Overview
Blowers, commonly referred to as fans, are mechanical devices engineered to move air or gas by increasing its pressure and velocity. They play a vital role in electronics engineering, particularly in cooling and ventilation. This article underscores their significance in thermal management, as they facilitate the dissipation of heat from electronic components. By doing so, blowers ensure optimal performance and extend the longevity of devices across a multitude of applications.
Introduction
In the field of electronics engineering, blowers are not merely devices for air movement; they are essential for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency across a wide range of applications. These mechanical systems are meticulously engineered to produce airflow with elevated pressure, rendering them vital in cooling systems, ventilation, and various industrial processes. As technological advancements unfold, blower design continues to evolve, focusing on improving energy efficiency and minimizing noise levels.
From centrifugal to positive displacement blowers, each type fulfills a distinct role, safeguarding critical components and maintaining their operational integrity. This article investigates the fundamental principles of blowers, examines their diverse types and applications, and underscores the latest technological innovations that are shaping the future of air movement within the electronics sector.
Define Blower: Core Concept and Functionality
A fan, which is often referred to as a blower, is a mechanical device specifically engineered to move air or gas by increasing its pressure and velocity. It utilizes an impeller or rotor to generate airflow, directing it through a housing to achieve the desired output.
What distinguishes a blower from standard fans is that these devices are designed to generate higher pressure, enabling them to move air against resistance rather than just circulating it. This capability renders them essential in numerous electronics applications, including cooling systems, ventilation, and industrial processes.
Gagner-Toomey Associates, the globe’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offers an extensive product range of DC input tube axial fans and centrifugal fans, with dimensions varying from 15 to 280mm and 15 to 225mm respectively. These products are optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise, catering to diverse industrial applications. In HVAC systems, for example, fans play a crucial role in maintaining controlled airflow, ensuring efficient temperature regulation and air quality.
The advancement of fan technology, particularly with the introduction of variable-speed ECM (Electronically Commutated Motor) technology since the 2000s, has significantly improved their efficiency and adaptability across various environments. Furthermore, upkeep services and tailored solutions for electronics production are essential for guaranteeing the optimal functioning of fans in diverse applications. Overall, fans are integral to the functionality of electronic systems, providing reliable air movement that is essential for optimal performance.
Explore Types of Blowers: Variations and Applications
Blowers stand as essential components in electronics engineering, categorized into several types based on their design and operational principles:
- Centrifugal Fans: By employing a rotating impeller, these devices significantly enhance air velocity and pressure, making them suitable for applications that necessitate high air movement rates, such as cooling electronic components. The centrifugal fan market is projected to expand considerably, particularly in the Asia Pacific region, with an anticipated CAGR of 2% from 2023 to 2033.
- What is a blower? Positive displacement blowers are devices that work by capturing a fixed volume of air and expelling it, which ensures a steady movement of air despite variations in pressure. They are commonly employed in pneumatic conveying systems, where reliability is paramount.
- Regenerative Fans: Known for their efficiency, regenerative fans generate a continuous stream of air through a rotating impeller. This design renders them suitable for applications such as vacuum generation and aeration, where sustaining a consistent air current is critical.
- Axial Fans: These devices move air parallel to the axis of the fan, delivering high flow rates at low pressure. They are frequently utilized in ventilation systems, where space and air management are essential.
Each type of fan, including what is a blower, offers unique benefits that are tailored to specific operational needs such as airflow rate, pressure, and energy efficiency. However, the fan market faces challenges, such as managing unnecessary capacity expansions and mitigating equipment downtime due to leaks and inadequate practices. Understanding these variations and the broader market dynamics is crucial for engineers seeking optimal solutions in their projects.
As Mr. Ali Zali, Commercial Director, remarked, “We have purchased recently a report from SkyQuest Technology, and we are happy to inform you that this report was so useful and practical for our team. Skyquest Team was very active and our queries were followed up completely. It was amazing.” This highlights the importance of market research in navigating the complexities of ventilation applications.
Understand Importance: Role of Blowers in Electronics Engineering
In electronics engineering, an important aspect is understanding what is a blower, as it plays a pivotal role in effective thermal management and ventilation control. Excessive heat in electronic devices can lead to performance decline and potential failure, making the role of fans indispensable. By directing air movement over components, fans facilitate heat dissipation and maintain optimal operating temperatures. For instance, in high-performance computing systems, fans are critical for cooling processors and preventing overheating, which significantly impacts system reliability and efficiency. Moreover, fans fulfill multiple functions, including dust removal, essential for preserving the integrity of sensitive electronic components. Their ability to provide directed airflow makes them vital in various electronic applications, ranging from consumer devices to industrial equipment.
