Overview
Static pressure in HVAC systems represents the resistance to airflow as air traverses ductwork and components, a critical factor in ensuring efficient and effective heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Maintaining optimal static pressure levels, typically around 0.5 inches of water column, is essential for achieving consistent airflow. Neglecting this aspect can lead to increased energy consumption and uneven temperature distribution, underscoring the necessity for regular monitoring and adjustment to uphold system performance.
Introduction
Static pressure serves as a pivotal force in the efficiency and effectiveness of HVAC systems, acting as the unseen element that governs airflow through ductwork and components. Recognizing this critical parameter not only enhances system performance but also ensures optimal comfort levels within indoor environments. Despite its importance, the implications of static pressure are frequently overlooked, leading to challenges such as increased energy consumption and uneven temperature distribution.
What does static pressure truly signify, and how can it be accurately measured and managed to avert common HVAC issues?
Define Static Pressure in HVAC Systems
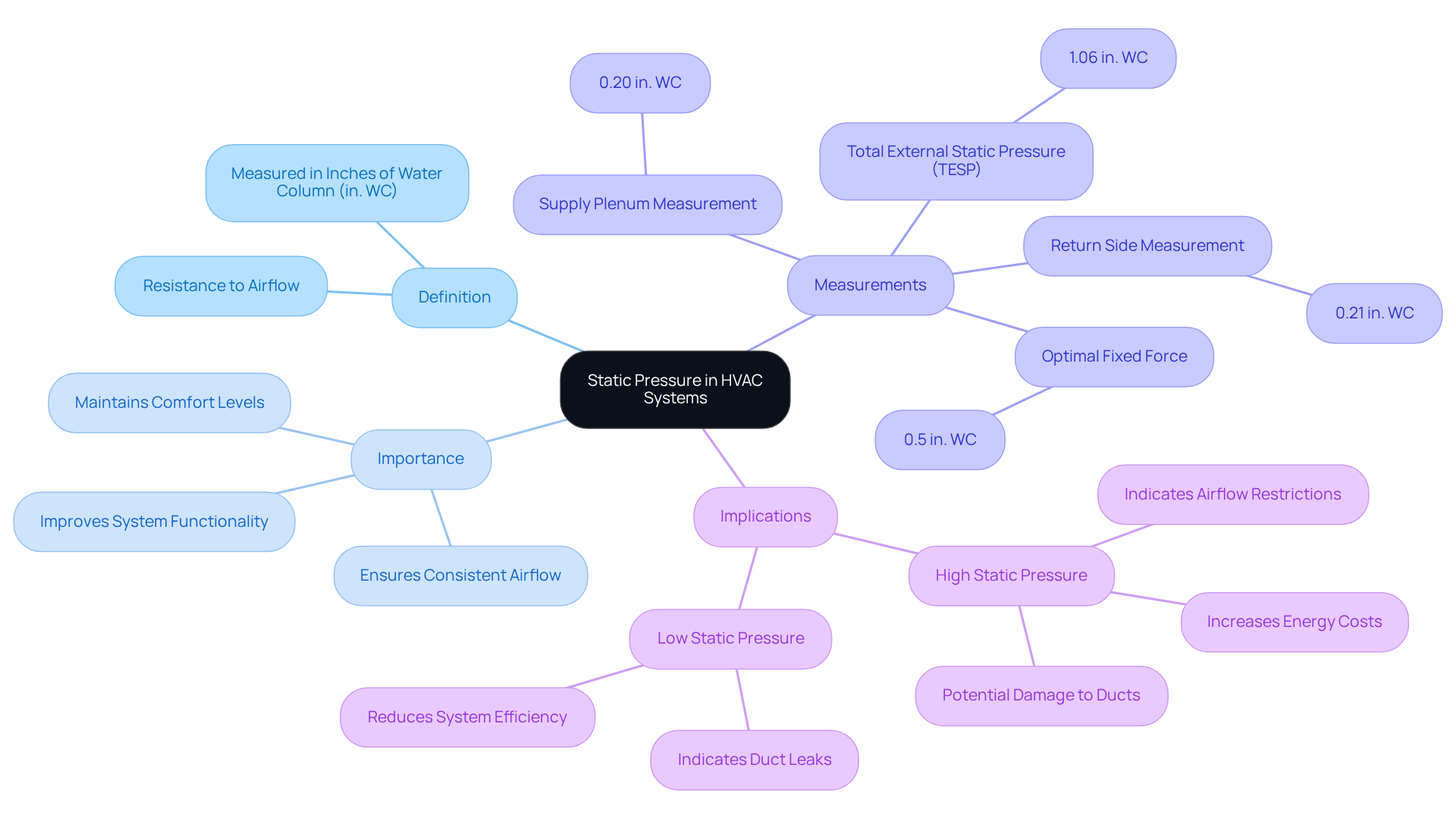
Static force in HVAC setups represents the resistance to airflow encountered as air moves through ductwork and various components. This critical parameter is essential for understanding what does static pressure mean in the efficiency and effectiveness of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Measured in inches of water column (in. WC), static force is essential for ensuring consistent airflow, which is vital for achieving uniform air distribution throughout a building. For instance, a typical fixed measurement in a supply plenum may be around 0.20 in. WC, while the return side measurement during air conditioning mode is approximately 0.21 in. WC.
