Introduction
Mini fans have become essential components in the electronics landscape, crucial for maintaining optimal temperatures and enhancing device performance. As technology advances, the need for efficient cooling solutions intensifies, particularly in compact and high-performance applications. However, the challenge lies in selecting the right mini fan and integrating it effectively into designs. Engineers must navigate these complexities to ensure reliable cooling and extend the lifespan of electronic devices.
What strategies can be employed to tackle these challenges head-on?
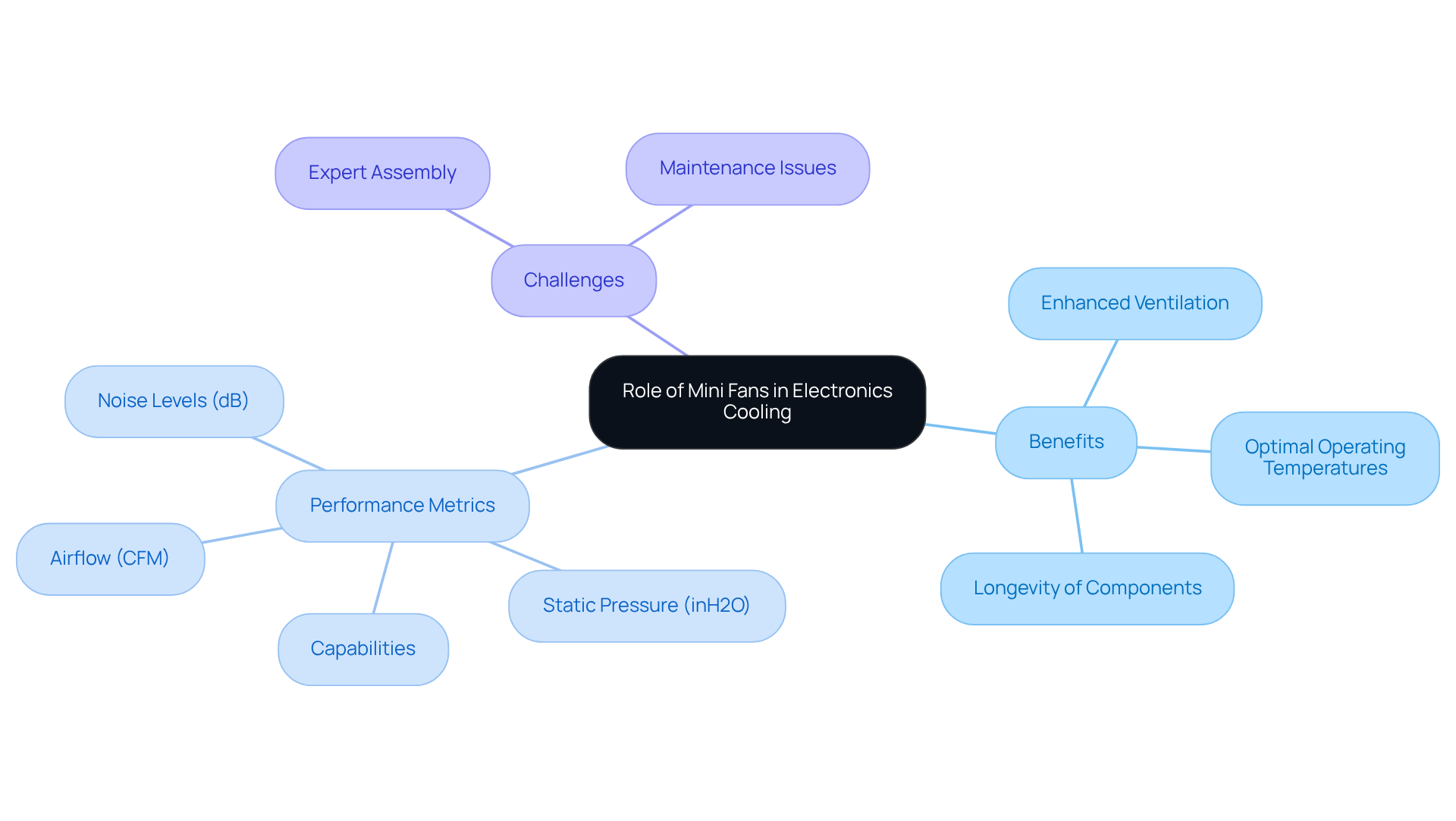
Understand the Role of Mini Fans in Electronics Cooling
Mini blowers play a vital role in the efficient regulation of temperature within electronic devices. They significantly enhance ventilation and disperse heat generated by various components. Their compact design is particularly advantageous in applications where traditional temperature control methods fall short, such as those using minifans. By improving airflow over heat sinks and circuit boards, minifans help maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing thermal throttling and prolonging the lifespan of electronic components.
