Overview
This article addresses four essential practices for selecting custom mini fans in design:
- Understanding fan types and specifications
- Evaluating compatibility and performance
- Selecting based on project-specific requirements
- Implementing testing and validation for reliability
Each practice is vital, as it ensures that the chosen fan effectively meets thermal management needs, adheres to design constraints, and maintains long-term operational reliability. Practical examples and testing protocols support these practices, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance.
Introduction
Selecting the right custom mini fan is a pivotal decision in the design process, significantly impacting thermal management and overall system performance. Engineers are confronted with a diverse array of fan types and specifications, navigating this complexity to identify the perfect fit for their specific applications.
How can one ensure that the chosen fan not only meets technical requirements but also enhances the efficiency and reliability of the entire system? This article delves into four essential practices for selecting custom mini fans, offering insights that streamline the decision-making process and optimize design integration.
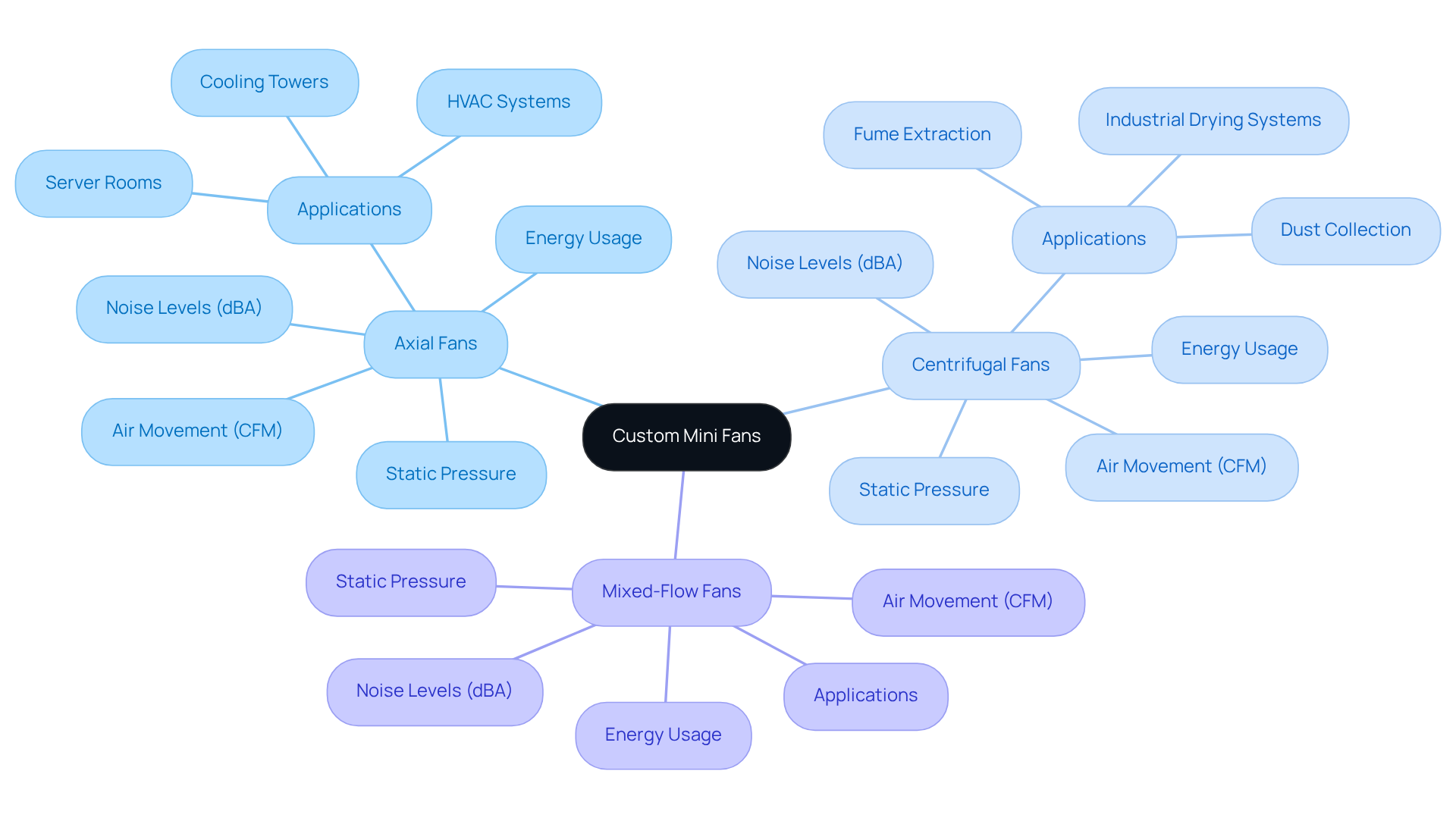
Understand Types and Specifications of Custom Mini Fans
Custom mini fans are available in various types, including axial, centrifugal, and mixed-flow models, each with unique characteristics suited for different applications. Gagner-Toomey Associates, recognized as the globe’s largest producer of standard and custom mini fans, offers an extensive range of DC input tube axial units, varying from 15 to 280mm, and centrifugal blowers, available in dimensions from 15 to 225mm, optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise.
