Introduction
In the dynamic world of electronics, engineers face a critical choice: CPU fan PWM versus DC technologies. This decision is pivotal for achieving optimal thermal management in their designs. With over 70% of engineers now incorporating these cooling solutions, grasping the nuances between these two fan types is essential.
PWM fans stand out for their superior energy efficiency and noise reduction, making them an attractive option for many applications. In contrast, DC fans are often simpler and more cost-effective, appealing to those with budget constraints. However, the real question is how these differences translate into performance in real-world scenarios. Which fan type ultimately excels in efficiency and effectiveness?
Understanding these distinctions not only informs design choices but also enhances overall system performance. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore the implications of each technology, backed by technical examples and data-driven insights, guiding you toward making an informed decision.
Differentiate Between PWM and DC Fans
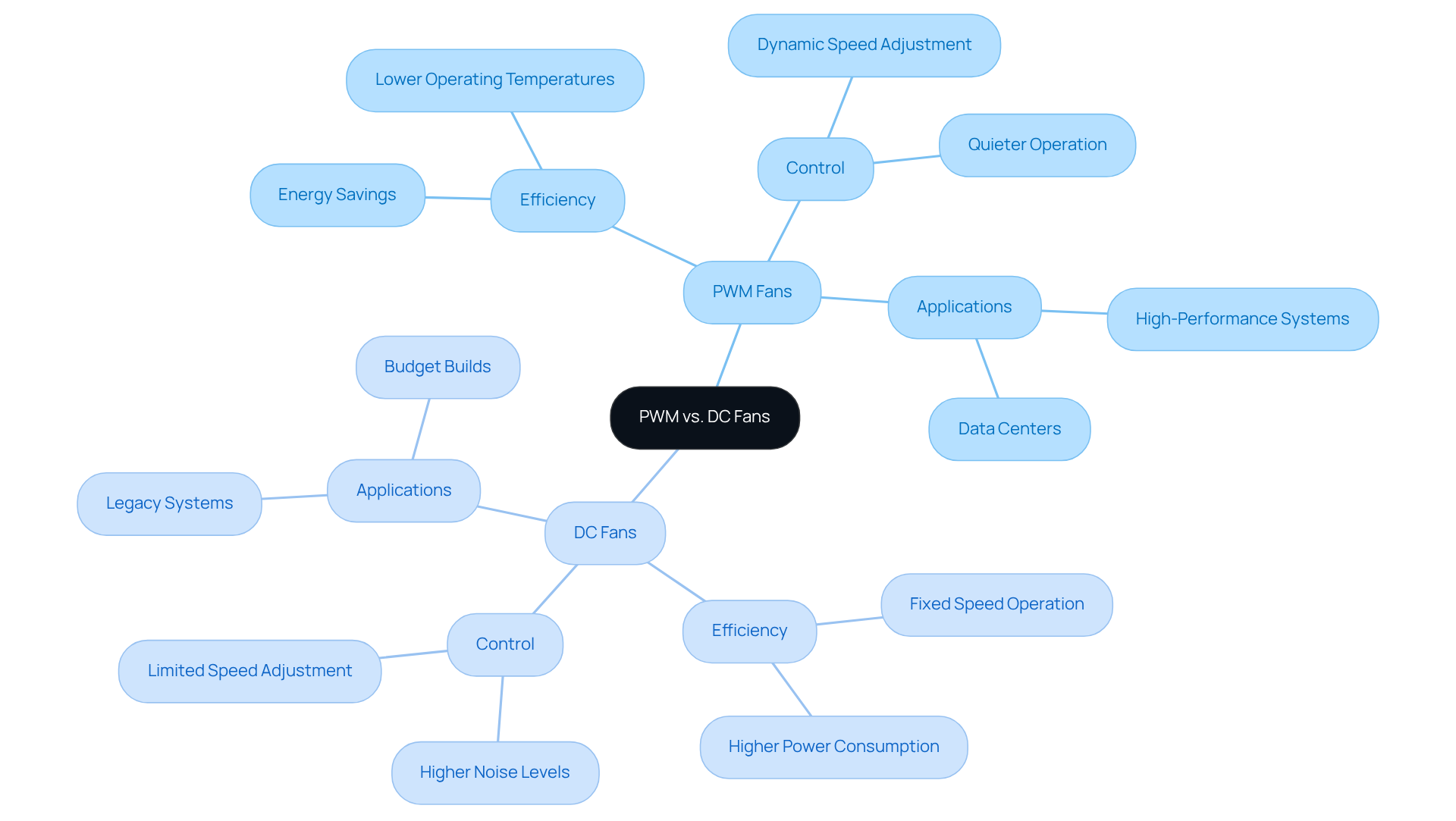
PWM units, characterized by their 4-pin connectors, utilize pulse width modulation, commonly referred to as cpu fan pwm or dc, to dynamically adjust their operational rate by varying the width of electrical pulses sent to the motor. This capability allows for precise control, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency and quieter operation, particularly at lower speeds. In contrast, DC devices typically feature a 3-pin connector and operate at a constant speed determined by the supplied voltage, unlike CPU fan PWM or DC configurations. Although some models of