In high-performance computing environments, for example, minifans are essential for managing the heat generated by CPUs and GPUs, which can produce substantial amounts of heat during operation. Engineers emphasize that understanding fluid dynamics and thermal profiles is crucial when selecting the appropriate small fan. This knowledge ensures effective cooling and optimal performance, especially in space-constrained applications.
When choosing a small blower, performance metrics such as:
- airflow (measured in CFM)
- static pressure (inH2O)
- noise levels (dB)
- the capabilities of minifans
are essential for making informed decisions. Additionally, engineers must be mindful of potential challenges associated with small ventilation devices, including the need for expert assembly and maintenance to avoid issues like imbalance and increased noise.
Incorporating small ventilators not only enhances thermal regulation but also boosts the reliability and longevity of electronic devices. By prioritizing these factors, engineers can ensure that their designs meet the demands of modern technology.
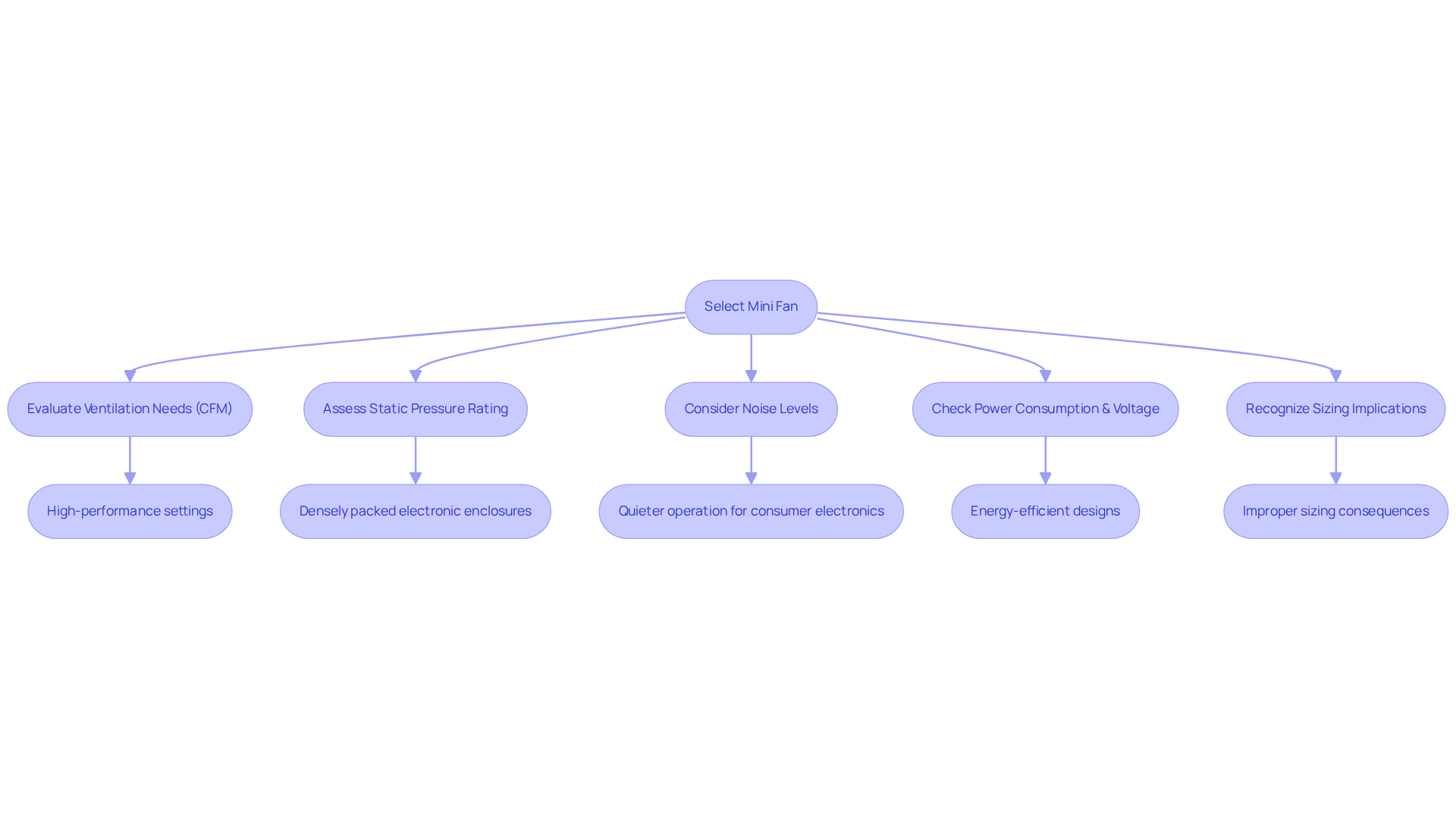
Select the Right Mini Fan for Your Application
Choosing the appropriate minifans is essential for achieving optimal performance in various applications. Gagner-Toomey Associates, the world’s largest manufacturer of standard and custom air-movers, offers an extensive product line of DC input tube axial fans, ranging from 15 to 280mm, and centrifugal blowers, from 15 to 225mm. These products are optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise, making them ideal for a range of environments.