When choosing a fan, it is essential to consider details such as:
- Air movement (measured in CFM)
- Static pressure
- Noise levels (measured in dBA)
- Energy usage
For instance, axial blowers are generally more efficient for high airflow applications, whereas centrifugal blowers excel in situations requiring greater static pressure. Notably, centrifugal blowers expel air at a 90-degree angle from the air intake, a key operational characteristic that distinguishes them from axial models. Furthermore, centrifugal fans tend to be larger and more substantial than axial fans, which is a crucial factor for engineers regarding space and weight limitations in their designs. Understanding these specifications ensures that the selected custom mini fan will effectively address the thermal management needs of the electronic system. IP protection is available in most models upon request, allowing for a custom mini fan feature tailored for specific applications.
Additionally, it is important to consider the physical dimensions and mounting options of the custom mini fan to ensure compatibility with the layout. For example, a compact design may necessitate the use of a custom mini fan size, which could impact airflow and cooling efficiency. Axial blowers are frequently favored in applications such as cooling towers and server rooms, where substantial amounts of air must be displaced with minimal resistance. The compact and cost-effective nature of the custom mini fan makes it suitable for tight spaces. In contrast, centrifugal blowers are ideal for industrial environments where overcoming resistance in ducts or filters is necessary, such as in dust collection and fume extraction systems. Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of fan varieties and specifications, including Gagner-Toomey’s extensive offerings and the custom mini fan, is crucial for optimal integration and functionality.