CPU fan PWM or DC can be regulated through voltage modulation, they do not offer the same level of precise control as PWM units, rendering them less effective in dynamic cooling scenarios. Current trends reveal that over 70% of electronics engineers are integrating cooling devices such as cpu fan pwm or dc into their designs, acknowledging their superior performance in thermal management. Real-world applications indicate that systems employing a CPU fan PWM or DC can maintain CPU temperatures an average of 5°C lower than those relying solely on DC units, significantly extending component lifespan by up to 50%.
To assist engineers in selecting the appropriate fan type, consider the following points:
- Efficiency: PWM fans deliver superior energy efficiency, particularly at lower speeds.
- Control: CPU fan PWM or DC units facilitate more accurate speed adjustments compared to standard DC units.
- Application: Evaluate the temperature management requirements of your specific application to determine the optimal fan type.
As engineers increasingly focus on efficiency and noise reduction, understanding the distinctions between a CPU fan PWM or DC is essential for selecting the right fan type for specific applications, particularly in environments where effective thermal management is critical. Gagner-Toomey Associates, the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offers a comprehensive portfolio of cooling solutions, including DC input Tube Axial units and Centrifugal Blowers, further enhancing the options available for engineers.
Evaluate Performance Metrics of PWM and DC Fans
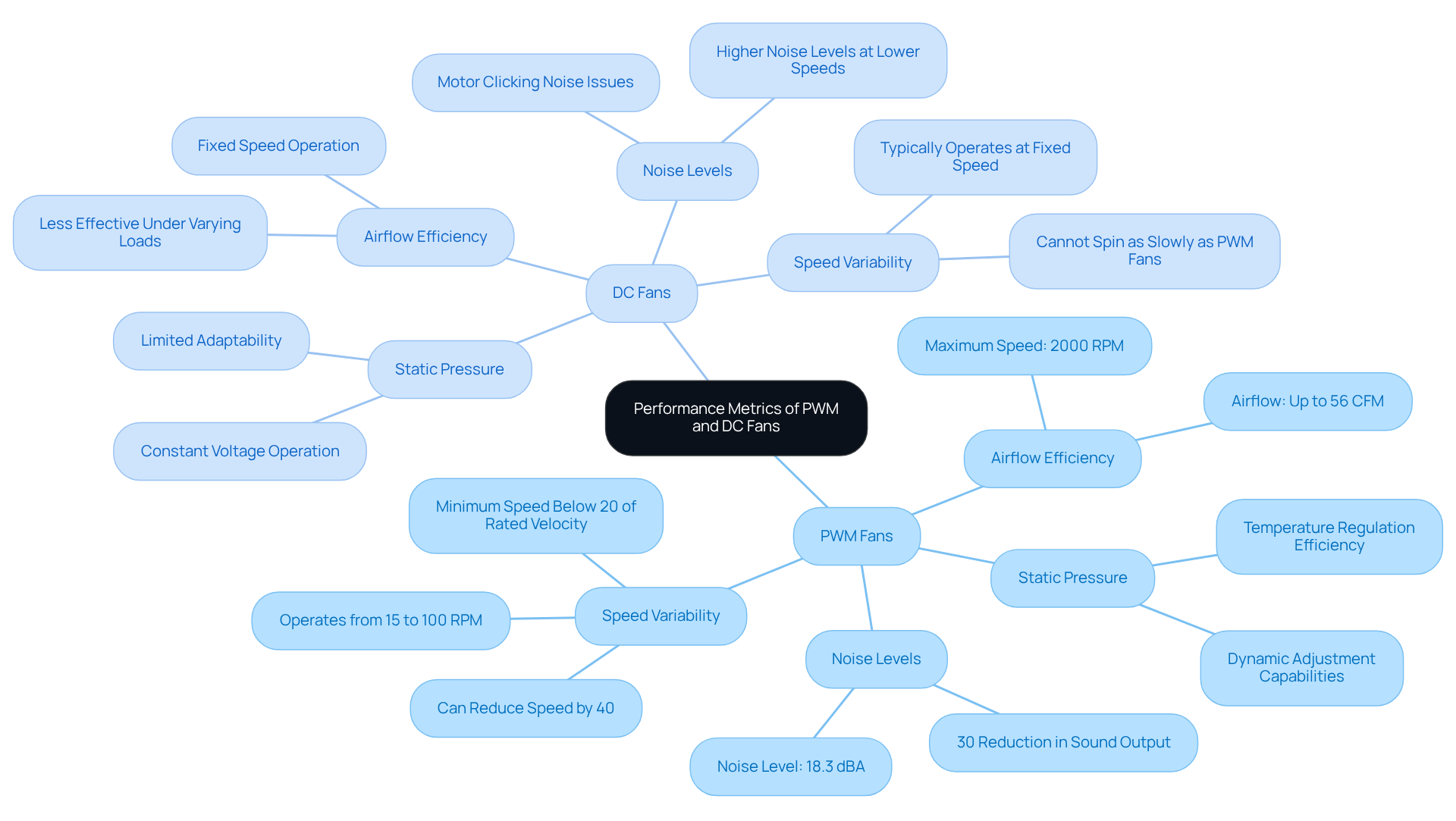