The optimal fixed force for heating and cooling units is about 0.5 inches of water column (in. WC), a level that minimizes pressure-related leaks and potential damage to air ducts. In practical applications, a reading exceeding 0.9 in. WC signifies possible airflow restrictions, and a Total External Static Pressure (TESP) reading above this threshold indicates similar concerns.
Understanding fixed force empowers engineers to develop frameworks that , maintain comfort levels, and improve overall system functionality, which raises the question of what does static pressure mean. As noted, “Static resistance in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning refers to the opposition air faces as it travels through ductwork, filters, and other components.”
Maintaining the correct fixed force is crucial for ensuring adequate airflow, operational efficiency, and system durability.
Explain the Importance of Static Pressure in HVAC Performance
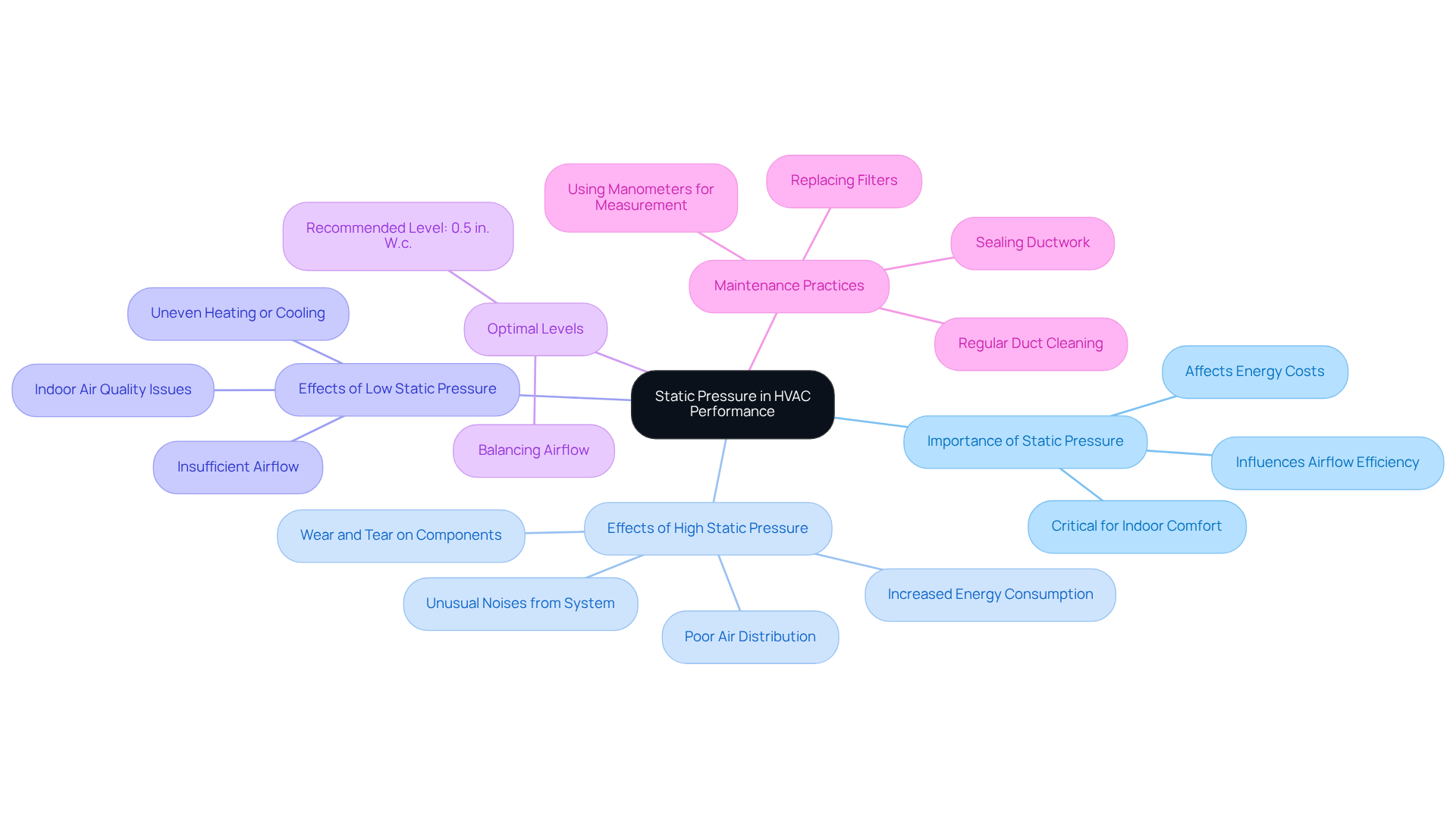
Understanding what does mean is essential, as it represents a fundamental aspect of HVAC performance that significantly influences airflow rates and overall efficiency. Elevated air resistance can restrict airflow, leading to discomfort in climate-controlled spaces and necessitating increased system effort to achieve desired temperatures. This heightened workload can escalate energy usage by as much as 30% due to elevated fixed resistance, consequently resulting in larger utility expenses. Conversely, low atmospheric force can cause insufficient airflow, resulting in uneven heating or cooling and potential indoor air quality issues stemming from pollutants being drawn in through duct leaks.