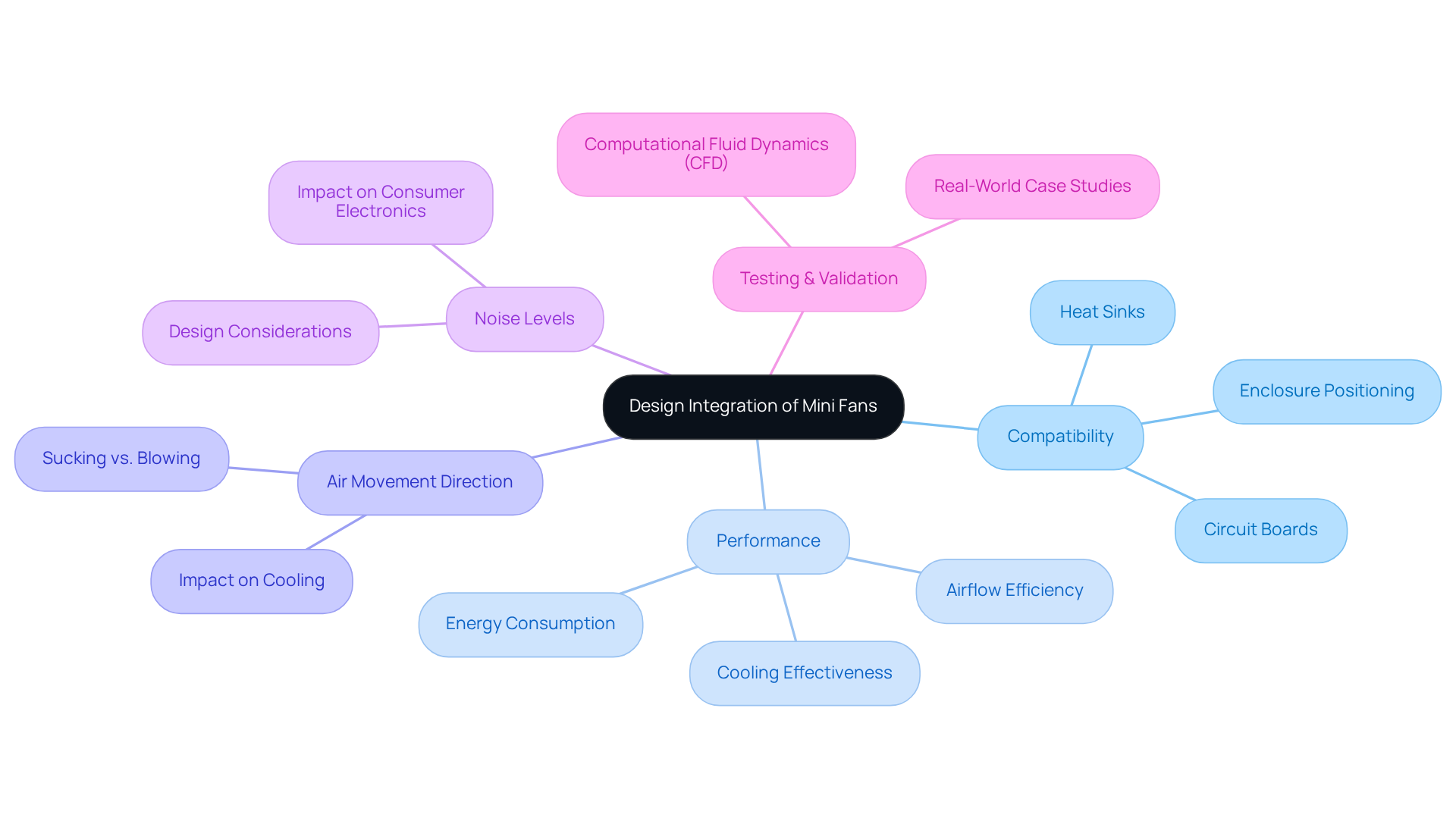
Evaluate Compatibility and Performance in Design Integration
Integrating custom mini fans into electronic designs requires a careful assessment of their compatibility with components like heat sinks, circuit boards, and enclosures. The direction of air movement is critical; for instance, in enclosed areas, improper positioning can lead to diminished effectiveness due to restricted air circulation. Engineers emphasize that aligning the fan’s circulation with the system’s cooling requirements is vital for efficient thermal management. As Ricardo notes, “Sucking is more effective than blowing for reducing temperature,” underscoring the significance of movement direction in cooling efficiency.
Noise levels are equally important, particularly in consumer electronics where sound quality is essential. Utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) tools or simulations can provide valuable insights into and thermal performance, enabling designers to implement informed modifications prior to project completion. This proactive approach not only boosts efficiency but also alleviates potential challenges, ultimately conserving time and resources throughout the development process.
Real-world examples highlight the integration challenges faced. A case study illustrates the impact of fan orientation (sucking versus blowing) on cooling efficiency, revealing that a fan operating in ‘suck’ mode may outperform others in specific configurations. Such findings reinforce the necessity for thorough testing and validation to achieve optimal performance in electronic applications. Furthermore, ensuring that outdoor air intakes are positioned at least 8 inches above horizontal surfaces can prevent blockage and improve ventilation management, further emphasizing the need for thoughtful design considerations.
