Introduction
The essential role of cooling fans in electronic devices cannot be overstated. As technology evolves, the need for effective heat management becomes increasingly critical. Engineers are now tasked with finding thermal solutions that not only boost system performance but also prolong the lifespan of components. Yet, with a plethora of options and specifications at their disposal, how can engineers confidently select the right cooling fans for their specific applications?
This article explores key strategies and considerations for the effective integration of cooling fans. By delving into these insights, engineers can significantly improve thermal management in electronics design, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Understand the Role of Cooling Fans in Electronics Design
Cooling units, such as top cooling fans, are essential for the thermal management of electronic devices, effectively dissipating heat generated by components like CPUs, GPUs, and power supplies. In compact, high-performance systems, the risk of overheating escalates, making robust thermal management solutions critical. Engineers must understand that top cooling fans not only boost efficiency but also prolong the lifespan of electronic components by maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Consider high-density environments such as data centers: insufficient ventilation can lead to heat throttling, where devices intentionally reduce performance to prevent damage. By thoroughly assessing the specific temperature regulation needs of each application, engineers can select the most suitable configurations of top cooling fans, ensuring effective heat dissipation and enhancing system reliability.
Recent advancements in temperature regulation technology, including variable speed control and low noise operation, further refine thermal management strategies. These modern DC ventilation devices have become indispensable in electronics design, addressing the limitations of traditional refrigeration solutions while improving the longevity and efficiency of electronic systems.
In summary, the integration of advanced cooling technologies is not just a technical necessity; it is a strategic imperative for engineers aiming to optimize performance and reliability in electronic devices.
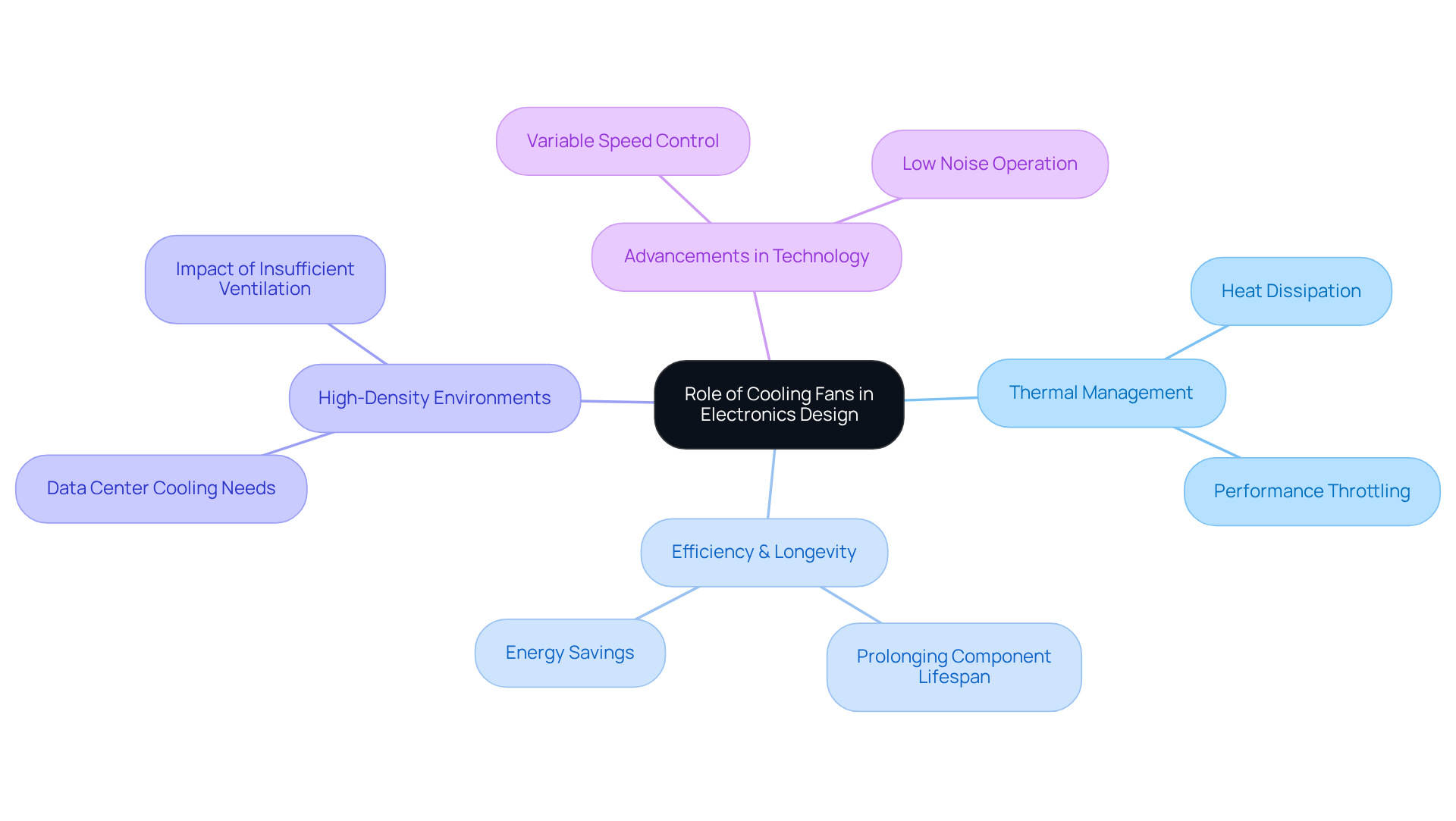
Identify Key Features for Selecting Cooling Fans
When selecting cooling fans, engineers must consider several key features that directly impact performance and efficiency:
-
Airflow Rate (CFM): This metric quantifies the volume of air a fan can move, which is essential for effective cooling. Applications generating significant heat typically require higher CFM ratings to maintain optimal temperatures.
-
Static Pressure: This measurement is crucial for fans operating in restrictive environments, as it reflects the fan’s capability to push air through obstacles such as heatsinks or filters. Recent trends indicate that static pressure ratings are increasingly important for ensuring efficient airflow in compact designs.
-
Noise Levels: Balancing performance with noise is vital, particularly in consumer electronics where quiet operation is preferred. Fans with lower decibel (dB) ratings are ideal for these applications, as they provide effective cooling without disruptive sound levels. For instance, some models have been noted for their silent operation while maintaining excellent thermal management.
-
Energy Efficiency: Selecting devices that use less power without compromising performance is crucial for lowering operational expenses and attaining sustainability objectives. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on energy-efficient designs in the electronics industry.