In performance assessments, CPU fan PWM or DC units consistently outperform each other in terms of airflow efficiency and static pressure, primarily due to their dynamic adjustment capabilities. PWM units operate efficiently across a wide range of velocities, typically from 15% to 100% of their rated RPM, and can even reach a minimum rate below 20% of their rated pace. This adaptability allows them to respond effectively to changing thermal requirements, enhancing temperature regulation, particularly in high-performance environments.
Conversely, CPU fan PWM or DC fans typically operate at a constant speed, which can lead to inefficiencies and inadequate temperature control under varying loads. For example, PWM devices can reduce their rotation by up to 40% of their rated performance, maintaining effective airflow while minimizing noise levels. In fact, PWM technology can achieve up to a 30% reduction in sound output compared to traditional cooling systems, making PWM devices particularly suitable for noise-sensitive applications.
Engineers must prioritize these performance metrics when designing systems, as the choice of fan can significantly impact overall thermal management and energy efficiency. With over 70% of electronics engineers now incorporating CPU fan PWM or DC devices into their designs—recognized for their quiet operation and efficient airflow—the trend underscores the growing awareness of their advantages in modern applications.
A prime example of PWM performance is the Fractal Design Aspect 12 Fan, which operates at a maximum rotation of 2000 RPM, achieving airflow of up to 56 CFM while maintaining a noise level of just 18.3 dBA. This showcases the potential of PWM technology to meet the demands of contemporary cooling solutions.
