Introduction
Selecting the right industrial mini fans for electronic applications is not merely a matter of preference; it’s a pivotal decision that can profoundly influence performance and reliability. As electronic devices grow increasingly complex, grasping essential specifications – such as airflow, static pressure, and noise levels – becomes crucial for engineers aiming to optimize cooling efficiency. But how can one ensure that these fans not only meet technical requirements but also integrate seamlessly into existing systems? This article explores best practices for utilizing industrial mini fans in electronics, providing insights designed to help you avoid common pitfalls and enhance overall functionality.
Understand Technical Specifications of Industrial Mini Fans
Selecting industrial mini fans for electronic applications necessitates a comprehensive understanding of several key technical specifications:
-
Airflow (CFM): Airflow, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), indicates the volume of air a fan can move. Aligning ventilation with the cooling needs of electronic components is crucial. For instance, mid-tower enclosures typically require fans with a CFM range of 50 to 100, while larger configurations may demand 500 to 2,000 CFM for adequate ventilation.
-
Static Pressure: This specification evaluates the resistance to air movement within the system. Higher static pressure ratings are essential in scenarios where airflow is obstructed, such as in densely packed enclosures. Engineers must recognize that static pressure affects airflow resistance, and blowers should be assessed under identical conditions to ensure optimal performance.
-
Noise Level (dBA): In environments where silent operation is critical, understanding the noise levels produced by fans is vital. Choosing fans that adhere to noise regulations can significantly enhance user experience, particularly in sensitive applications.
-
Voltage and Power Requirements: It is essential to ensure that the fan’s voltage aligns with the power source to avoid compatibility issues. Engineers should prioritize this aspect to maintain the reliability of the setup.
-
Size and Form Factor: The physical dimensions of the fan must conform to the design constraints of the electronic device. Compact blowers are particularly effective in tight spaces, ensuring efficient cooling without compromising capability.
