Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of sleeve bearings and ball bearings, focusing on their performance, cost, and applications. Sleeve bearings are particularly advantageous in low-speed, high-load situations, whereas ball bearings are designed to excel in high-speed applications. This distinction is substantiated by evidence of their durability, cost-effectiveness, and specific use cases. Consequently, it is imperative for engineers to meticulously evaluate operational requirements when selecting the appropriate bearing type to meet their needs.
Introduction
In the intricate world of machinery and electronics, the choice between sleeve and ball bearings can significantly influence performance and efficiency. Sleeve bearings, often favored for their cost-effectiveness and ability to handle heavy loads, stand in stark contrast to ball bearings, which excel in high-speed applications due to their reduced friction and durability.
As industries evolve, understanding the nuances of these bearing types becomes increasingly crucial, particularly in sectors where precision and reliability are paramount. With market trends indicating a surge in demand for both bearing types, this exploration delves into their distinct characteristics, performance comparisons, and cost implications, guiding engineers and decision-makers in selecting the most suitable option for their specific applications.
Understanding Sleeve and Ball Bearings
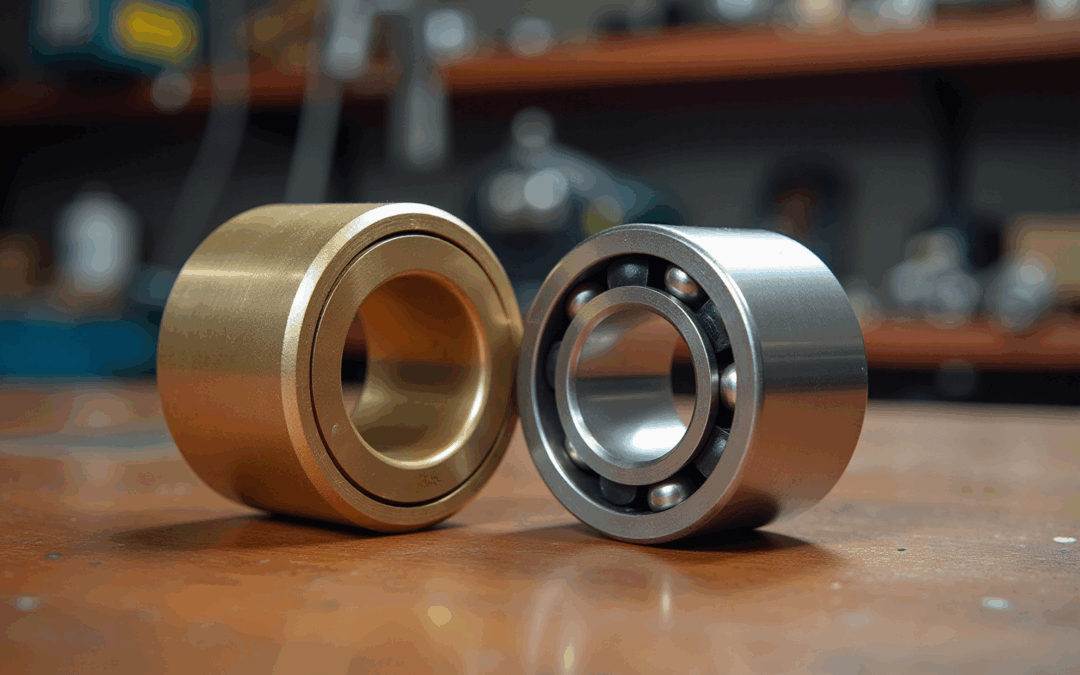
Cylindrical supports, often referred to as plain supports, consist of a cylindrical tube designed to hold a rotating shaft. They function through a sliding motion, which effectively minimizes friction, although this can lead to wear over time. Typically constructed from materials such as bronze or plastic, sleeve supports excel in applications demanding low-speed and high-load capabilities. Conversely, ball elements utilize small spheres to maintain distance between the inner and outer races, facilitating smoother rotation and significantly reducing friction. This design allows them to support higher speeds and loads, making them particularly suitable for motors and high-performance machinery. In the electronics sector, both types fulfill distinct roles. Sleeve supports are frequently employed in cooling systems and power management devices, where their ability to handle significant loads proves advantageous. Meanwhile, sphere rollers are preferred in applications requiring high-speed performance and precision, such as in RF devices and interconnection technologies.