Assess Noise Levels in Fan Operation
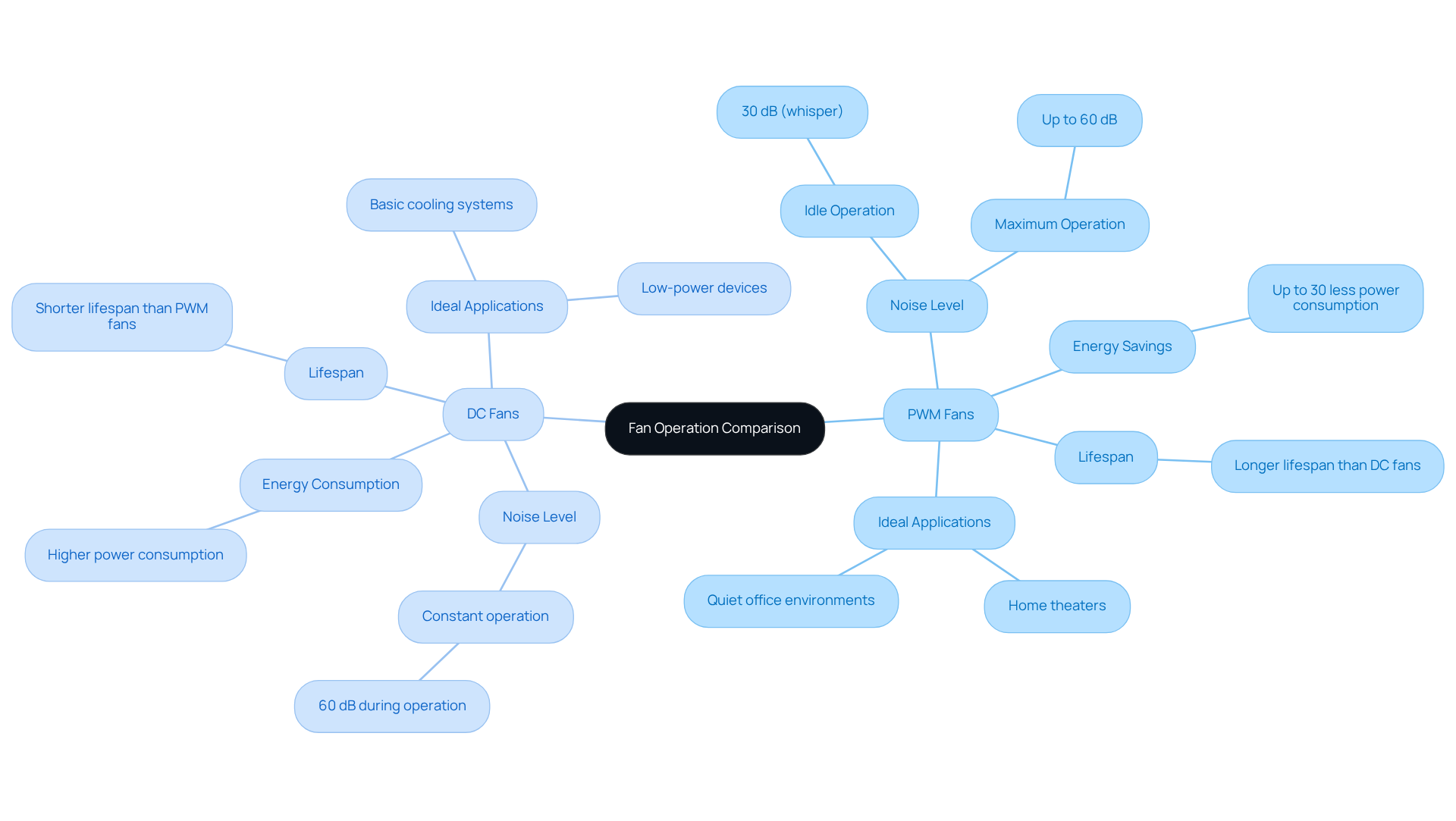
When choosing between CPU fan PWM or DC models, PWM fans stand out as a quieter alternative, especially when operating at reduced rates. This advantage stems from PWM technology’s ability to significantly lower fan operation during minimal cooling requirements, leading to a notable decrease in noise production. For instance, a PWM fan can operate at as low as 15% capacity during idle conditions, producing sound levels akin to a soft whisper at approximately 30 dB, while an ordinary conversation registers around 60 dB. In contrast, a DC fan typically maintains a constant higher speed, resulting in noise levels that can soar up to 60 dB during operation.
