Introduction
Understanding the complexities of impeller fan design is crucial for optimizing airflow and enhancing performance across various applications, particularly in electronics engineering. This article explores the essential features of impeller fans, illustrating how their design significantly impacts efficiency, cooling capabilities, and overall system reliability.
As technology advances, engineers face a pressing challenge: how can they balance performance with energy efficiency while addressing the unique demands of modern electronic environments? This inquiry not only underscores the importance of innovative design but also sets the stage for a deeper examination of the strategies that can lead to effective solutions.
Define Impeller Fan Design
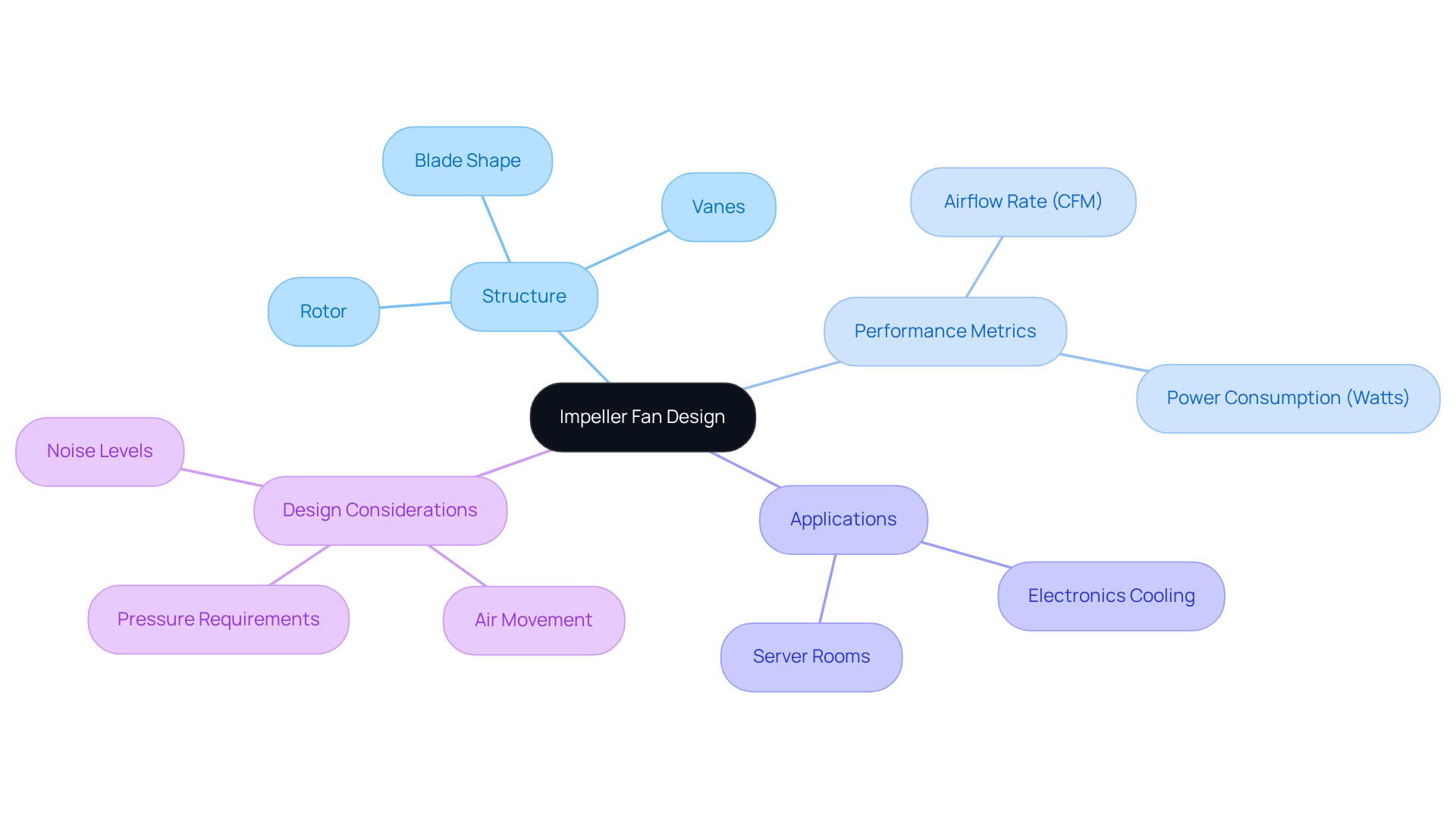
The structure of an impeller fan design encompasses the engineering and configuration of the rotating component that drives air or gas movement within a fan. At the heart of this system is the rotor, composed of vanes attached to a central hub, which spins to generate airflow. The impeller fan design involves crucial elements such as blade shape, size, and arrangement, which directly influence the fan’s performance, efficiency, and suitability for specific applications. In the electronics sector, where effective cooling and ventilation are paramount, centrifugal blowers are essential for maintaining optimal operating conditions for components.