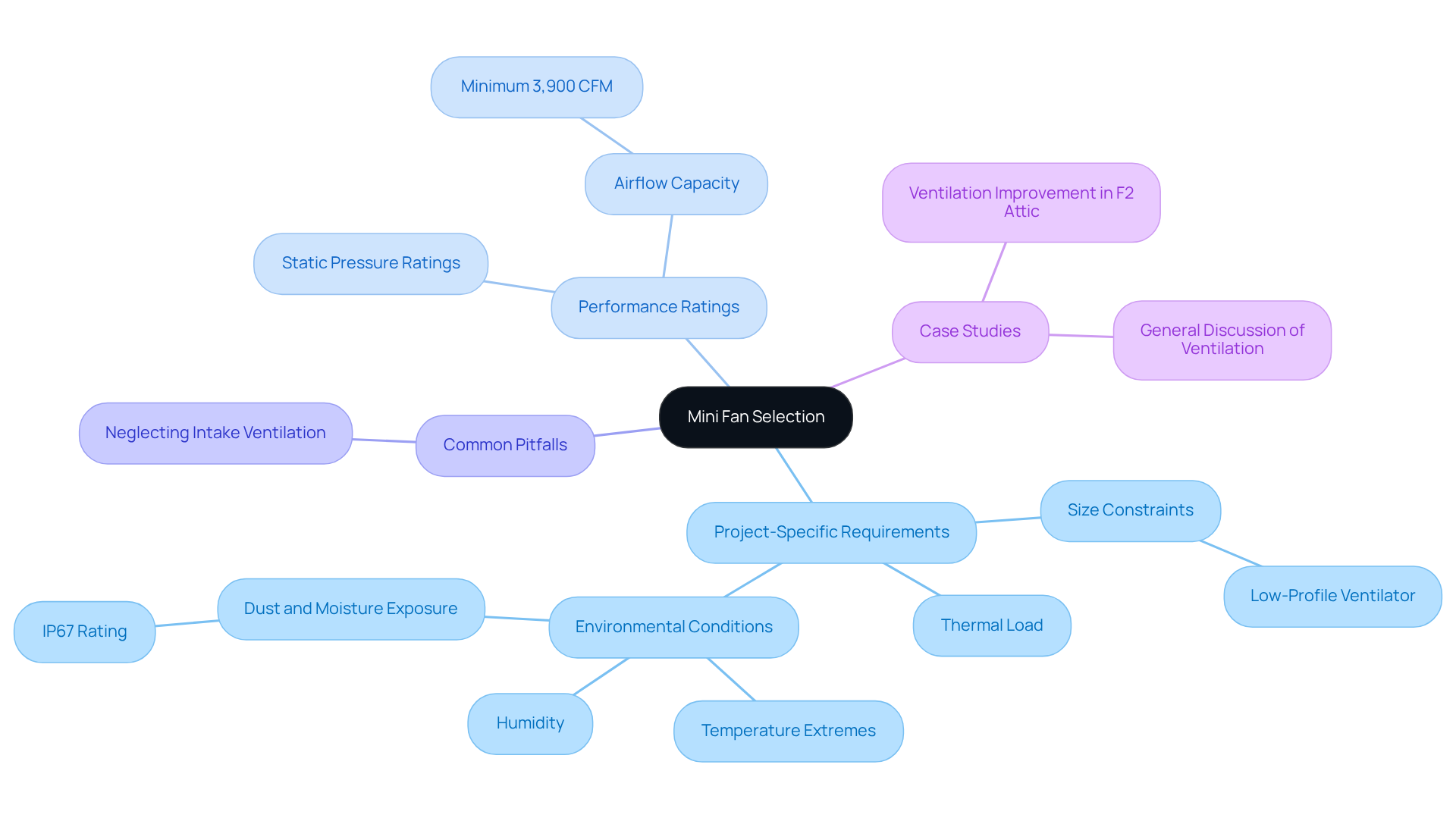
Select Mini Fans Based on Project-Specific Requirements
Each project may have distinct requirements based on factors such as size constraints, thermal load, and environmental conditions. In scenarios where space is restricted, a low-profile ventilator may be essential, while high-performance situations may necessitate devices with greater airflow and static pressure ratings. Statistics indicate that supporters capable of exchanging a minimum of can significantly improve outcomes in challenging environments.