Current market trends indicate a growing demand for cylindrical supports. The Global High Voltage Motor Cylindrical Support Market is valued at USD 1.71 billion in 2023, with projections to reach USD 5.14 billion by 2032, as reported by Zhuji Zhouwa Company. This growth is driven by rapid urban development and industrial advancement, particularly in regions like China, where the market for supports is experiencing robust expansion.
Engineers have underscored the advantages of cylindrical supports in specific applications, highlighting their durability and cost-effectiveness. A recent case study showcased NBI Bearing Europe’s strategic acquisition of Industrias Beta, enhancing their capabilities within the electric and automotive sectors. This acquisition underscores the increasing significance of cylindrical supports in contemporary applications, especially as industries seek reliable and efficient solutions, particularly when considering sleeve bearing vs ball bearing. While sleeve bearings offer substantial benefits, they also have limitations, such as reduced speed potential compared to ball bearings. Conversely, spheres for rotation, although exceptional for rapid applications, may not perform as effectively under heavy loads. As technology advances, both cylindrical and spherical components continue to evolve, with innovations aimed at improving performance and extending service life, thereby ensuring their vital role in the electronics sector.
Performance Comparison: Sleeve vs. Ball Bearings
In performance evaluations, rolling elements consistently outperform cylindrical supports in high-speed applications, primarily due to their reduced friction and superior capacity to manage higher RPMs. Their durability represents another significant advantage, as they frequently demonstrate a longer lifespan under continuous operation. For example, dual ball components can operate effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to 85°C, making them suitable for diverse environmental conditions.
Conversely, cylindrical supports excel at sustaining heavier loads in confined spaces but tend to deteriorate more quickly, particularly in high-speed scenarios. While sleeve supports can operate quietly at lower speeds in cooling fans, they may struggle with heat dissipation as speeds increase, leading to premature failure. In contrast, sphere components maintain their efficiency and performance even at elevated speeds, positioning them as the preferred choice for applications demanding reliable, high-performance operation.
A case study titled ‘Choosing the Right Type of Support’ underscores the necessity of selecting the appropriate support based on speed, temperature, load capacity, and environmental conditions, which is critical for optimizing cooling system performance. Moreover, fluid dynamic supports integrate characteristics of both cylindrical and spherical supports, enhancing functionality for specific applications.
Understanding the differences between sleeve bearing vs ball bearing is essential for engineers when selecting the suitable type of support for particular applications, especially in cooling systems where performance is paramount. As Jack Funkhouser, Vice President at Sofasco TM International, asserts, ‘With over 23 years of experience in the industrial sector, I am dedicated to driving SOFASCO towards new heights and making it a preferred choice for industrial cooling solutions.
Cost Analysis: Evaluating Sleeve and Ball Bearings
When evaluating the costs associated with sleeve bearing vs ball bearing, it is evident that sleeve bearings often present a lower initial expenditure, making them appealing for cost-sensitive projects. Notably, bulk purchases of sleeve components can yield savings of up to 40% relative to spherical supports.
However, the initial cost advantage when comparing sleeve bearing vs ball bearing can be deceptive. When comparing sleeve bearing vs ball bearing, it is evident that sleeve supports typically exhibit a shorter lifespan and generate more heat than spherical supports, potentially leading to increased replacement costs over time, thereby making them less suitable for high-speed applications.
Conversely, while sleeve bearing vs ball bearing components necessitate a higher initial investment, ball bearings are celebrated for their durability and lower maintenance requirements, ultimately delivering superior long-term value. This is particularly evident in scenarios where reliability and longevity are critical.
Common applications for cylindrical supports include:
- Construction
- Agricultural equipment
- Shipbuilding
For instance, case studies indicate that roller components maintain consistent performance across various mounting positions, whereas cylindrical supports may experience reduced lifespans in horizontal configurations. Furthermore, sleeve supports are generally quiet during their initial phase but tend to produce more noise as they age.
Consequently, when considering the total cost of ownership, the upfront expense for ball components may be justified when evaluating sleeve bearing vs ball bearing, as they offer an extended service life and reduced overall project costs.
Choosing the Right Bearing: Application Suitability and Recommendations
Selecting the appropriate type of support requires a thorough understanding of specific usage needs, particularly when considering sleeve bearing vs ball bearing. Sleeve supports are particularly effective in low-speed, high-load scenarios, making them well-suited for heavy machinery and certain automotive components where cost-effectiveness is paramount. Their design also contributes to noise reduction, which is beneficial in environments where sound levels must be minimized. Conversely, spherical rollers are preferred for high-speed applications, such as cooling fans and precision motors, where performance and durability are critical.
