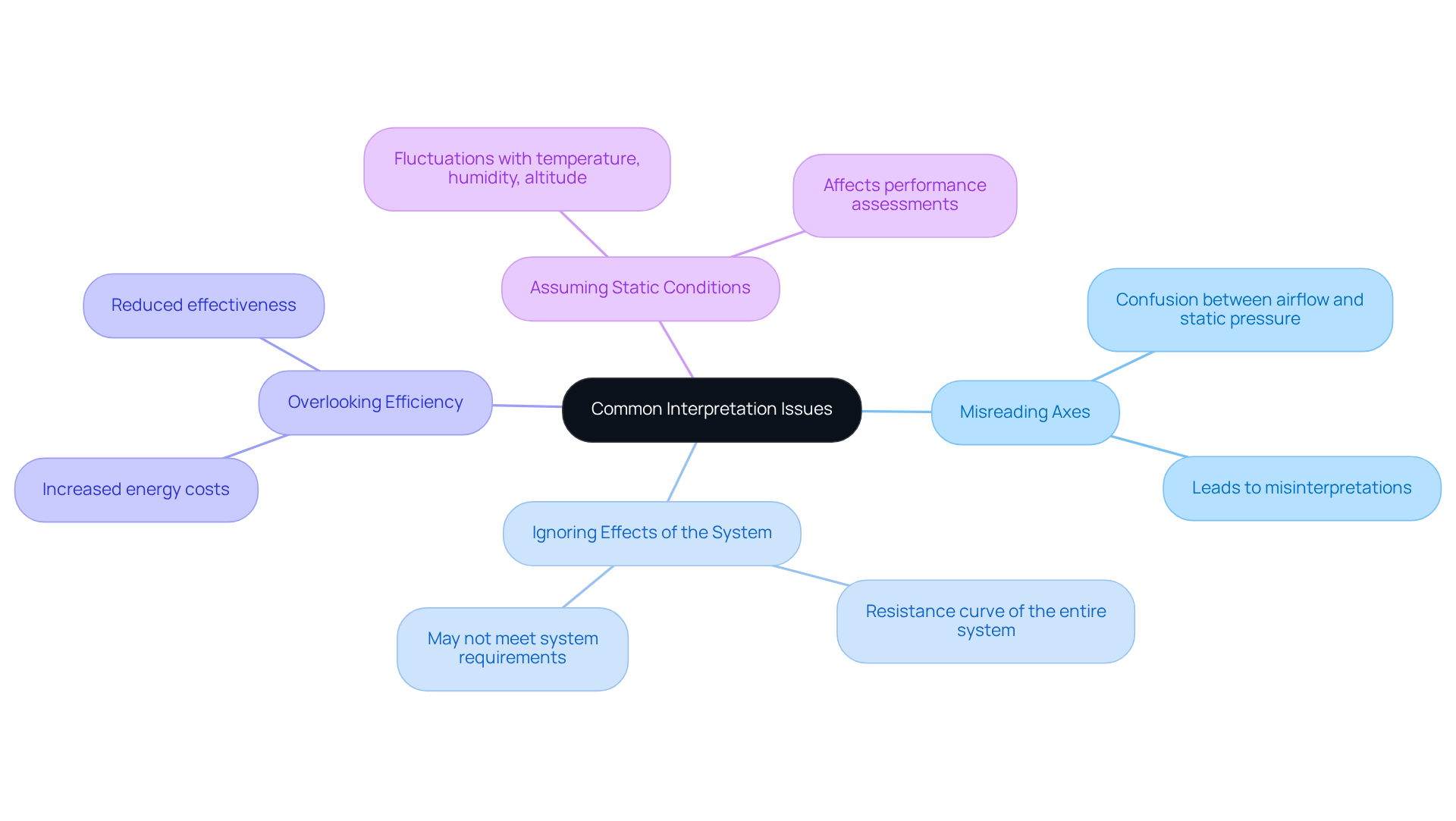
Troubleshoot Common Interpretation Issues
When interpreting fan performance curves, engineers often face several common challenges that can impact their analysis and design decisions:
- Misreading Axes: It’s crucial to accurately identify the axes on performance curves. Confusion between airflow and static pressure can lead to significant misinterpretations and incorrect conclusions.