Additionally, it is vital to consider environmental factors, including temperature extremes, humidity, and exposure to dust or moisture. Selecting devices with appropriate ingress protection (IP) ratings can enhance durability and reliability in harsh conditions. For instance, an IP67-rated fan is suitable for outdoor applications where water and dust exposure is a concern. As noted by H. C. Fennell, Inc.:
- “Heating and ventilating ducts that pass through the attic should be well sealed and insulated, and the heat they add to the attic should be considered when sizing the ventilation system.”
By aligning fan selection with project-specific needs, engineers can ensure optimal functionality and durability of their systems. It is also crucial to avoid common pitfalls, such as neglecting the necessity for adequate intake ventilation, which can hinder fan effectiveness. A case study on ventilation improvement in an attic demonstrated that proper fan selection and configuration can lead to significant enhancements in temperature regulation, underscoring the importance of these considerations.
Implement Testing and Validation for Reliability Assurance
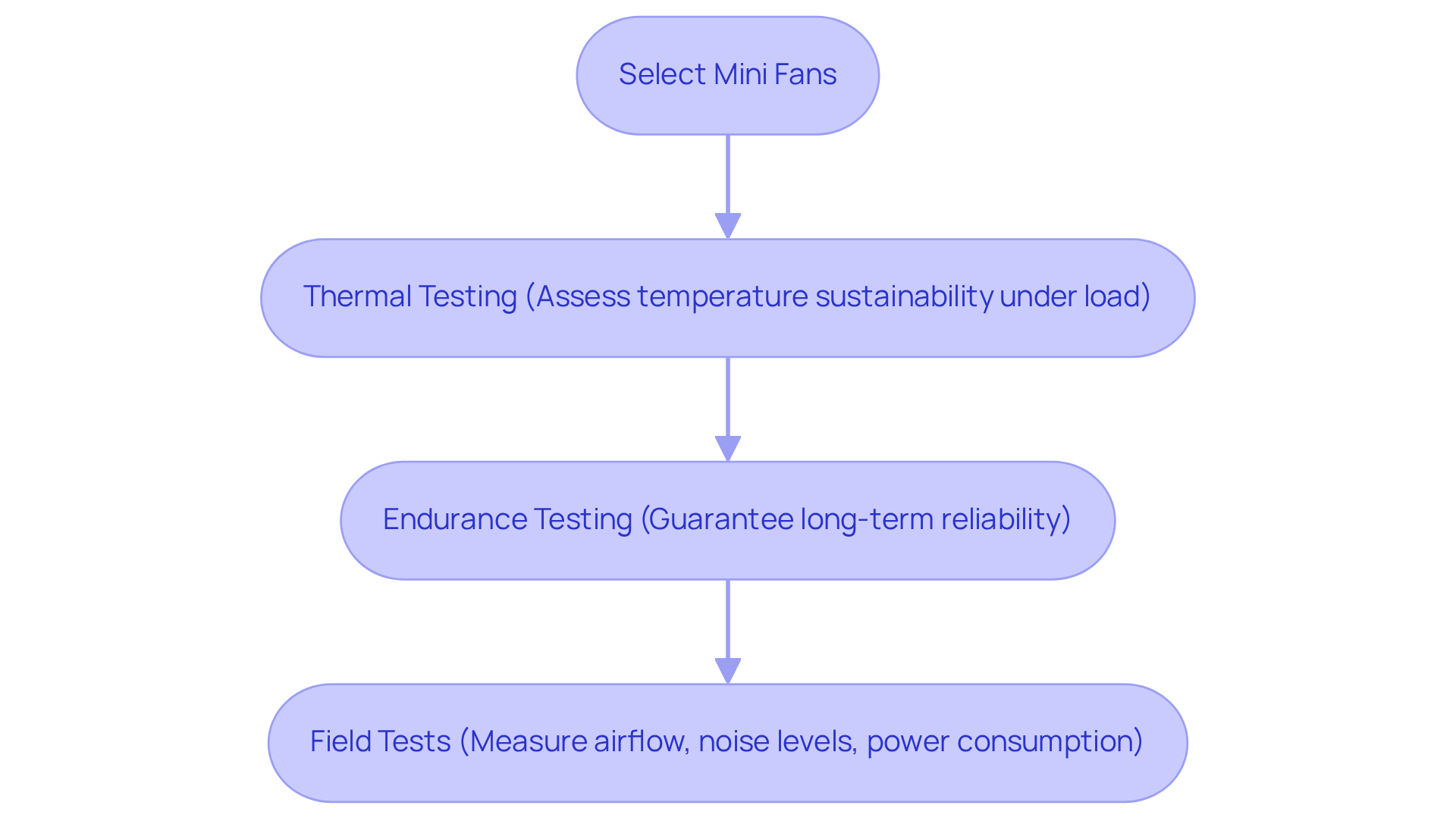
After selecting and integrating mini fans into a design, it is imperative to conduct thorough testing to validate their functionality. This process must encompass:
- Thermal testing to assess the fan’s capability to sustain optimal temperatures under load.