By thoroughly evaluating these specifications, engineers can select an industrial mini fan that not only maximizes cooling efficiency but also enhances overall performance. Understanding airflow dynamics and static pressure is especially significant; as one engineer noted, ‘Choosing the appropriate fan according to CFM ratings is vital for efficient cooling.’ Real-world examples demonstrate that inadequate ventilation can lead to overheating, underscoring the importance of precise fan selection in electronic devices.
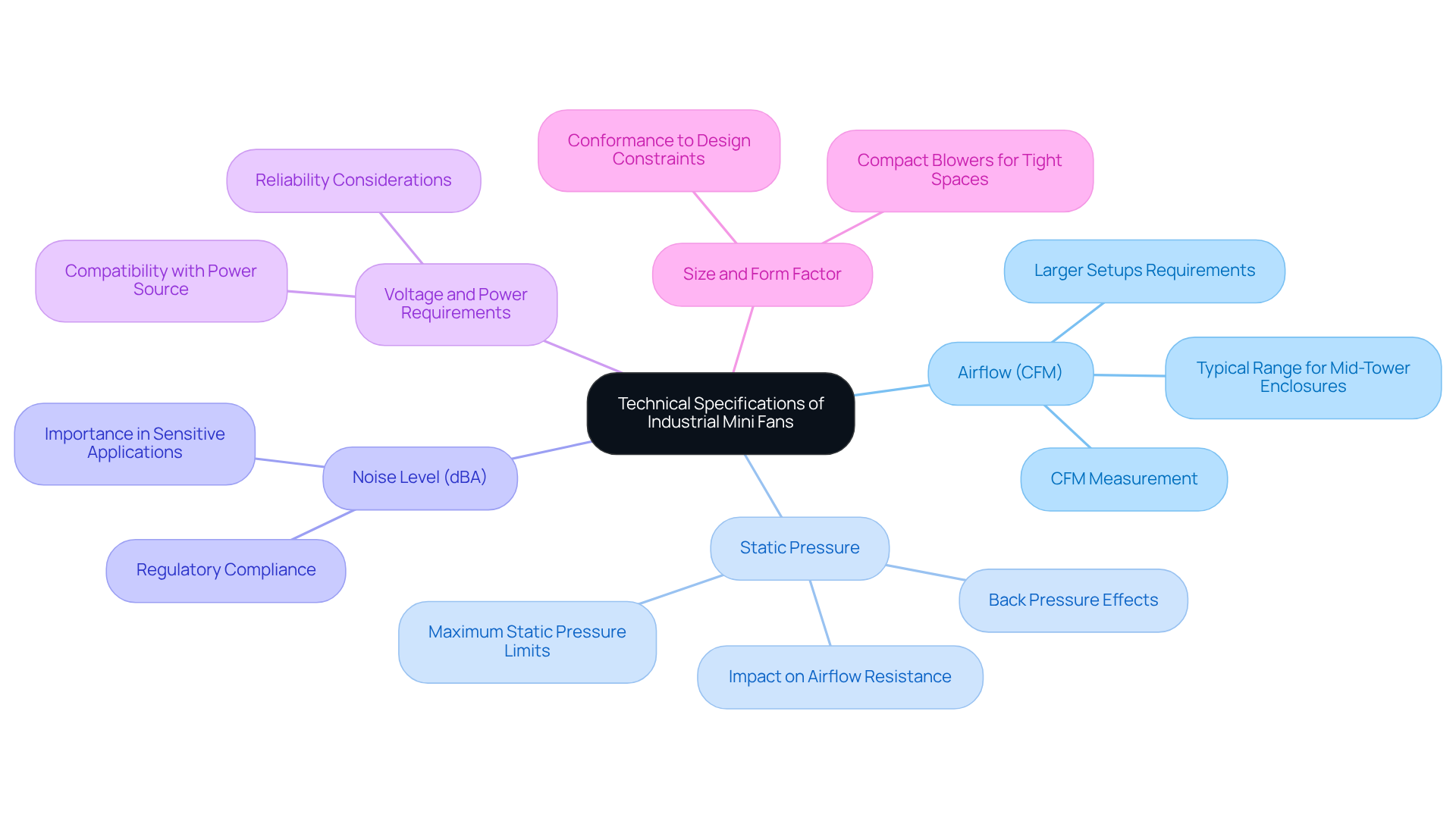
Evaluate Compatibility with Electronic Systems
To ensure optimal performance of the industrial mini fan within electronic setups, a comprehensive compatibility assessment is essential. This evaluation not only addresses potential issues but also enhances the overall functionality of mini devices in electronic applications.
-
Integration with Existing Components: It’s crucial to evaluate how the fan will interface with other components, such as circuit boards and heat sinks. Ensuring that the fan’s airflow direction aligns with the cooling needs of the setup is vital; incorrect airflow can lead to overheating and diminished efficiency.
-
Electrical Compatibility: Confirming that the fan’s voltage and current ratings match the specifications of the setup is imperative. Mismatched electrical parameters can result in fan failure or suboptimal performance, jeopardizing the reliability of the entire system.
-
Physical Space Constraints: Measuring the available space within the enclosure is necessary to guarantee that the fan can be installed without obstruction. Consideration of the fan’s mounting options and orientation is essential, as these factors significantly impact airflow and cooling efficiency.
-
Environmental Conditions: Assessing the operating environment-including temperature, humidity, and exposure to dust or contaminants-is critical. Selecting devices rated for specific conditions ensures longevity and reliability, particularly in harsh environments.
By performing a detailed compatibility evaluation, engineers can alleviate typical issues and significantly improve the functionality of devices, including industrial mini fans, in electronic applications.