-
Size and Form Factor: The physical dimensions of the fan must align with the design constraints of the device while still providing sufficient ventilation. Bigger ventilators typically provide greater CFM because of their wider blades, rendering them appropriate for uses demanding substantial airflow.
By thoroughly assessing these characteristics, engineers can choose devices that enhance efficiency while conforming to design specifications, guaranteeing effective solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
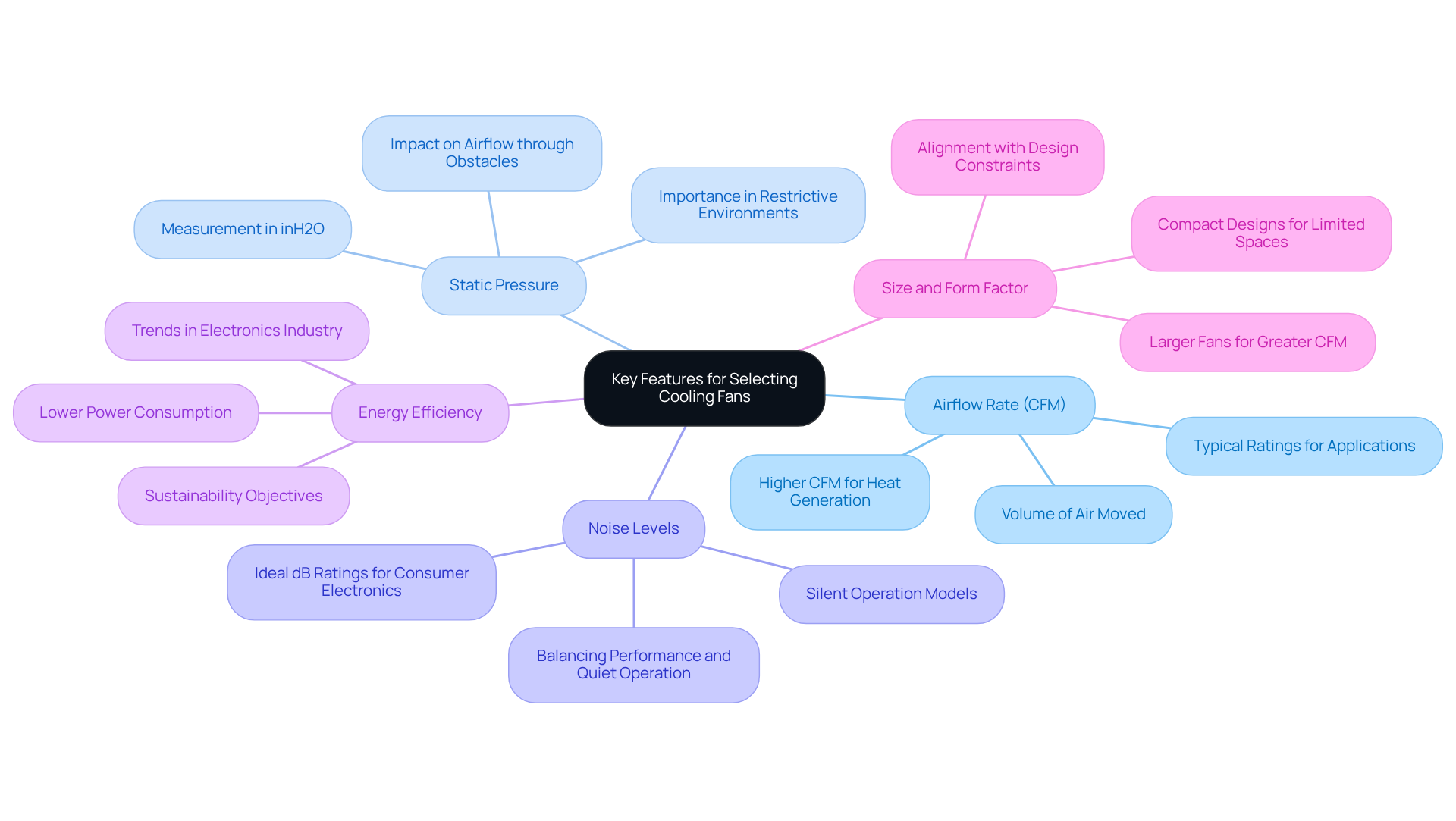
Implement Best Practices for Cooling Fan Integration
To ensure optimal performance of cooling fans, engineers must adhere to several best practices during integration:
-
Proper Placement: Position air circulators strategically to create effective airflow paths. Intake fans should draw in cool air from unobstructed areas, while exhaust fans must efficiently expel hot air, ideally positioned at the highest points of the enclosure.
-
Avoid Airflow Obstructions: Eliminating any obstructions in the airflow path, such as cables or components, is crucial. These obstructions can significantly impede fan performance. For example, airflow obstruction issues have been observed in various electronic devices, where improper component placement led to insufficient temperature regulation and overheating.
-
Use of Ducting: In larger enclosures, ducting can effectively direct airflow, ensuring that cool air reaches critical components. This method enhances cooling efficiency, particularly in systems where airflow paths are convoluted or restricted.
-
Regular Maintenance: Implementing a maintenance schedule is essential for cleaning fans and checking for wear. Dust buildup can significantly diminish fan efficiency and longevity, resulting in heightened heat stress on electronic components.
