Introduction
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) has transformed the landscape of fan speed control for engineers, presenting a sophisticated approach that significantly boosts efficiency and performance in electronic systems. By fine-tuning electrical pulse widths, PWM allows for precise regulation of fan operation, optimizing cooling while dramatically lowering energy consumption. Yet, as this technology advances, engineers encounter the challenge of mastering the intricacies of PWM fan control.
How can they guarantee their systems function at peak efficiency while addressing common issues? This guide explores the essential steps and tools necessary for effectively managing PWM fans, equipping engineers to leverage this technology for superior thermal management.
Understand PWM Basics for Fan Control
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) stands as a cutting-edge technique for regulating fan speeds by adjusting the width of electrical pulses in a transmission. Utilizing a 4-pin connector, standard PWM fan regulation employs the fourth pin to carry a PWM pulse that dictates the fan’s rotational speed by modifying the duty cycle of these pulses. A higher duty cycle results in increased power delivery, leading to faster fan speeds, while a lower duty cycle corresponds to reduced speeds.
To effectively harness PWM for fan control, engineers must understand several essential concepts:
- Duty Cycle: This indicates the ratio of time the signal is ‘on’ versus ‘off’ within a given timeframe. For example, a 50% duty cycle means the fan operates for half the time.
- Frequency: PWM signals are typically transmitted at frequencies around 25 kHz, optimizing performance while minimizing audible noise – an important factor in noise-sensitive environments. PWM devices can achieve noise levels as low as 20 dBA, significantly quieter than traditional units that may exceed 30 dBA.
- Audience Reaction: PWM cooling devices offer smoother speed transitions compared to conventional DC units, enhancing thermal regulation and energy efficiency. Research shows that PWM units can cut energy consumption by up to 30% compared to direct current devices, all while effectively managing temperature. This makes them a preferred choice in modern electronics. Furthermore, the Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) in systems using PWM devices has been shown to decrease from 1.55 to 1.42 during control periods in data centers.