Engineers should seriously consider PWM devices for applications where noise reduction is paramount, such as in home theaters or quiet office environments. These fans not only enhance user comfort but also maintain effective cooling performance. Moreover, CPU fan PWM or DC units can provide energy savings of up to 30% compared to DC devices, making them an ideal choice for modern electronic applications.
Additionally, PWM devices generally boast a longer lifespan than DC models, further increasing their appeal for engineers focused on long-term solutions. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that CPU fan PWM or DC devices may require compatible hardware and can be more expensive than typical DC models. This factor should be carefully weighed when making a selection.
Analyze Power Consumption of Fan Types
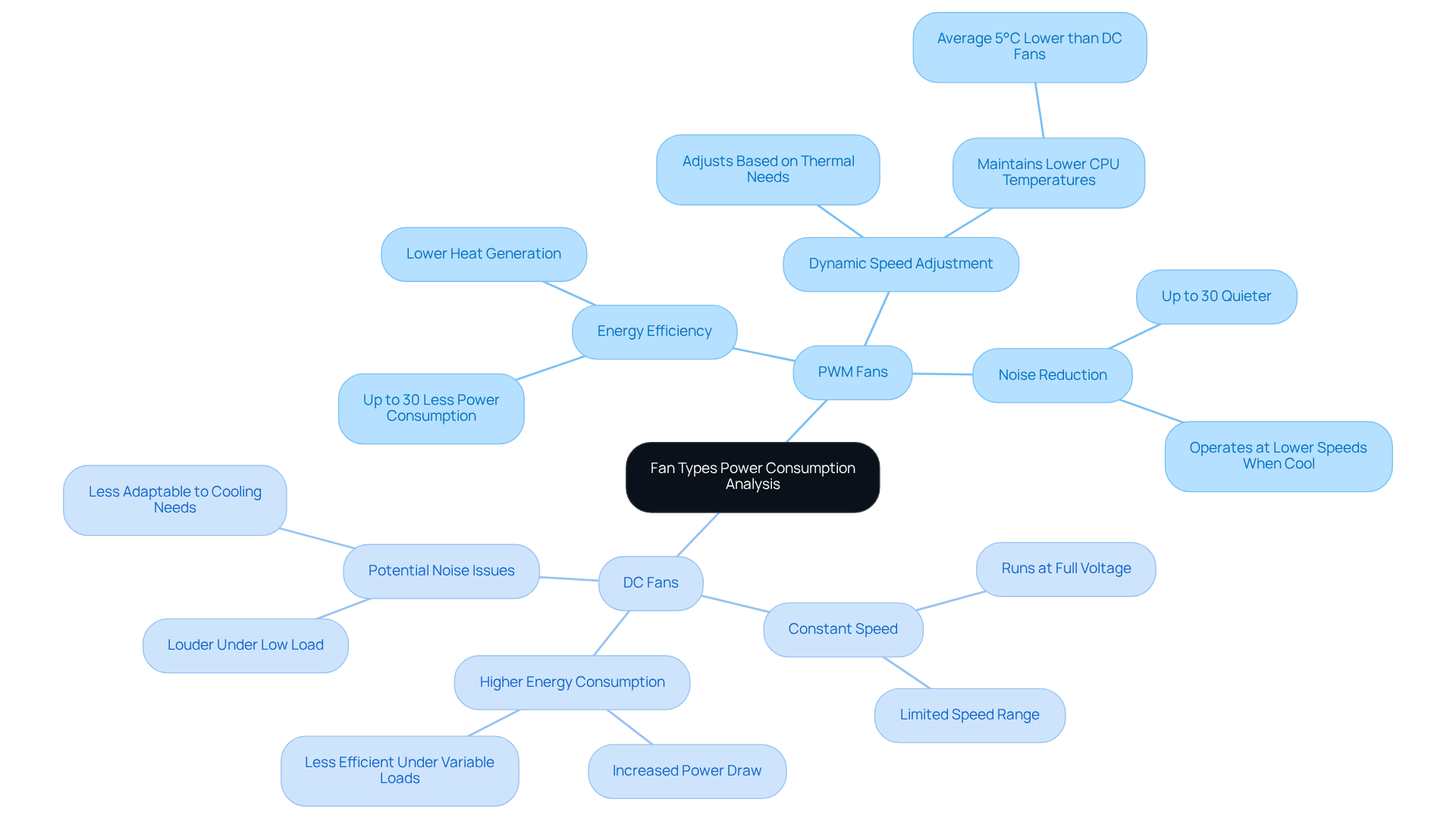
PWM devices offer superior energy efficiency compared to their DC counterparts, utilizing up to 30% less power. This efficiency stems from their ability to dynamically adjust speed based on the system’s temperature needs. When the system heats up, PWM devices can rotate faster, generating increased airflow. In contrast, DC fans typically operate at a constant speed, leading to unnecessary energy consumption, especially during periods of lower thermal demand.