Maintaining ideal fixed force is essential for ensuring that heating and cooling units operate within their intended parameters, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. For instance, achieving a balanced fixed force of approximately 0.5 inches of water column (in. W.c.) is deemed optimal for most residential applications and is critical for peak performance. Failure to regulate fixed levels can lead to various heating and cooling performance challenges, including unusual noises from the system, increased wear on components such as blower motors and compressors, and ultimately, a diminished lifespan for the equipment.
Professional insights underscore the importance of routine maintenance practices, such as cleaning duct systems and replacing filters, to prevent airflow complications. As highlighted by heating and cooling specialists, measuring static force with instruments like manometers is vital for diagnosing static force-related issues, which raises the question of what does static pressure mean. By proactively addressing these concerns, HVAC professionals can enhance efficiency, improve indoor comfort, and reduce energy costs, ensuring a reliable and efficient heating and cooling solution.
Detail Methods for Measuring Static Pressure in HVAC Systems
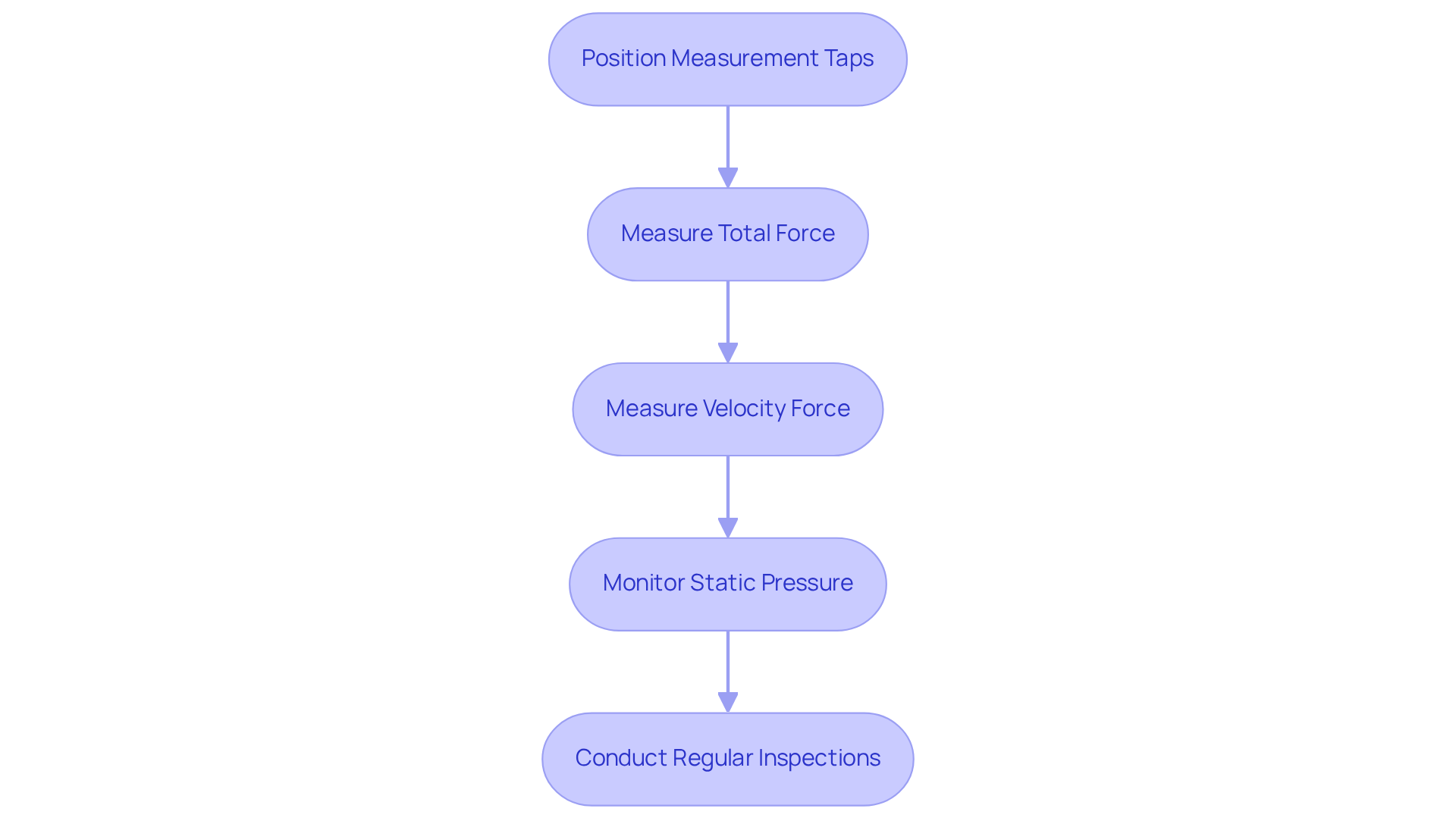
In HVAC setups, understanding what does static pressure mean is primarily evaluated using instruments such as manometers and digital gauges. Technicians typically position measurement taps within the ductwork at critical locations, including upstream and downstream of filters, coils, and fans. This strategic placement facilitates precise readings that can reveal areas of high resistance or obstructions within the network.
To achieve a , both total force and velocity force must be measured, providing a complete overview of the system’s performance. Regular monitoring of static force is essential for understanding what does static pressure mean in ensuring optimal operational efficiency and for identifying potential issues before they escalate into larger complications.