When engineers make their selection, they should consider several factors:
- Operational Environment: Sleeve bearings generally function effectively within a temperature range of up to 70°C (158°F), potentially limiting their application in high-temperature settings.
- Load Requirements: Sleeve supports are designed for high-load situations, while spherical supports are engineered to handle more demanding conditions, thereby ensuring enhanced reliability and durability.
- Budget Constraints: Cost-effectiveness plays a significant role in the choice of support.
Practical examples illustrate these differences in sleeve bearing vs ball bearing; ball components are commonly found in precision motors due to their ability to sustain high speeds and reduce friction. Moreover, case studies highlight the successful implementation of sleeve supports in heavy machinery, showcasing their efficiency in high-load scenarios. For instance, the introduction of radial needle components by Radial Needle Bearing Quotes demonstrates their high precision and durability across various sectors, underscoring the importance of selecting the right type.
Expert recommendations emphasize the necessity of aligning component selection with specific application requirements to ensure optimal performance and durability. As noted by a spokesperson for Stick Bearing Suppliers, “The company’s dedication to quality, performance, and customer satisfaction ensures that it will continue to be a trusted partner for businesses worldwide.” This statement reinforces the importance of expert guidance in making informed bearing choices.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between sleeve and ball bearings is essential for engineers and decision-makers aiming to optimize performance in their respective applications. Sleeve bearings offer distinct advantages in low-speed, high-load scenarios, providing cost-effectiveness and durability in environments such as heavy machinery and cooling systems. Conversely, ball bearings excel in high-speed applications, delivering superior efficiency, longevity, and reduced friction, making them ideal for precision motors and high-performance machinery.
While sleeve bearings may present a lower initial investment, their shorter lifespan and higher heat generation can lead to increased long-term costs. In contrast, ball bearings, despite their higher upfront price, provide better overall value through reduced maintenance and enhanced reliability. This underscores the importance of considering the total cost of ownership when selecting the appropriate bearing type.
Ultimately, the choice between sleeve and ball bearings should be guided by specific application needs, operational environments, and budget constraints. By meticulously evaluating these factors, industries can ensure they select the most suitable bearing type, thereby enhancing both performance and efficiency. As technology continues to advance, staying informed about the characteristics and innovations of these bearings will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the ever-evolving landscape of machinery and electronics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are cylindrical supports and how do they function?
Cylindrical supports, also known as plain supports, consist of a cylindrical tube designed to hold a rotating shaft. They operate through a sliding motion that minimizes friction, although this can lead to wear over time.
What materials are typically used to construct sleeve supports?
Sleeve supports are typically constructed from materials such as bronze or plastic.
In what applications are sleeve supports most effective?
Sleeve supports excel in applications that demand low-speed and high-load capabilities, such as cooling systems and power management devices.
How do ball elements differ from sleeve supports?
Ball elements utilize small spheres to maintain distance between the inner and outer races, facilitating smoother rotation and significantly reducing friction, allowing them to support higher speeds and loads.
Where are ball elements commonly used?
Ball elements are particularly suitable for motors and high-performance machinery, as well as applications requiring high-speed performance and precision, such as in RF devices and interconnection technologies.
What is the current market trend for cylindrical supports?
The Global High Voltage Motor Cylindrical Support Market is valued at USD 1.71 billion in 2023, with projections to reach USD 5.14 billion by 2032, driven by urban development and industrial advancement, particularly in regions like China.
What advantages do engineers see in cylindrical supports?
Engineers highlight the durability and cost-effectiveness of cylindrical supports in specific applications.
What recent industry development emphasizes the importance of cylindrical supports?
NBI Bearing Europe’s acquisition of Industrias Beta showcases the increasing significance of cylindrical supports in the electric and automotive sectors.
What are the limitations of sleeve bearings compared to ball bearings?
Sleeve bearings have reduced speed potential compared to ball bearings, while ball bearings may not perform as effectively under heavy loads.
How are cylindrical and spherical components evolving with technological advancements?
Both cylindrical and spherical components continue to evolve with innovations aimed at improving performance and extending service life, ensuring their vital role in the electronics sector.