For instance, in systems with fluctuating thermal loads, PWM devices optimize power usage by modulating their speed to meet current cooling requirements, effectively reducing overall energy expenditure. Research shows that systems utilizing a CPU fan PWM or DC can maintain temperatures up to 5°C lower than those relying solely on DC fan units. This adaptability not only results in significant cost savings but also aligns with the increasing focus on energy-efficient designs within the electronics industry.
Moreover, PWM fans can achieve noise level reductions of up to 30%, enhancing acoustic comfort in sensitive environments. While a small, high-quality, efficient DC fan may consume less power than a large, low-quality, inefficient PWM fan, the comprehensive benefits of PWM technology position it as the optimal choice for engineers who prioritize sustainability and performance.
Conclusion
Maximizing efficiency in thermal management is not just important; it’s essential for engineers striving for optimal performance. Understanding the differences between CPU fan PWM and DC fans is a critical step in this journey. PWM fans, with their dynamic speed control capabilities, significantly outperform DC fans in energy efficiency, noise reduction, and overall thermal regulation. This distinction is vital for engineers aiming to enhance both system longevity and performance.
Key points highlighted throughout this article include:
- The superior efficiency and quieter operation of PWM fans
- Their adaptability to varying thermal loads
- The substantial energy savings they provide
Selecting the right fan type based on specific application needs can lead to improved cooling performance and reduced operational costs, making this choice paramount.
Engineers are urged to integrate these insights into their designs for effective thermal management. As the industry evolves, prioritizing PWM technology not only aligns with sustainability goals but also enhances user experience in noise-sensitive environments. Embracing these advancements can pave the way for innovative solutions that set new standards in cooling efficiency and performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between PWM and DC fans?
The primary difference is that PWM fans use pulse width modulation with a 4-pin connector to dynamically adjust their speed, while DC fans typically have a 3-pin connector and operate at a constant speed based on the supplied voltage.
How do PWM fans enhance energy efficiency and noise reduction?
PWM fans enhance energy efficiency and reduce noise, particularly at lower speeds, by allowing for precise control of the fan speed through varying the width of electrical pulses sent to the motor.
Can DC fans be regulated for speed adjustments?
Some models of DC fans can be regulated through voltage modulation, but they do not offer the same level of precise control as PWM fans, making them less effective in dynamic cooling scenarios.
What percentage of electronics engineers are integrating PWM or DC fans into their designs?
Over 70% of electronics engineers are integrating PWM or DC cooling devices into their designs due to their superior performance in thermal management.
How do systems using CPU fan PWM or DC compare to those using only DC fans in terms of CPU temperatures?
Systems that employ CPU fan PWM or DC can maintain CPU temperatures an average of 5°C lower than those relying solely on DC units.
What impact does the choice of fan type have on component lifespan?
Using CPU fan PWM or DC can significantly extend component lifespan by up to 50% compared to using only DC fans.
What factors should engineers consider when selecting a fan type?
Engineers should consider efficiency, control, and the specific temperature management requirements of their applications to determine the optimal fan type.
Who is Gagner-Toomey Associates and what do they offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offering a comprehensive portfolio of cooling solutions, including DC input Tube Axial units and Centrifugal Blowers.