By mastering these fundamentals, engineers can understand how to control PWM fans in their cooling solutions, ensuring optimal performance and reliability across various applications. Notably, over 70% of electronics engineers are now integrating PWM cooling devices into their designs, reflecting a growing trend toward more efficient temperature regulation.
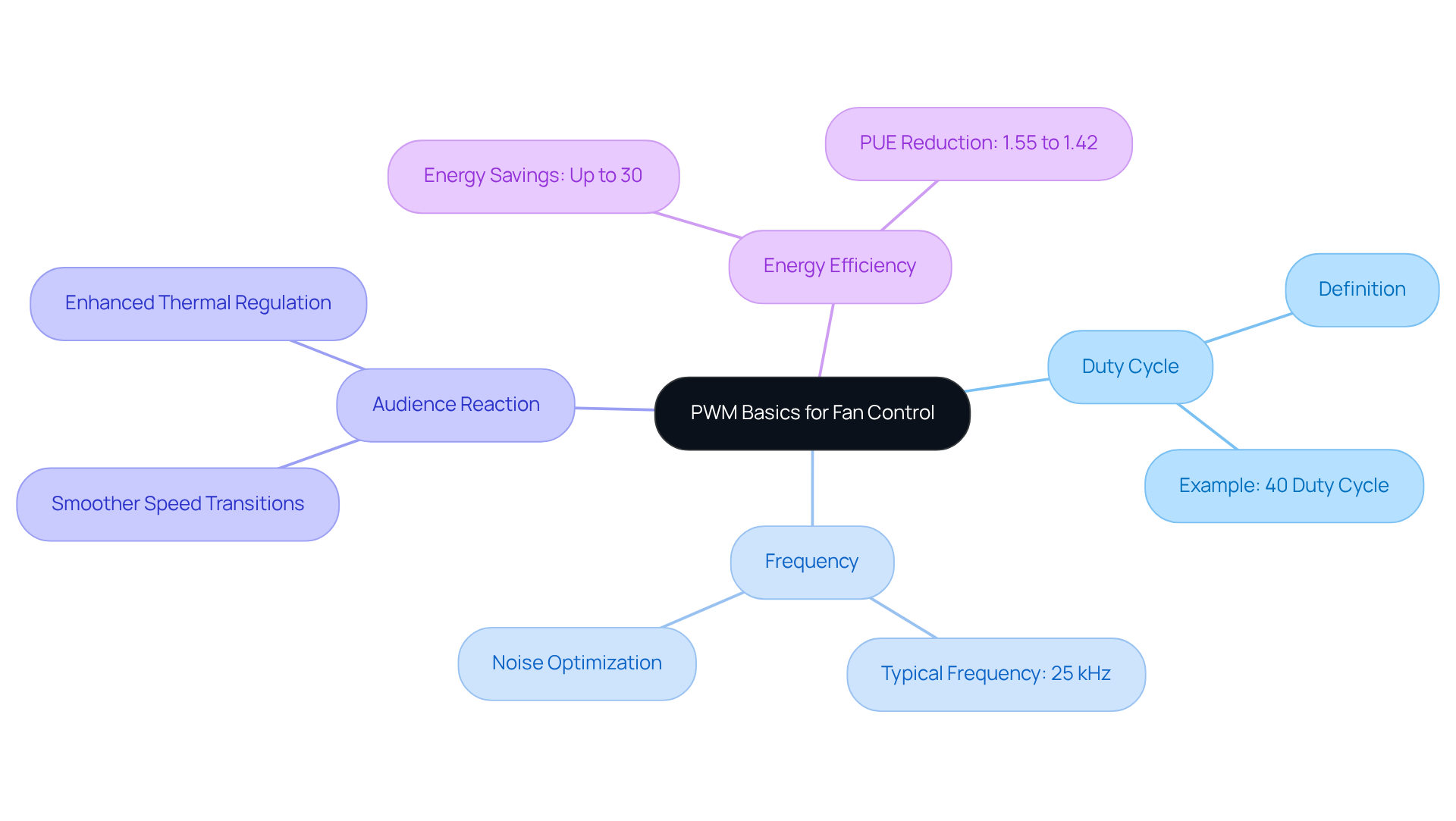
Gather Necessary Tools and Components
To effectively control PWM fans, it’s essential to have the right tools and components at your disposal:
- PWM Devices: Utilize 4-pin PWM devices specifically designed to accept PWM inputs. This ensures accurate speed regulation, which is crucial for optimal performance across various applications.
- A microcontroller or PWM controller, like an Arduino, is crucial for generating the PWM signal, which is important for learning how to control PWM fans.
- Power Supply: A stable power source that meets the voltage requirements of your devices-typically 12V-is critical for reliable operation.
- Wiring and Connectors: Employ appropriate gauge wires and connectors to guarantee safe and dependable connections between the devices and the controller.
- Soldering Kit: For custom connections, a soldering kit is indispensable, allowing for tailored setups as needed.
- Multimeter: This tool is essential for testing connections and verifying that voltage levels are accurate, ensuring the system functions correctly.
- Software: If using a microcontroller, programming software is necessary to upload the PWM control code, enabling effective fan management.
Equipping yourself with these tools and components simplifies the setup process, allowing you to focus on how to control PWM fans for optimal performance. As the market for PWM controllers is projected to grow significantly, with a CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2033, understanding these components is crucial for engineers aiming to implement efficient thermal management solutions.