-
Testing and Validation: After installation, performing thermal testing is essential to confirm that the temperature management solution meets the required specifications. This procedure aids in recognizing any necessary modifications to enhance efficiency, ensuring that the refrigeration system functions effectively under practical conditions.
By following these practices, engineers can maximize the effectiveness of fans in their designs, ultimately enhancing the reliability and longevity of electronic devices.
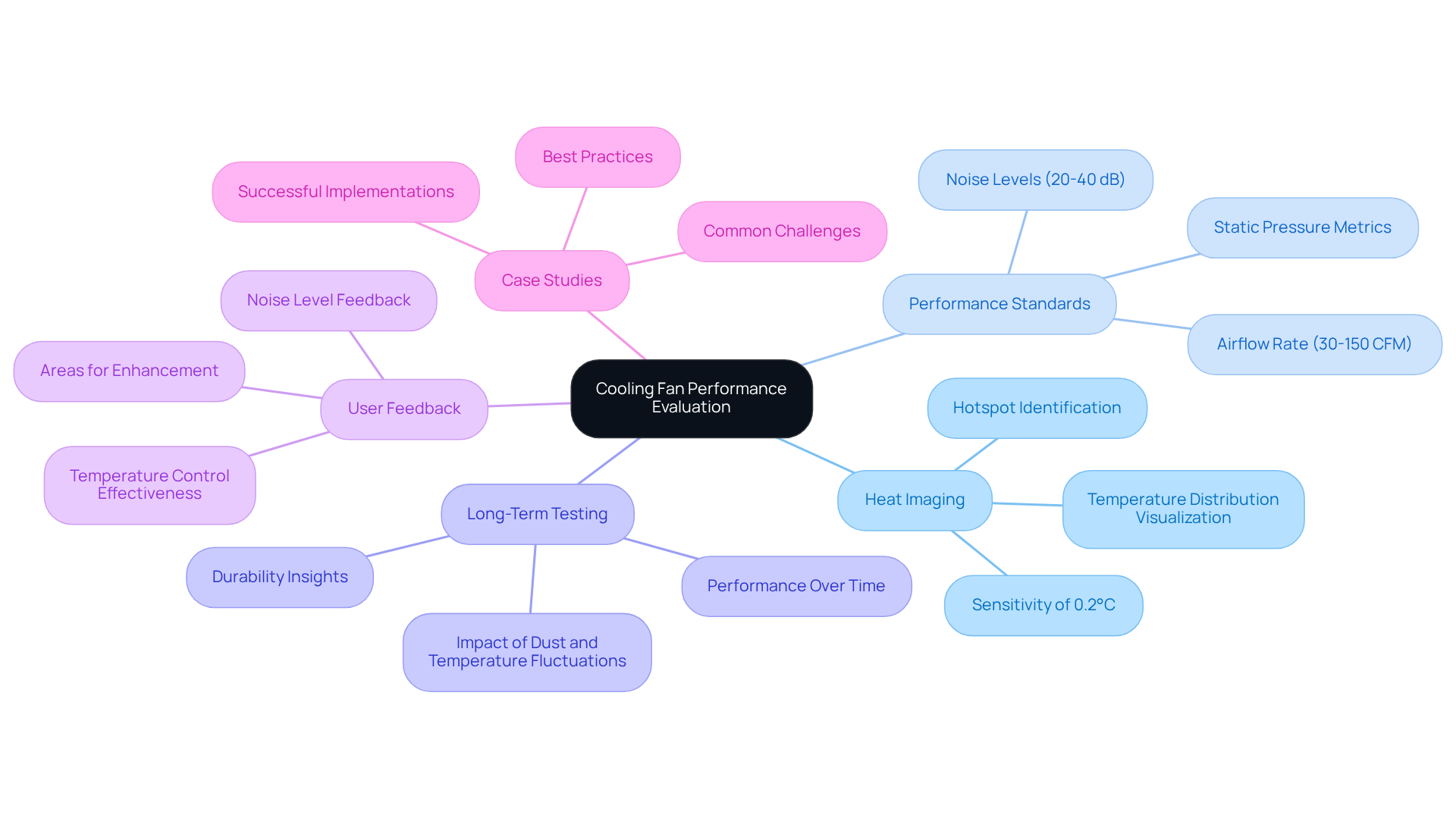
Evaluate Cooling Fan Performance in Real-World Applications
To effectively evaluate cooling fan performance, engineers must consider several key metrics and methodologies:
-
Heat Imaging: Employ uncooled infrared cameras to visualize temperature distribution across components. This technique identifies hotspots that may require additional cooling, detecting temperature differences as small as 0.2°C. Such precise insights into thermal dynamics are invaluable for optimizing performance.