Start by evaluating the ventilation needs of your application, typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). This measurement is essential for ensuring adequate temperature regulation, particularly in high-performance settings. Next, assess the static pressure rating, which indicates the fan’s ability to overcome resistance in airflow paths. This factor is especially critical in densely packed electronic enclosures where airflow is restricted.
Noise levels are another significant consideration in fan selection, particularly for consumer electronics where quieter operation is preferred. Gagner-Toomey’s devices are engineered to maintain low noise levels while providing effective cooling, making them suitable for use with minifans in laptops and desktop computers. Conversely, applications that require high static pressure, such as those in compact server environments, benefit from fans specifically designed for that purpose.
Additionally, consider the fan’s power consumption and voltage requirements to ensure compatibility with your system. Current trends show a growing preference for energy-efficient designs, which not only enhance battery life in portable devices but also contribute to overall system reliability. Furthermore, Gagner-Toomey offers IP protection in most models, adding an extra layer of reliability.
Engineers must recognize the implications of improper sizing; selecting a fan that is too small or too large can lead to insufficient or excessive circulation, ultimately compromising system efficiency. By meticulously matching these specifications to your application needs and adhering to regular maintenance and monitoring protocols, engineers can significantly enhance cooling efficiency and prolong the lifespan of electronic devices.
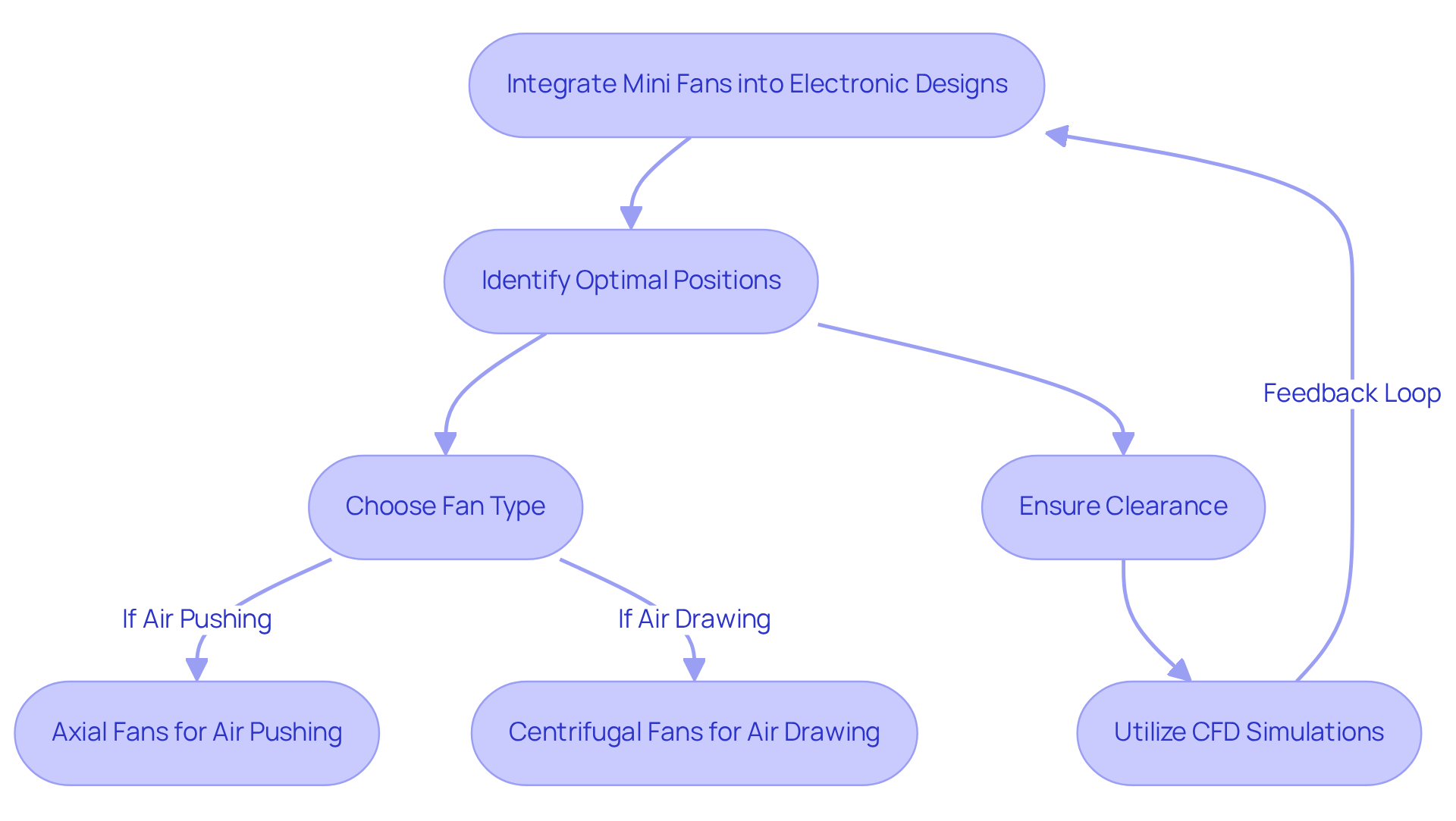
Integrate Mini Fans Effectively into Electronic Designs
To effectively integrate small ventilators into electronic designs, it’s crucial to identify optimal positions for air circulation. Start by arranging fans to direct airflow towards heat-producing components, such as CPUs or power supplies. Consider the orientation of the fan:
- Axial fans are typically employed for pushing air.
- Centrifugal fans excel at drawing air through confined spaces.
Ensure ample clearance around the fan for unobstructed circulation, and secure the fan to prevent vibrations that could disrupt performance.
Utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations can significantly enhance your design process. These simulations allow you to visualize airflow patterns and optimize fan placement. For example, in a compact device, positioning the fan directly above the heat sink can markedly improve cooling efficiency.
By implementing these integration strategies, engineers can substantially enhance the thermal management of their designs, leading to more reliable and efficient electronic systems.
Maintain and Optimize Mini Fans for Longevity
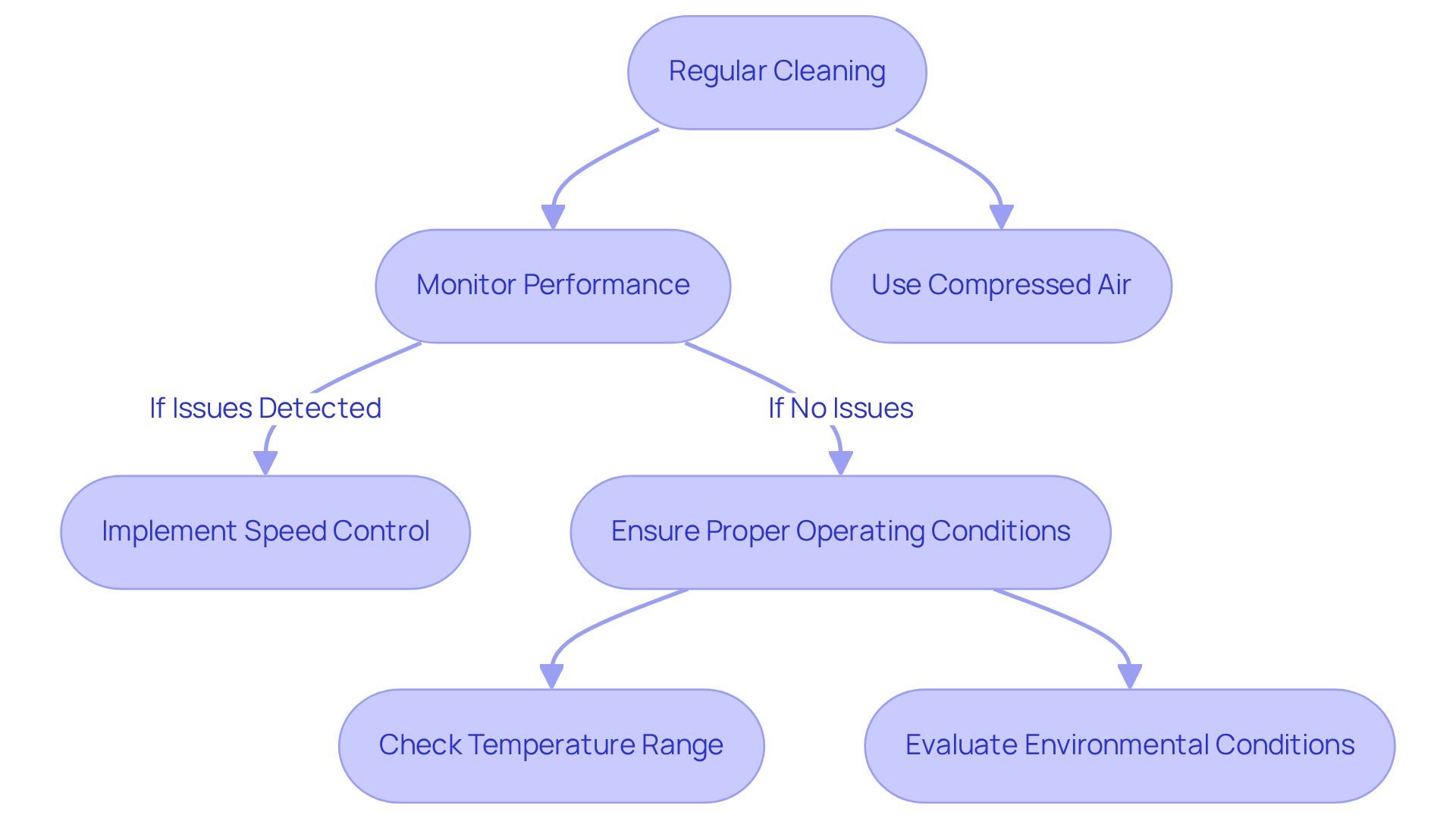
To ensure the longevity and performance of small ventilators, regular cleaning is essential. Dust accumulation can obstruct air movement and increase noise levels, leading to inefficiencies. Utilize compressed air to effectively blow out dust from the fan blades and housing, steering clear of liquids that might damage electronic components.
Monitoring the fan’s performance is equally important. If you observe increased noise or diminished airflow, it may indicate that a fan replacement is necessary. Implementing speed control mechanisms can optimize fan operation; for instance, employing pulse-width modulation (PWM) allows for adjustments in fan speed based on temperature, thereby reducing wear and energy consumption.
It’s crucial to ensure that the fan operates within its specified temperature range to prevent overheating, which can result in premature failure. Additionally, consider the environmental conditions where the fan operates. Exposure to dust, moisture, or corrosive gases can significantly impact its lifespan. Utilizing IP-rated designs can enhance the device’s resistance to external contaminants, thereby improving reliability.
By adhering to these maintenance practices, you can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of minifans used in your electronic applications.