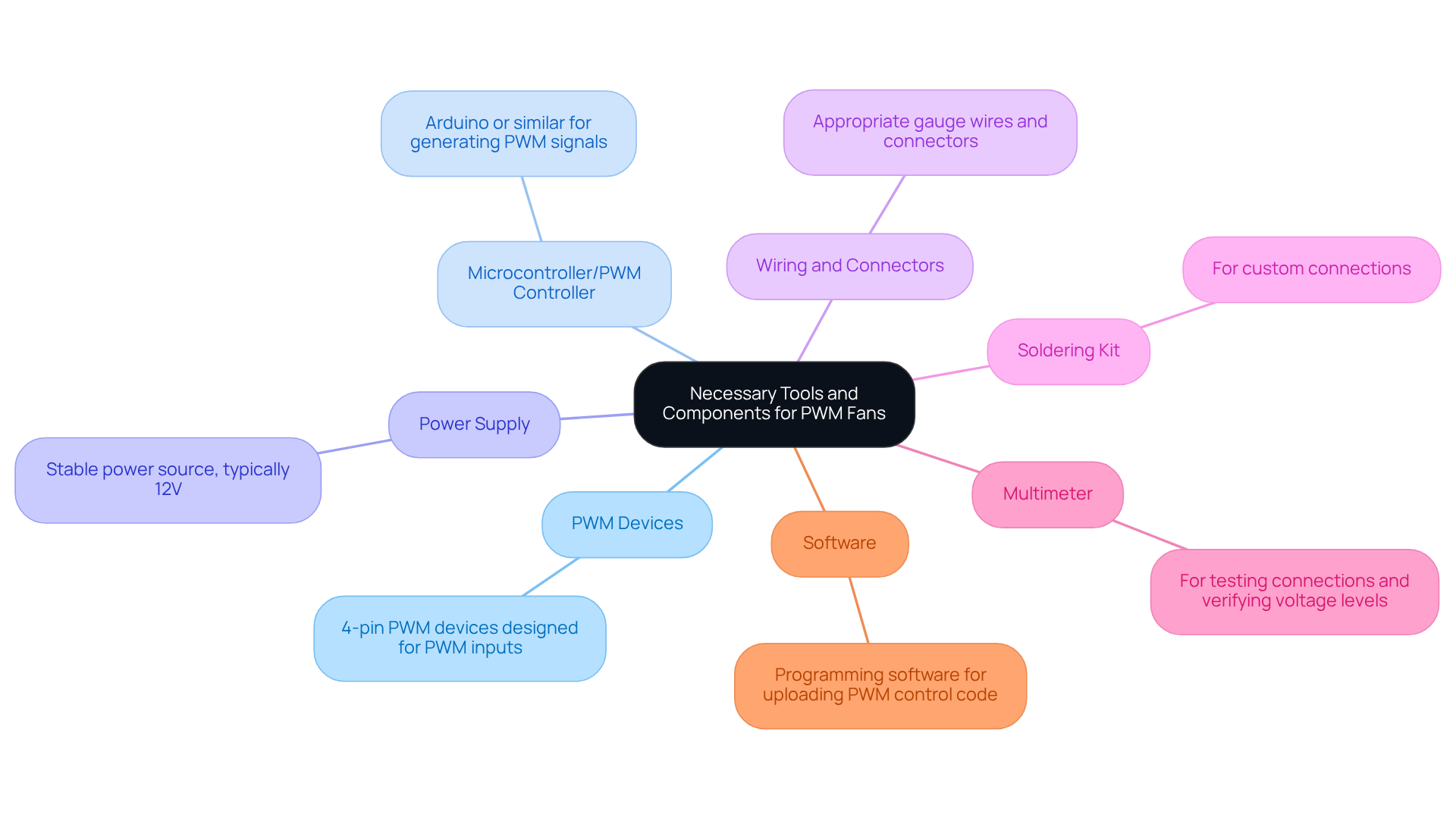
Configure PWM Fans for Optimal Performance
To configure your PWM fans for optimal performance, follow these essential steps:
-
Connect the Blowers: Start by attaching the PWM blowers to the appropriate headers on your microcontroller or PWM controller. Ensure that the PWM pin is connected correctly to understand how to control pwm fans for precise speed control.
-
Set Up the Power Supply: Next, connect the power supply to the fans, making sure that the voltage aligns with the fan specifications, which is typically 12V.
This is a guide on how to control pwm fans. If you’re using a microcontroller, write a program to generate the PWM signal, which is essential for understanding how to control pwm fans. Set the frequency to approximately 25 kHz and adjust the duty cycle according to the desired fan rate. For instance, a duty cycle of 50% will operate the fan at half its maximum speed, while a 25% duty cycle will lower the rate to around 500 RPM for quieter operation. PWM units can function at rates as low as 10% of their maximum capacity, providing versatility for various applications.
-
Test the Configuration: Power on the system and observe the fan rates. Utilize a multimeter to check the voltage levels at the fan connectors, ensuring they align with your settings. This verification step is crucial for confirming that the fans respond appropriately to the PWM commands.