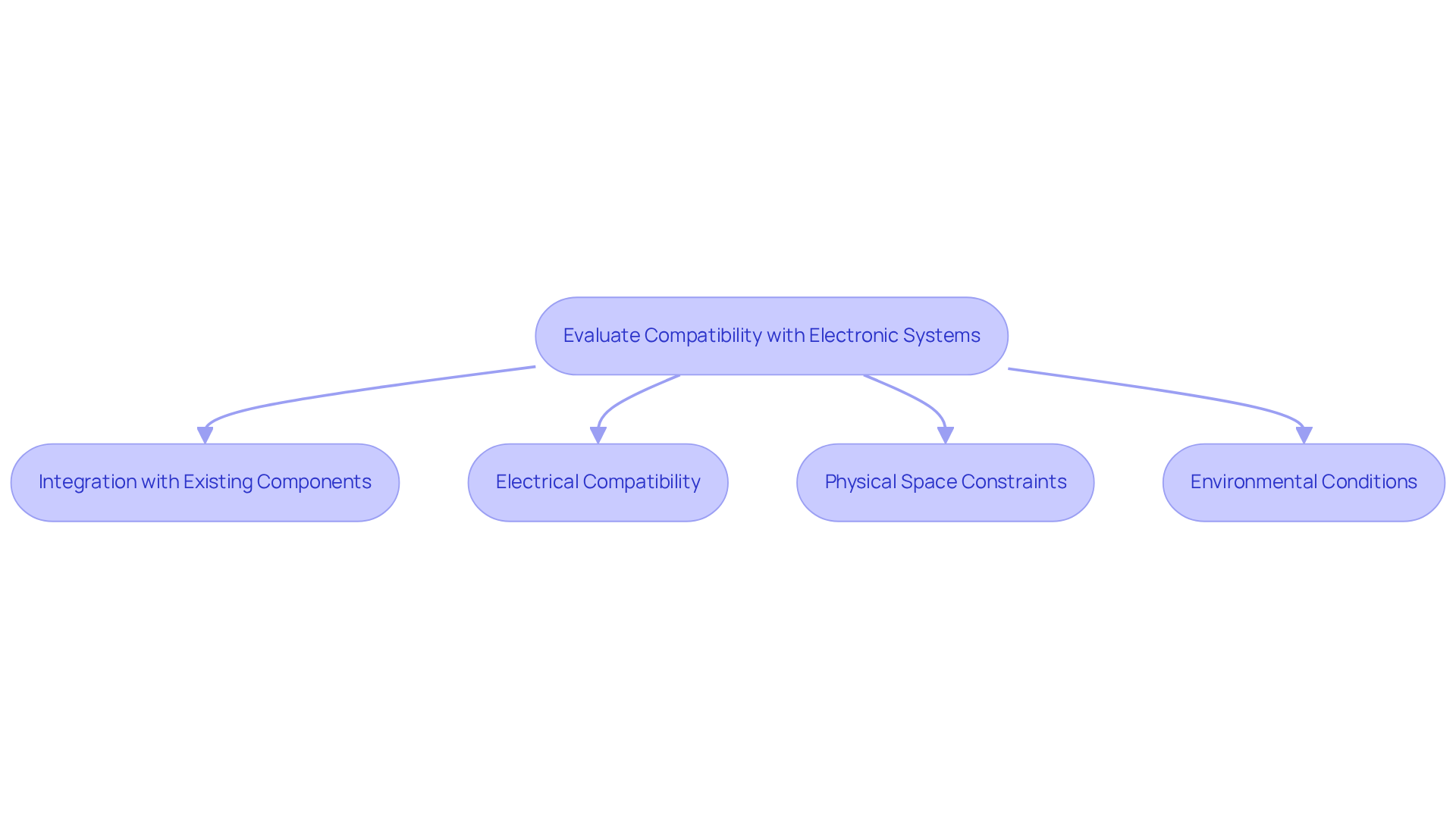
Implement Effective Installation and Configuration Strategies
Achieving optimal cooling efficiency relies on the proper installation and configuration of industrial mini fans. To ensure success, follow these best practices:
- Mounting: Securely mount the fan using appropriate hardware to minimize vibration and noise. Position the fan to allow clear air movement. Utilizing rubber isolators can effectively reduce vibrations that may compromise performance.
- Orientation: Install the fan in the correct orientation to facilitate effective airflow. For exhaust fans, ensure they are positioned to expel hot air from the enclosure. Research shows that optimal fan orientation can enhance cooling performance by up to 30%, directly impacting the thermal management of electronic devices. As emphasized by SkyBlade Fan Company, ‘Placement should be centered in open spaces to maximize circulation.’
- Wiring and Connections: Employ high-quality connectors and ensure that all electrical connections are secure. Avoid loose wires that can lead to intermittent operation. Professional installation is essential for safety compliance with electrical and mechanical standards, which is vital for optimal fan operation.
- Testing: After installation, conduct a thorough test to verify that the fan operates correctly. Check for adequate ventilation and listen for unusual sounds that may indicate installation issues. Regular testing can help identify potential problems early, ensuring ongoing effectiveness.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of the installation process, including fan specifications and configuration settings, to assist with future maintenance and troubleshooting. This documentation is invaluable for efficient problem resolution.