- Endurance testing to guarantee long-term reliability.
Research indicates that effective thermal testing significantly enhances the reliability of cooling solutions, with established protocols from organizations such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) providing a framework for safety and quality assurance.
Field tests in real-world conditions are equally vital, as they yield invaluable data on efficiency metrics including:
- Airflow
- Noise levels
- Power consumption
For example, engineers have noted that mini fans subjected to rigorous thermal testing frequently exhibit a substantial improvement in both efficiency and longevity. This empirical data not only supports prior to final production but also ensures adherence to regulatory standards, ultimately resulting in a product that meets or surpasses performance expectations.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate custom mini fan for a design project is a multifaceted process that hinges on a thorough understanding of various fan types, specifications, and their compatibility with specific applications. By recognizing the distinctions between axial, centrifugal, and mixed-flow fans, designers can make informed choices that best suit their thermal management needs. This comprehensive approach guarantees that the selected fans not only meet performance requirements but also align with the physical constraints of the design.
Throughout the article, key practices have been delineated, underscoring the importance of evaluating air movement, noise levels, and energy consumption, alongside the physical dimensions of the fans. The integration of custom mini fans into electronic systems necessitates careful consideration of airflow direction and environmental factors, while rigorous testing and validation processes are imperative to ensure reliability and performance. By adhering to these best practices, engineers can circumvent common pitfalls and enhance the effectiveness of their designs.
Ultimately, the significance of selecting custom mini fans transcends mere functionality; it plays a critical role in ensuring the longevity and efficiency of electronic systems. As design challenges continue to evolve, embracing these practices will not only optimize thermal management but also foster innovation in product development. Taking the time to meticulously select and test mini fans based on project-specific requirements is a vital step towards achieving superior performance and reliability in any design endeavor.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of custom mini fans are available?
Custom mini fans are available in three main types: axial, centrifugal, and mixed-flow models, each designed for different applications and characteristics.
What specifications should be considered when choosing a custom mini fan?
Important specifications to consider include air movement (measured in CFM), static pressure, noise levels (measured in dBA), and energy usage.
How do axial blowers differ from centrifugal blowers?
Axial blowers are generally more efficient for high airflow applications, while centrifugal blowers are better for situations requiring greater static pressure. Centrifugal blowers expel air at a 90-degree angle from the air intake, distinguishing them from axial models.
What are the size ranges for the mini fans offered by Gagner-Toomey Associates?
Gagner-Toomey Associates offers DC input tube axial units ranging from 15 to 280mm and centrifugal blowers from 15 to 225mm.
Why is it important to understand the physical dimensions and mounting options of a custom mini fan?
Understanding the physical dimensions and mounting options is crucial to ensure compatibility with the layout, as a compact design may require a specific fan size that could impact airflow and cooling efficiency.
In what applications are axial blowers commonly used?
Axial blowers are frequently used in applications such as cooling towers and server rooms, where large amounts of air need to be displaced with minimal resistance.
Where are centrifugal blowers typically utilized?
Centrifugal blowers are ideal for industrial environments where overcoming resistance in ducts or filters is necessary, such as in dust collection and fume extraction systems.
Can custom mini fans be tailored for specific applications?
Yes, IP protection is available in most models upon request, allowing for customization of features to suit specific application needs.
What is the significance of understanding fan varieties and specifications?
A comprehensive understanding of fan varieties and specifications is crucial for optimal integration and functionality in addressing the thermal management needs of electronic systems.