Statistics reveal that rotor devices come in sizes ranging from 15 to 280mm for tube axial types and 15 to 225mm for centrifugal blowers, underscoring their versatility. The efficiency of these devices is often measured by airflow rate in cubic feet per minute (CFM) and power consumption in watts, highlighting the objective of achieving high CFM with low wattage for energy-efficient solutions.
Real-world examples illustrate the critical role of fan structure across various applications. For instance, case studies on the integration of blower units in server rooms demonstrate how these devices enhance temperature control, thereby improving the reliability of server operations and preventing critical failures. Furthermore, advancements in impeller fan design, including the adoption of curved blades that minimize drag and optimize airflow, are increasingly prevalent, reflecting current industry trends.
Engineers emphasize the necessity of considering factors like air movement, pressure requirements, and noise levels when selecting blower units. As industry expert Ryan Smoot articulates, “The choice between centrifugal and axial devices should be guided by the intended application, available space, and thermal requirements of the system.” This insight underscores the vital importance of customized impeller fan design in achieving effective thermal management in electronic systems.
Explain the Importance of Impeller Fan Design in Electronics Engineering
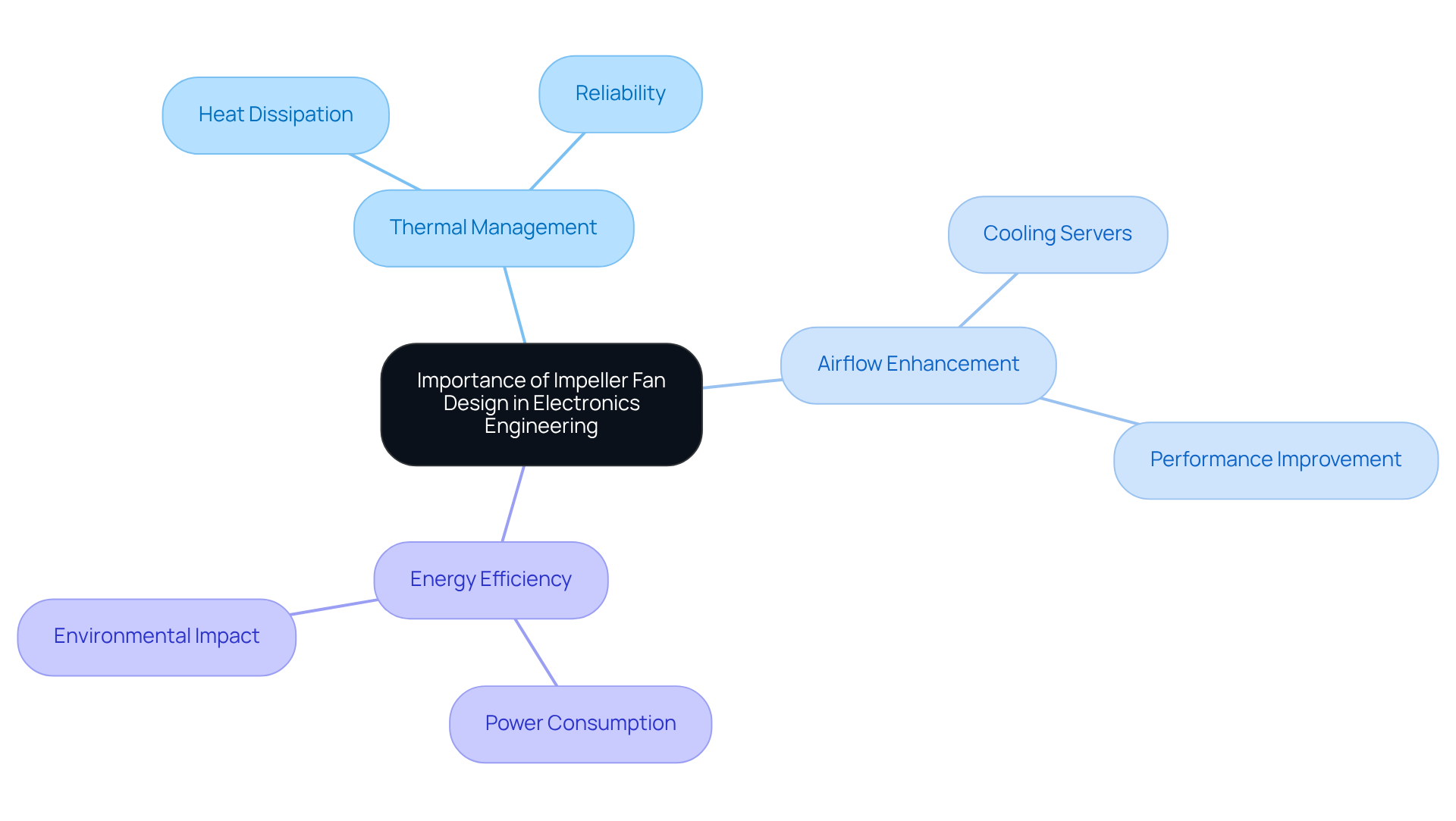
In electronics engineering, the design of rotor blades is crucial for effective thermal management. Electronic devices generate substantial heat during operation, making it vital to maintain optimal temperatures. This prevents overheating and ensures reliability. Impeller blowers significantly enhance airflow across components, facilitating heat dissipation, which in turn improves performance and extends the lifespan of devices.
For example, in data centers, turbine blowers are essential for cooling servers, ensuring they operate within safe temperature ranges. Statistics reveal that excessive heat can lead to performance throttling and component degradation, with semiconductor reliability decreasing by up to 50% for every 10 °C increase in operating temperature. This highlights the importance of effective cooling solutions.
Moreover, well-designed EC axial units contribute to energy efficiency, consuming up to 70% less power compared to conventional AC systems. This efficiency is increasingly important in today’s environmentally conscious market. Case studies underscore that efficient cooling solutions, including those related to impeller fan design as discussed in the ‘Role of Impeller Fans in Electronics,’ not only enhance operational reliability but also reduce overall operational expenses. This makes these devices indispensable in contemporary electronics development.