Current trends indicate a growing preference for air movers with reduced noise levels, as businesses aim to minimize costs associated with noise pollution. This shift reflects a broader commitment to enhancing user experience while upholding performance standards.
The global market for electronics thermal management solutions is projected to reach approximately $11.65 billion by 2031, highlighting the increasing significance of effective cooling solutions in the industry. Notably, Inovair’s recent product launch of the IM30/IM-40 and IM-40/IM-50 fan models exemplifies advancements in fan technology, with horsepower ratings ranging from 40 to 600, designed to improve cooling efficiency in high-speed applications.
Additionally, the integration of magnetic bearings in fan designs provides excellent cooling with minimal energy consumption, further underscoring the technological advancements that enhance thermal management. Consequently, fans not only prevent overheating but also improve the overall efficiency and longevity of electronic devices, reinforcing their status as a cornerstone in electronics engineering.
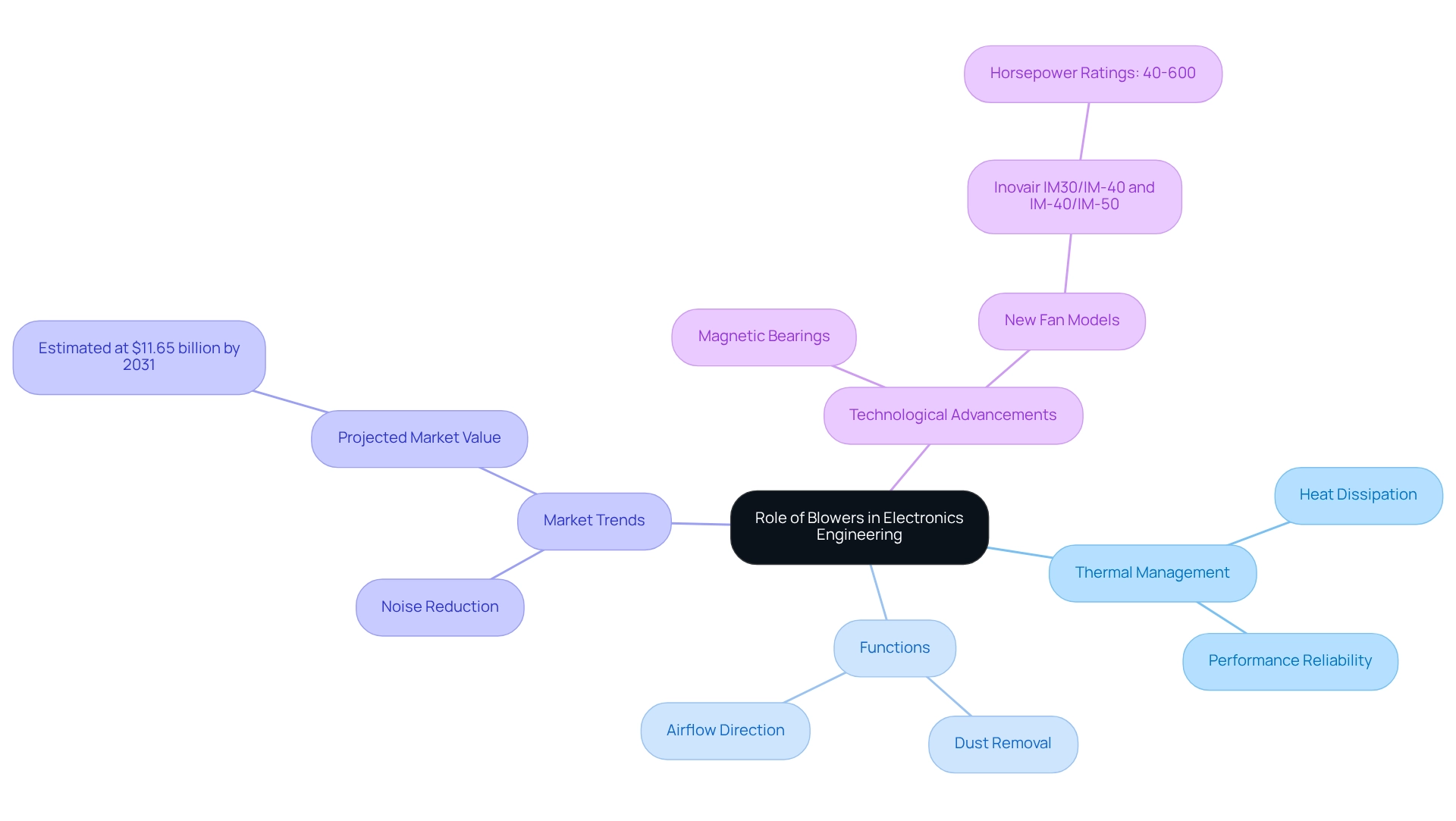
Examine Innovations: Advancements in Blower Technology
Recent advancements in air movement technology have prioritized energy efficiency, noise reduction, and enhanced performance. Gagner-Toomey Associates, the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, plays a pivotal role in this evolution by offering a broad product line of DC input tube axial fans ranging from 15 to 280mm and centrifugal fans from 15 to 225mm, optimized for various applications, including electronics and automotive.