-
Performance Standards: Assess fan functionality against established industry guidelines to evaluate efficiency and effectiveness. Key metrics include airflow rate, typically ranging from 30 to 150 CFM for electronic devices, static pressure, and noise levels. These can vary from 20 dB for quiet models to over 40 dB for high-performance units under load conditions. Understanding these metrics is essential for ensuring optimal temperature regulation in electronic devices.
-
Long-Term Testing: Implement long-term performance tests to evaluate how fans operate over time, especially in environments with fluctuating temperatures and dust levels. This method provides insights into the durability and reliability of temperature regulation solutions in real-world scenarios.
-
User Feedback: Gather qualitative input from end-users regarding noise levels and temperature control effectiveness. This feedback offers valuable insights into real-world performance and highlights areas for enhancement, ensuring that temperature control solutions meet user expectations.
-
Case Studies: Analyze case studies of successful temperature regulation implementations to learn from best practices and common challenges faced by other engineers. These real-world examples can guide decision-making and improve the effectiveness of temperature control strategies.
By systematically assessing fan functionality through these methodologies, engineers can ensure their cooling solutions are both effective and dependable in practical applications. Notably, a 10% drop in RPM can lead to a significant 27% decline in horsepower, underscoring the critical importance of understanding RPM in fan performance.
Conclusion
The integration of top cooling fans is a fundamental aspect of electronics design, playing a critical role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures and enhancing the performance and reliability of electronic devices. As technology advances, engineers must recognize that effective thermal management is not merely a technical requirement but a strategic necessity that can significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of their systems.
Key insights on selecting the right cooling fans are essential. Consider features such as:
- Airflow rate
- Static pressure
- Noise levels
- Energy efficiency
- Size
Best practices for fan integration include:
- Proper placement
- Avoiding airflow obstructions
- Conducting thorough testing
By adhering to these guidelines, engineers can ensure their cooling solutions are tailored to meet the specific demands of their applications.
The significance of cooling fans in electronics cannot be overstated. As the industry evolves, engineers are encouraged to stay informed about the latest advancements in cooling technologies and methodologies. This knowledge not only enhances the performance of their designs but also contributes to the development of more efficient, reliable electronic systems. Embracing these best practices will improve thermal management and help achieve sustainability goals within the rapidly changing landscape of electronics design.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of cooling fans in electronics design?
Cooling fans are essential for thermal management in electronic devices, dissipating heat generated by components like CPUs, GPUs, and power supplies to prevent overheating.
Why is thermal management critical in compact, high-performance systems?
In compact, high-performance systems, the risk of overheating increases, making robust thermal management solutions necessary to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prolong the lifespan of electronic components.
What can happen if there is insufficient ventilation in high-density environments like data centers?
Insufficient ventilation can lead to heat throttling, where devices intentionally reduce their performance to prevent damage from overheating.
How can engineers ensure effective heat dissipation in electronic devices?
Engineers can assess the specific temperature regulation needs of each application and select suitable configurations of top cooling fans to enhance system reliability and ensure effective heat dissipation.
What recent advancements have been made in temperature regulation technology for cooling fans?
Recent advancements include variable speed control and low noise operation, which refine thermal management strategies and address the limitations of traditional refrigeration solutions.
Why is the integration of advanced cooling technologies important for engineers?
The integration of advanced cooling technologies is a strategic imperative for engineers to optimize performance and reliability in electronic devices, improving both longevity and efficiency.