Identify Key Characteristics and Components of Impeller Fan Design
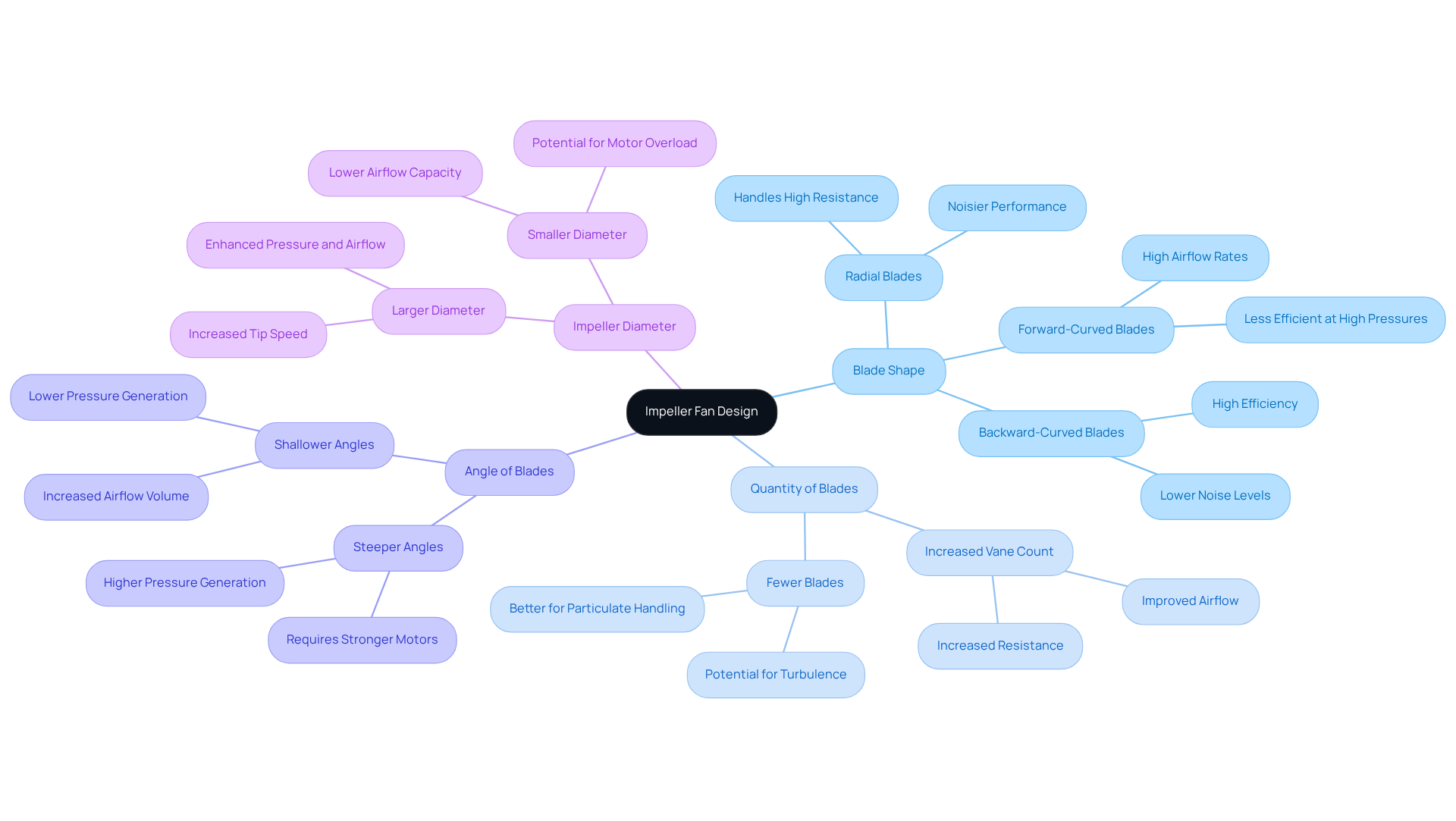
Key features of impeller fan design are critical to understanding their performance. These include:
- The shape of the blades
- The quantity of blades
- The angle of the blades
- The impeller diameter
Gagner-Toomey Associates, recognized as the globe’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, showcases these principles through a diverse range of DC input Tube Axial fans, varying from 15 to 280mm, and Centrifugal Blowers, from 15 to 225mm.
Common designs for cutting edges – forward-curved, backward-curved, and radial – each offer unique performance benefits. The quantity of vanes significantly affects airflow and pressure; typically, an increase in vane count improves airflow but may also raise resistance. For instance, backward-curved edges are acknowledged for their high efficiency and decreased noise levels, making them suitable for applications requiring optimal airflow with minimal disruption.
The angle of the blades plays a crucial role in determining airflow efficiency, directly influencing the balance between pressure generation and airflow volume. Additionally, the rotor’s diameter and width are vital in influencing the fan’s overall performance, affecting both the amount of air displaced and the pressure generated. A well-designed rotor, akin to those available in Gagner-Toomey’s extensive range of cooling solutions, not only meets specific application requirements but also enhances energy efficiency and system longevity, ultimately helping to reduce power costs.