The integration of variable frequency drives (VFDs) allows for precise control of fan speed, optimizing airflow according to real-time system demands. This innovation is crucial, as it not only improves performance but also significantly reduces energy consumption. According to AMCA 214-21, fan laws can be utilized to calculate fan shaft power at non-tested speeds, enhancing the technical understanding of fan performance and energy efficiency.
Furthermore, the introduction of high-efficiency motors and advanced aerodynamic impeller designs has led to remarkable improvements in performance. These advancements are complemented by intelligent fan technologies that incorporate IoT capabilities, enabling remote monitoring and control, which further enhances operational efficiency. The Department of Energy (DOE) has suggested that fan models fitting the criteria of both axial panel fans and air circulating fans undergo testing following particular procedures, emphasizing the regulatory framework influencing fan technology.
Together, these innovations enhance the sustainability of electronic systems by reducing energy consumption and operational expenses, rendering them crucial for contemporary electronics applications. Industry leaders emphasize the importance of differentiating between air circulating fans based on remarkable air velocity and wire-to-air efficiency, which enhances the credibility of the discussion on fan performance metrics. The market for fan technology continues to expand, propelled by these advancements, transforming the landscape of energy-efficient solutions in the electronics sector. Additionally, the case study on Manufacturer Selection Programs for Fan Certification illustrates the practical applications of these advancements, emphasizing the importance of compliance and efficiency in manufacturing. The ongoing developments in technology, particularly in what is a blower, are expected to significantly impact market size and growth rates across different regions, further underscoring their relevance in the electronics sector. Notably, most models also offer IP protection upon request, ensuring durability and reliability in various environments.
Conclusion
The exploration of blowers within electronics engineering underscores their critical role in enhancing performance and ensuring efficiency across diverse applications. Understanding the core functionality of blowers—ranging from centrifugal to positive displacement types—reveals that each variation is meticulously tailored to meet specific operational needs, particularly in thermal management and airflow control. The capacity of blowers to manage heat and maintain optimal temperatures is essential in preventing device failures, thereby safeguarding the integrity of electronic systems.
Moreover, advancements in blower technology highlight a commitment to improving energy efficiency and minimizing noise levels. Innovations such as variable frequency drives, high-efficiency motors, and smart technologies have transformed blowers into sophisticated systems capable of adapting to real-time demands. These enhancements not only contribute to the sustainability of electronic systems but also emphasize the importance of ongoing research and development within the industry.
As the market for blower technology continues to expand, the focus on energy-efficient solutions remains paramount. The integration of advanced designs and regulatory compliance will shape the future landscape of blowers in electronics, ensuring they remain indispensable for effective air movement and thermal management. Ultimately, the evolution of blower technology is poised to significantly influence operational efficiencies and performance standards in the electronics sector, reinforcing their vital role in modern engineering applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a fan and how does it work?
A fan, often referred to as a blower, is a mechanical device designed to move air or gas by increasing its pressure and velocity. It uses an impeller or rotor to generate airflow, directing it through a housing to achieve the desired output.
What distinguishes a blower from a standard fan?
A blower is designed to generate higher pressure, allowing it to move air against resistance, rather than just circulating it like standard fans. This capability makes blowers essential in various applications, including cooling systems and industrial processes.
What types of fans does Gagner-Toomey Associates produce?
Gagner-Toomey Associates produces a wide range of DC input tube axial fans and centrifugal fans, with dimensions varying from 15 to 280mm and 15 to 225mm, respectively. These products are optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise.
How do fans contribute to HVAC systems?
In HVAC systems, fans play a crucial role in maintaining controlled airflow, which ensures efficient temperature regulation and air quality.
What technological advancements have improved fan efficiency?
The introduction of variable-speed ECM (Electronically Commutated Motor) technology since the 2000s has significantly improved the efficiency and adaptability of fans across various environments.
Why are upkeep services important for fans?
Upkeep services and tailored solutions are essential for ensuring the optimal functioning of fans in diverse applications, particularly in electronics production.