-
Adjust Fan Curves: Depending on your specific application, implement fan curves that modify the rate based on temperature readings. Integrate temperature sensors into your setup and adjust the PWM signal accordingly. For example, configure the fan to operate at 100% speed at 70°C and reduce to 0% at lower temperatures, enhancing both cooling efficiency and noise reduction.
By following these steps, you will understand how to control pwm fans to ensure that your PWM devices operate efficiently and effectively within your electronic systems. Proper configuration not only improves cooling performance but can also extend the lifespan of critical components by up to 50%, significantly reducing the risk of thermal-related failures. Additionally, PWM technology can lead to a reduction in power consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional direct current devices.
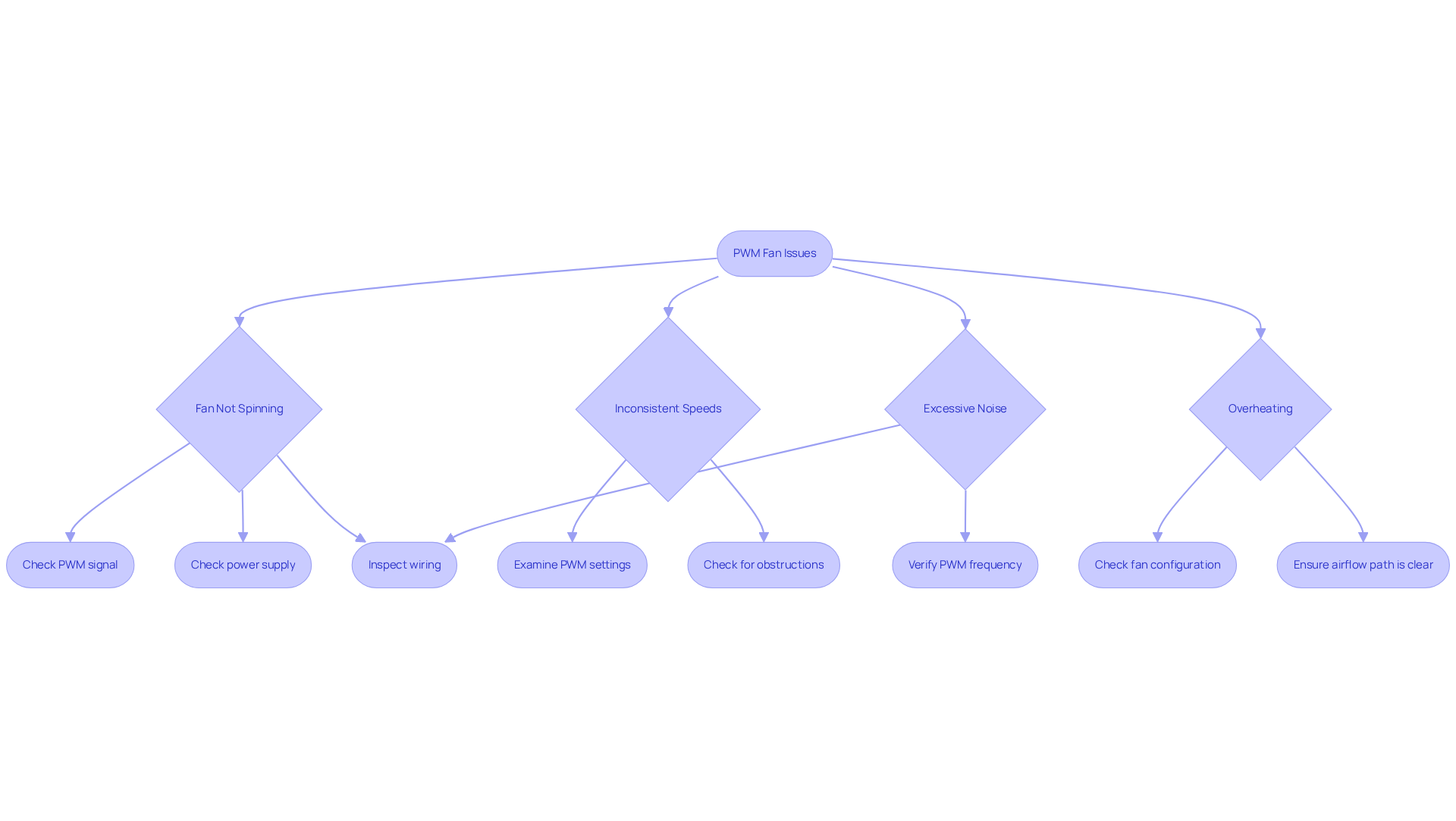
Troubleshoot Common PWM Fan Issues
When considering how to control pwm fans, several common issues may arise that can hinder performance. Here’s how to troubleshoot them effectively:
-
Fan Not Spinning: If the fan fails to spin, consider these steps:
- Confirm that the PWM signal is being transmitted correctly from the controller.