Additionally, a comprehensive site analysis is recommended for optimal fan placement, considering facility layout, obstructions, and airflow patterns. By applying these strategies, engineers can ensure that mini blowers are installed accurately and set up for optimal functionality. This not only improves the cooling efficiency of electronic systems but also achieves potential cost reductions linked to proper installation.
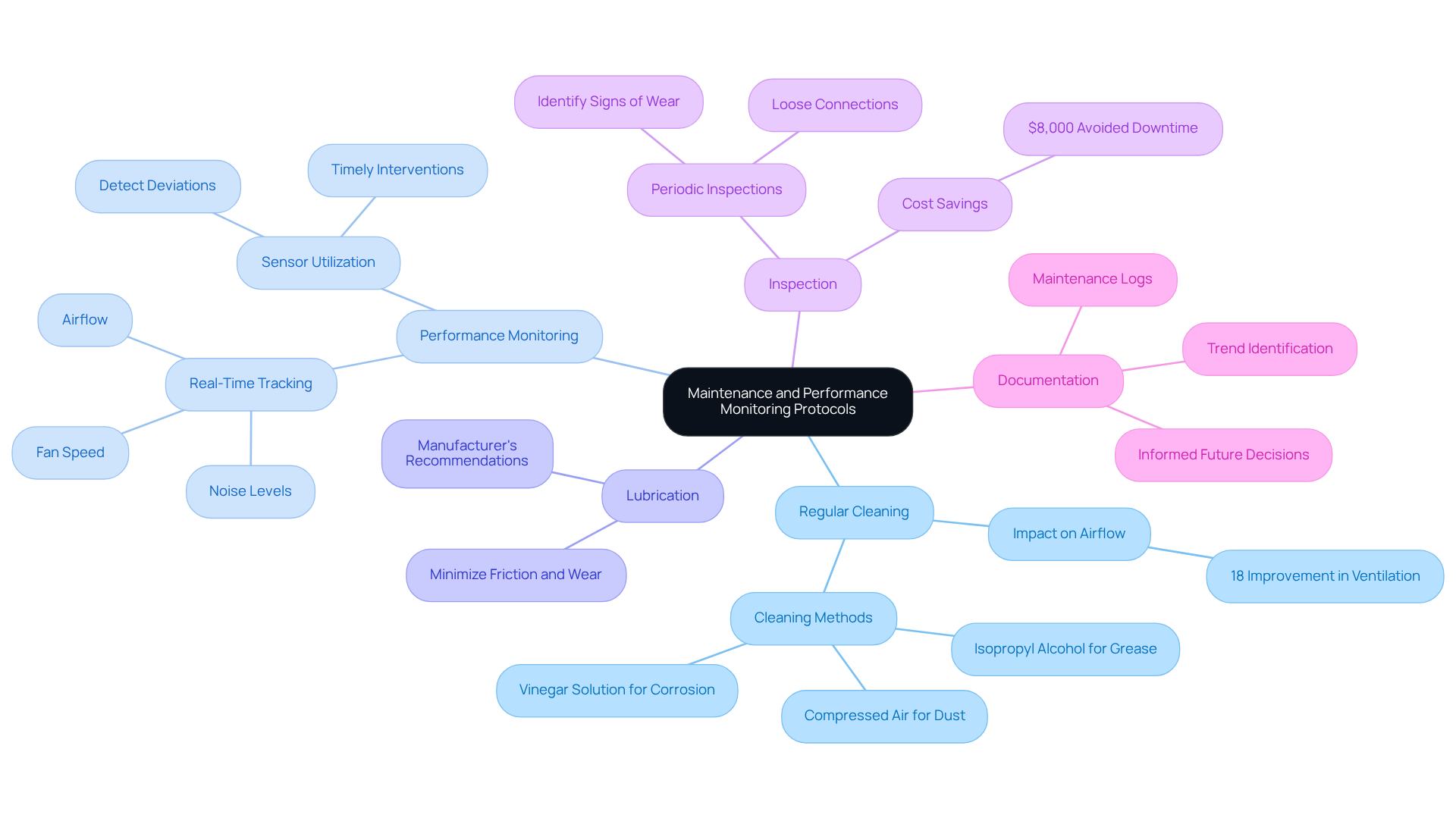
Establish Maintenance and Performance Monitoring Protocols
Establishing a comprehensive maintenance and performance monitoring protocol is crucial to ensure the efficiency and reliability of industrial mini fans. Key practices include:
- Regular Cleaning: Accumulated dust and debris on fan blades and housing can significantly reduce airflow. For instance, a Vietnamese factory enhanced ventilation by 18% after thoroughly cleaning fan blades that had 5mm of caked-on dust. Scheduling routine cleaning is essential to maintain optimal performance and prevent operational inefficiencies.