Moreover, material choice is essential for performance and durability, particularly in specialized applications such as the food and pharmaceutical industries. Understanding these traits is crucial for engineers tasked with selecting or designing components, such as impeller fan design, that optimize airflow, energy efficiency, and system longevity.
Provide Examples of Impeller Fan Designs and Their Applications
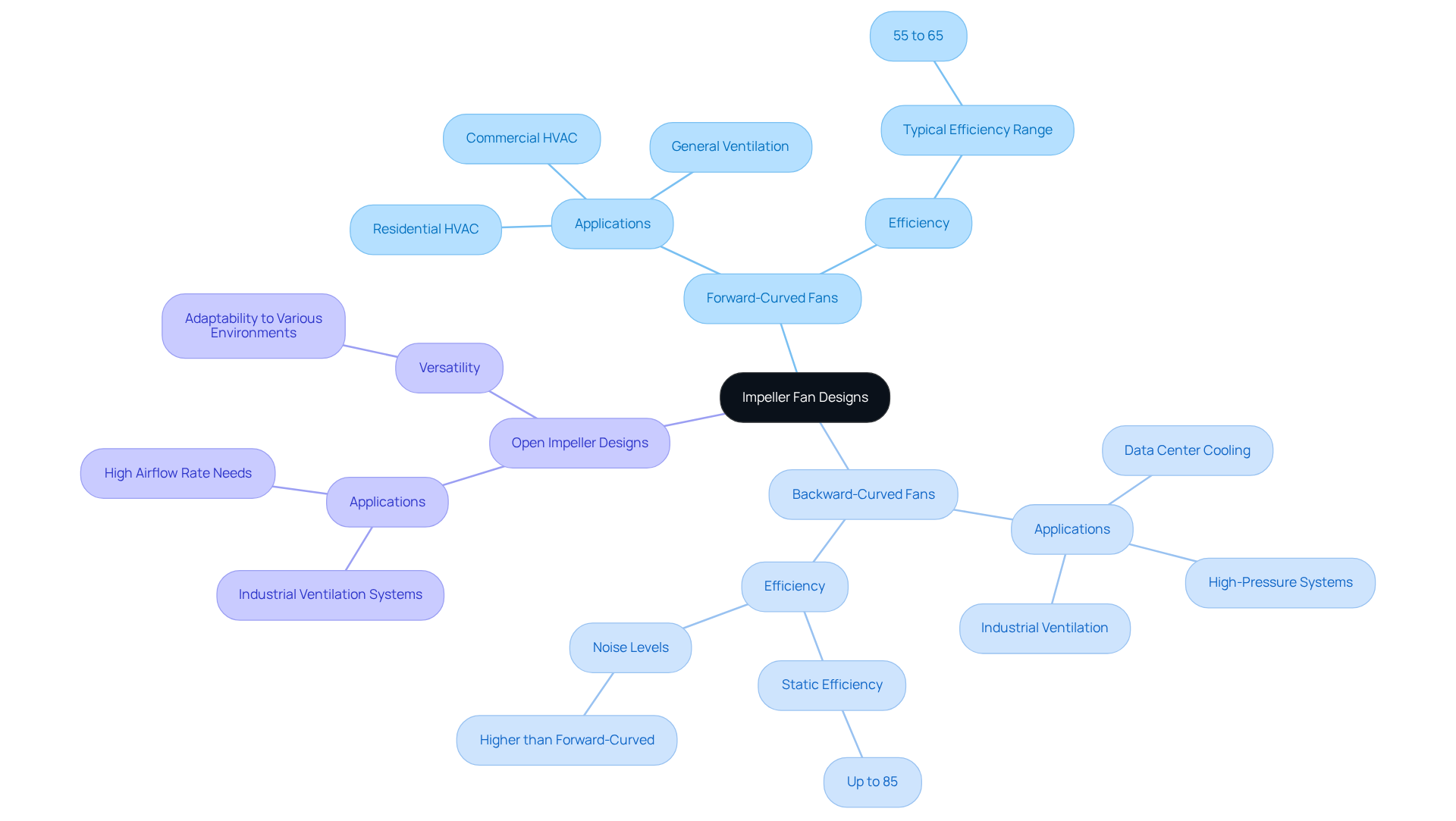
The design of impeller fans plays a crucial role in various applications, particularly in HVAC systems and electronics. The forward-curved model is often preferred for its ability to move large volumes of air quietly, making it ideal for residential and commercial environments. In contrast, the backward-curved version excels in high-pressure applications, where efficiency and reduced noise are paramount.