- Ensure the power supply is connected and delivering the appropriate voltage.
- Inspect the wiring for any loose connections or damage that could disrupt functionality.
-
Inconsistent Speeds: Should the fan speed fluctuate unexpectedly, take the following actions:
- Examine the PWM signal frequency and duty cycle settings, ensuring they remain stable and within recommended ranges.
- Check the fan for any mechanical obstructions that might impede its operation.
-
Excessive Noise: If the fan produces more noise than anticipated, follow these guidelines:
- Verify that the PWM frequency is set high enough (around 25 kHz) to minimize audible noise.
- Look for vibrations or loose mounting that could amplify noise levels.
-
Overheating: If the fan fails to provide adequate cooling, ensure:
- The fan is configured correctly and responsive to temperature changes.
- The airflow path is unobstructed and that the fan is suitable for the intended application.
By systematically addressing these issues, you can ensure optimal performance and reliability in your systems, which is essential when learning how to control pwm fans.
Conclusion
Mastering the control of PWM fans is crucial for engineers aiming to optimize cooling solutions in modern electronic systems. By leveraging Pulse Width Modulation, professionals can achieve precise fan speed regulation, enhance energy efficiency, and minimize noise levels. This leads to improved thermal management, a necessity in today’s technology-driven landscape. Understanding the intricacies of PWM technology not only facilitates better performance but also aligns with the growing trend of integrating these advanced cooling devices into electronic designs.
Key components such as duty cycle, frequency, and the necessary tools for setup have been highlighted throughout this guide. The process of configuring PWM fans involves:
- Connecting devices
- Setting up power supplies
- Adjusting fan curves based on temperature readings
Moreover, troubleshooting common issues like inconsistent speeds or excessive noise ensures that engineers can maintain optimal performance and reliability.
Incorporating PWM technology into engineering practices is not merely a trend; it represents a significant step toward more sustainable and efficient thermal management. By embracing these methods, engineers can contribute to the advancement of electronic systems, ensuring they operate effectively while minimizing energy consumption and prolonging component lifespan. The future of cooling solutions lies in the hands of those who understand and implement PWM fan control effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) in fan control?
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used to regulate fan speeds by adjusting the width of electrical pulses in a transmission, allowing for precise control of the fan’s rotational speed.
How does a PWM fan connector work?
A standard PWM fan utilizes a 4-pin connector, where the fourth pin carries a PWM pulse that dictates the fan’s speed by modifying the duty cycle of these pulses.
What is duty cycle in PWM?
Duty cycle refers to the ratio of time the PWM signal is ‘on’ versus ‘off’ within a specific timeframe. For instance, a 50% duty cycle means the fan operates for half the time.
What frequency do PWM signals typically operate at?
PWM signals are usually transmitted at frequencies around 25 kHz, which optimizes performance while minimizing audible noise.
How does PWM affect noise levels in fans?
PWM devices can achieve noise levels as low as 20 dBA, making them significantly quieter than traditional units, which may exceed 30 dBA.
What advantages do PWM cooling devices have over conventional DC units?
PWM cooling devices offer smoother speed transitions, enhance thermal regulation, and can reduce energy consumption by up to 30% compared to direct current devices.
What is Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) and how does PWM impact it?
Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) is a measure of how efficiently a computer data center uses energy. Systems using PWM devices have shown a decrease in PUE from 1.55 to 1.42 during control periods.
Why are PWM cooling devices becoming more popular among engineers?
Over 70% of electronics engineers are integrating PWM cooling devices into their designs due to their efficiency in temperature regulation and energy savings, reflecting a growing trend in modern electronics.