- Ignoring Effects of the System: Always consider the resistance curve of the entire system. A fan may demonstrate excellent fan performance in isolation, but it might not fulfill the specific requirements of the system it’s integrated into.
- Overlooking Efficiency: Failing to evaluate the efficiency at the operating point can result in increased energy costs and reduced effectiveness. Assessing efficiency is vital for optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Assuming Static Conditions: Fan performance is not static; it can fluctuate with changes in temperature, humidity, and altitude. Always factor in these variables during your analysis to ensure accurate performance assessments.
By recognizing and addressing these issues, engineers can make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to optimized designs and enhanced system performance.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering fan performance is crucial for engineers who seek to optimize system efficiency and reliability. This guide underscores the importance of analyzing fan performance curves, which reveal the intricate relationship between airflow, static pressure, and power consumption. By leveraging this knowledge, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance cooling solutions across various applications.
Key arguments highlighted in this article include critical metrics that must be evaluated, such as:
- Maximum airflow
- Peak static pressure
- Efficiency points
- Operating range
Each of these factors significantly influences the selection of the best fan for specific requirements, ensuring systems operate efficiently while minimizing energy consumption. Furthermore, this guide outlines a systematic approach to analyzing performance curves, assisting engineers in navigating common pitfalls and refining their design strategies.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of fan performance is not merely a technical necessity; it serves as a pathway to innovation in engineering design. Engineers are encouraged to engage with available resources, such as webinars and expert consultations, to deepen their knowledge and maintain a competitive edge in the field. By mastering fan performance analysis, engineers can contribute to the development of more effective and sustainable cooling solutions, driving progress in electronics and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do fan performance curves illustrate?
Fan performance curves visually depict the relationship between airflow (measured in CFM), static pressure (SP), and power consumption (BHP) for specific fan models, helping engineers understand how a fan operates under varying conditions.
What does the X-axis represent in a fan performance curve?
The X-axis represents the volume of air the fan can move, typically quantified in cubic feet per minute (CFM).
What does the Y-axis indicate in a fan performance curve?
The Y-axis indicates the resistance the fan must overcome to move air, measured in inches of water gauge (in. wg).
What do the lines on the fan performance graph represent?
Each line on the graph corresponds to a specific fan speed (RPM), illustrating how airflow and static pressure fluctuate with changing conditions.
Why is understanding fan performance and operation graphs important for engineers?
A comprehensive understanding of fan performance and operation graphs is crucial for enhancing system efficiency and selecting fans that operate near the peak of their efficiency curve, which minimizes energy consumption.
What types of fans does Gagner-Toomey Associates offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers a diverse range of DC input Tube Axial devices and Centrifugal Blowers, optimized for effectiveness, efficiency, and low noise.
What sizes are available for Tube Axial fans and Centrifugal Blowers from Gagner-Toomey?
Tube Axial fans are available in sizes ranging from 15 to 280mm, while Centrifugal Blowers range from 15 to 225mm.
How does static pressure affect HVAC systems?
Increased static pressure can lead to diminished airflow, ultimately affecting system efficiency, which highlights the critical role of static pressure in HVAC systems.
Why is understanding fan characteristics vital in the electronics sector?
As technology evolves, the demand for effective cooling solutions escalates, making it essential for engineers to leverage fan performance to ensure optimal design and implementation, extending the lifespan of electronic components and enhancing overall reliability.
What opportunities are available for engineers to deepen their understanding of cooling solutions?
Engineers are encouraged to participate in upcoming webinars, such as the one on Multimotor Plenum Fan Architecture, to learn more about Gagner-Toomey’s innovative cooling solutions.