Elevated air conditions can lead to increased energy consumption and operational costs, while reduced air conditions may result in fluctuating temperatures across different rooms and uneven heating or cooling throughout the house.
By conducting consistent inspections, including the replacement of air filters every 90 days, heating and cooling professionals can enhance reliability and extend the lifespan of equipment.
Identify Common Static Pressure Problems and Solutions
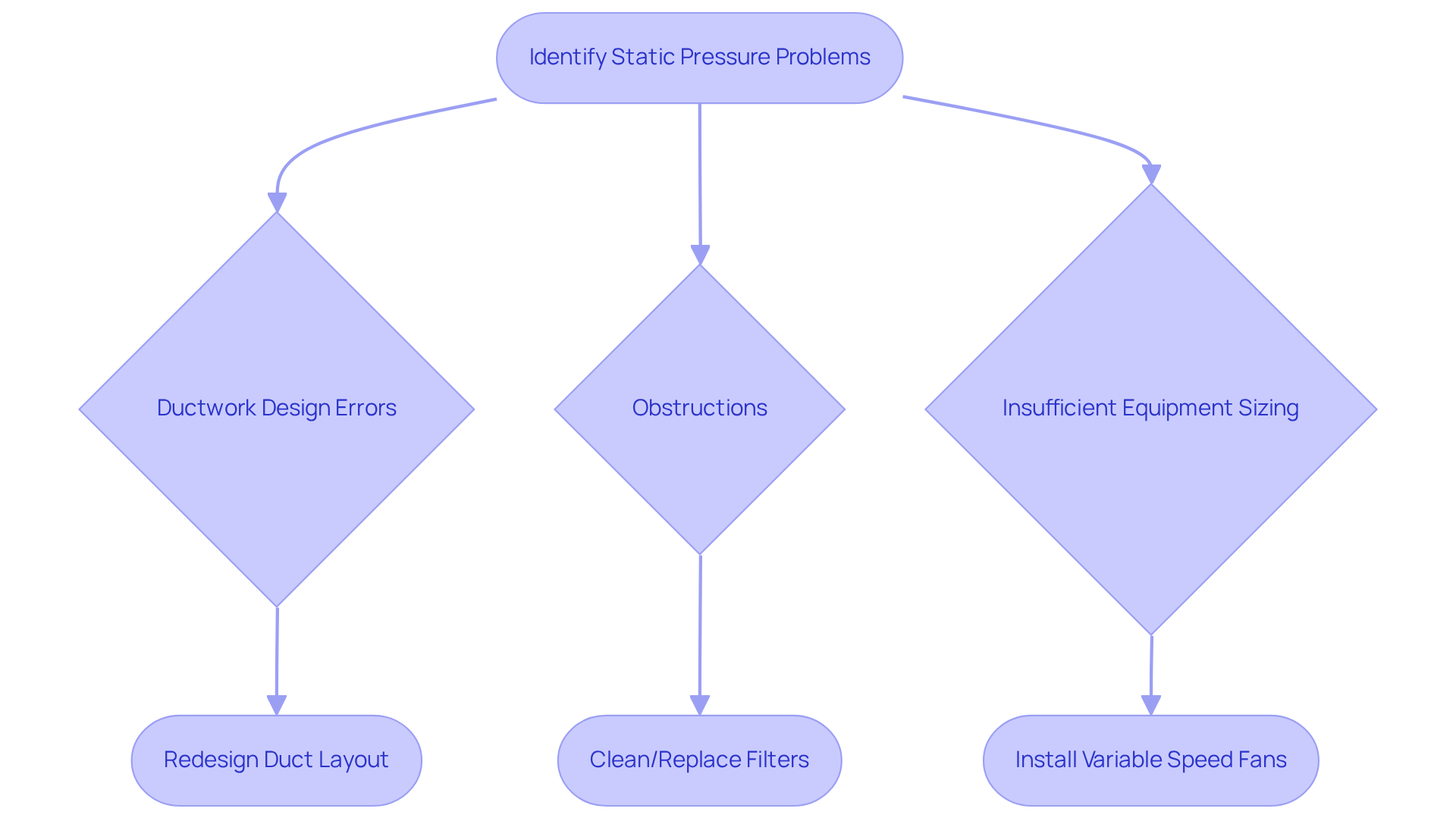
Frequent fixed airflow issues in HVAC setups stem from excessive airflow force, often due to ductwork design errors, obstructions from debris or incorrect installation, and insufficient equipment sizing. These challenges necessitate a thorough examination of duct layouts, where redesigning to minimize bends and restrictions can significantly enhance performance. Additionally, cleaning or replacing filters is crucial for improving airflow, and ensuring that the system is appropriately sized for the space it serves is essential.
To further , the installation of variable speed fans proves beneficial, allowing for dynamic adjustments that sustain optimal pressure levels. Regular maintenance and monitoring are imperative to prevent issues, particularly in understanding what does static pressure mean, ensuring efficient HVAC operation. By implementing these solutions, HVAC systems can operate at peak efficiency, ultimately leading to improved comfort and energy savings.
Conclusion
Understanding static pressure in HVAC systems is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring efficient airflow. This parameter not only influences comfort levels within a space but also directly affects energy consumption and operational costs. By grasping the definition and importance of static pressure, HVAC professionals can make informed decisions that enhance system functionality and longevity.
Key insights discussed throughout the article highlight the significance of maintaining ideal static pressure levels, typically around 0.5 inches of water column. Elevated or insufficient static pressure can lead to various issues, including:
- Increased energy usage
- Uneven temperature distribution
- Potential equipment damage
Regular measurement and monitoring using appropriate tools are essential for diagnosing static pressure-related problems and implementing effective solutions, such as proper duct design and routine maintenance.
Ultimately, a proactive approach to managing static pressure in HVAC systems not only improves indoor comfort but also contributes to energy efficiency and cost savings. By prioritizing static pressure management, individuals and businesses can ensure their HVAC systems operate at peak performance, fostering a healthier and more comfortable environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is static pressure in HVAC systems?
Static pressure in HVAC systems refers to the resistance to airflow encountered as air moves through ductwork and various components. It is a critical parameter for understanding the efficiency and effectiveness of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
How is static pressure measured?
Static pressure is measured in inches of water column (in. WC).
Why is static pressure important in HVAC systems?
Static pressure is essential for ensuring consistent airflow, which is vital for achieving uniform air distribution throughout a building. It also helps maintain operational efficiency and system durability.
What are typical static pressure measurements in HVAC systems?
A typical fixed measurement in a supply plenum may be around 0.20 in. WC, while the return side measurement during air conditioning mode is approximately 0.21 in. WC. The optimal fixed force for heating and cooling units is about 0.5 in. WC.
What does it indicate if static pressure readings exceed 0.9 in. WC?
A reading exceeding 0.9 in. WC signifies possible airflow restrictions, and a Total External Static Pressure (TESP) reading above this threshold indicates similar concerns.
How does understanding static pressure benefit engineers?
Understanding static pressure empowers engineers to develop frameworks that enhance airflow, maintain comfort levels, and improve overall system functionality.