- Performance Monitoring: Implementing advanced monitoring systems allows for real-time tracking of fan speed, airflow, and noise levels. Utilizing sensors can help detect deviations from normal operating conditions, enabling timely interventions.
- Lubrication: Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubricating fan bearings is vital to minimize friction and wear, thereby extending the lifespan of the fans.
- Inspection: Conducting periodic inspections is necessary to identify signs of wear, loose connections, or other issues that could compromise functionality. A Philippine food plant avoided $8,000 in downtime when their annual service caught failing bearings before they seized. Promptly addressing these problems can prevent further damage and costly downtime.
- Documentation: Maintaining detailed logs of maintenance activities, including cleaning schedules, inspections, and repairs, is essential. This documentation aids in identifying trends and informs future maintenance decisions, ensuring a proactive approach to fan management.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider the implications of the CEC Title 20 regulation, which underscores the necessity for compliance in fan upkeep and monitoring. By implementing these protocols, engineers can enhance the operational efficiency and reliability of the industrial mini fan, ultimately contributing to improved system performance and longevity.
Conclusion
Selecting and utilizing industrial mini fans in electronic applications is not just a task; it’s a critical process that requires meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of various technical specifications. Engineers must focus on key factors such as:
- Airflow
- Static pressure
- Noise levels
- Compatibility with electronic systems
This focus ensures optimal performance and helps prevent issues that could compromise device efficiency.
Evaluating technical specifications is paramount when selecting the right fan. Compatibility with existing components, effective installation strategies, and robust maintenance protocols are essential steps in this process. Each of these elements plays a vital role in maximizing cooling efficiency and enhancing the reliability of electronic devices. The outcome? Improved performance and longevity of the systems we rely on.
In light of these best practices, it becomes clear that a proactive approach to selecting, installing, and maintaining industrial mini fans is essential for achieving desired operational outcomes. By prioritizing thorough assessments and adhering to established guidelines, engineers can significantly enhance the functionality of electronic systems. This commitment paves the way for innovation and efficiency across various applications. Embracing these strategies not only optimizes performance but also fosters a culture of excellence in the design and management of electronic devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is airflow (CFM) in relation to industrial mini fans?
Airflow, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), indicates the volume of air a fan can move. It is crucial to align the airflow with the cooling needs of electronic components, with mid-tower enclosures typically requiring fans with a CFM range of 50 to 100 and larger configurations needing 500 to 2,000 CFM.
Why is static pressure important in fan selection?
Static pressure evaluates the resistance to air movement within a system. Higher static pressure ratings are essential when airflow is obstructed, such as in densely packed enclosures. It affects airflow resistance, making it necessary to assess blowers under identical conditions for optimal performance.
How does noise level (dBA) impact the choice of industrial mini fans?
Understanding the noise levels produced by fans is vital in environments where silent operation is critical. Choosing fans that adhere to noise regulations can significantly enhance user experience, especially in sensitive applications.
What should be considered regarding voltage and power requirements for fans?
It is essential to ensure that the fan’s voltage aligns with the power source to avoid compatibility issues. This aspect is crucial for maintaining the reliability of the setup.
How do size and form factor influence fan selection?
The physical dimensions of the fan must conform to the design constraints of the electronic device. Compact blowers are particularly effective in tight spaces, ensuring efficient cooling without compromising capability.
Why is it important to evaluate these technical specifications when selecting industrial mini fans?
Thoroughly evaluating specifications like airflow, static pressure, noise level, voltage, and size ensures that engineers select an industrial mini fan that maximizes cooling efficiency and enhances overall performance, preventing issues such as overheating in electronic devices.