In the electronics sector, centrifugal fans are indispensable for cooling systems in servers and high-performance computing devices. Efficient heat dissipation is essential in these environments. For instance, the use of backward-curved blades in data center cooling systems significantly enhances airflow while minimizing energy consumption, achieving static efficiencies of up to 85%. This efficiency is further underscored by centrifugal blowers, which can reach up to 84% static efficiency, providing a comparative context for understanding cooling system performance.
Expert insights reveal that backward-curved blades not only improve cooling efficiency but also contribute to lower operational costs in data centers. These blowers require minimal maintenance, typically needing just a quick vacuuming of the motor and vents, which adds to their operational benefits. However, it is crucial to consider that backward-curved fans tend to generate more noise compared to their forward-curved counterparts, a factor that should be evaluated in noise-sensitive environments.
Moreover, open impeller designs are utilized in applications demanding high airflow rates, such as industrial ventilation systems. This versatility highlights the importance of impeller fan design across various sectors, showcasing their adaptability and efficiency in meeting diverse operational needs.
Conclusion
The design of impeller fans is crucial for achieving optimal performance across various engineering applications, especially in the electronics sector. Understanding the essential components and characteristics that define impeller fan design enables engineers to develop solutions that effectively manage airflow and thermal conditions, ensuring both reliability and efficiency in electronic devices.
Key elements such as blade shape, quantity, angle, and rotor dimensions are critical factors influencing performance. These features are exemplified through real-world applications, where tailored designs enhance cooling efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and ultimately contribute to the longevity of electronic systems. For instance, case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of centrifugal blowers and various fan types in maintaining safe operating temperatures, underscoring their role in preventing overheating and improving operational reliability.
Given the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions in electronics, the importance of impeller fan design is paramount. As technology evolves, integrating advanced designs will be essential to meet the cooling and ventilation needs of modern systems. Engineers and designers should prioritize customized fan solutions that not only address specific application requirements but also align with sustainability goals. This approach will ensure the continued advancement of efficient electronic systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an impeller fan design?
An impeller fan design refers to the engineering and configuration of the rotating component, known as the rotor, which drives air or gas movement within a fan. It includes elements such as blade shape, size, and arrangement that affect performance and efficiency.
What is the role of the rotor in an impeller fan?
The rotor, composed of vanes attached to a central hub, spins to generate airflow, playing a crucial role in the overall function of the fan.
What types of fans are mentioned in the article, and what are their sizes?
The article mentions tube axial types and centrifugal blowers. Rotor devices for tube axial types range from 15 to 280mm, while centrifugal blowers range from 15 to 225mm.
How is the efficiency of impeller fans measured?
The efficiency of impeller fans is measured by the airflow rate in cubic feet per minute (CFM) and power consumption in watts, with a focus on achieving high CFM with low wattage for energy efficiency.
Why are centrifugal blowers important in the electronics sector?
Centrifugal blowers are essential for effective cooling and ventilation in the electronics sector, helping to maintain optimal operating conditions for components and preventing critical failures.
What advancements in impeller fan design are currently prevalent?
Advancements include the adoption of curved blades that minimize drag and optimize airflow, reflecting current industry trends aimed at improving efficiency and performance.
What factors should be considered when selecting blower units?
Factors to consider include air movement, pressure requirements, noise levels, intended application, available space, and thermal requirements of the system.
Who is Ryan Smoot, and what does he emphasize regarding impeller fan design?
Ryan Smoot is an industry expert who emphasizes that the choice between centrifugal and axial devices should be guided by the intended application and thermal requirements, highlighting the importance of customized impeller fan design for effective thermal management.