Conclusion
Incorporating mini fans into electronic designs is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and extending the lifespan of devices. These compact cooling solutions not only enhance airflow but also prevent overheating, which can lead to thermal throttling and a diminished lifespan of components. By understanding the specific needs of each application and selecting the appropriate mini fan, engineers can guarantee that their systems operate efficiently and reliably.
Key considerations include:
- Evaluating airflow requirements
- Static pressure ratings
- Noise levels
Additionally, strategically integrating fans in key locations optimizes cooling. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and performance monitoring, is essential to sustain the effectiveness of mini fans over time. Furthermore, utilizing advanced tools like computational fluid dynamics can refine fan placement and airflow management.
Ultimately, the successful implementation of mini fans in electronic systems highlights the significance of effective cooling solutions in modern technology. By prioritizing best practices in selection, integration, and maintenance, engineers can significantly enhance device performance and reliability. This proactive approach not only contributes to the longevity of devices but also meets the increasing demand for energy-efficient and high-performance technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of mini fans in electronics cooling?
Mini fans play a vital role in regulating temperature within electronic devices by enhancing ventilation and dispersing heat generated by various components.
Why are mini fans advantageous in certain applications?
Their compact design is particularly beneficial in applications where traditional temperature control methods are insufficient, allowing for improved airflow over heat sinks and circuit boards.
How do mini fans affect the performance of electronic components?
By maintaining optimal operating temperatures, mini fans help prevent thermal throttling and prolong the lifespan of electronic components.
In what environments are mini fans particularly essential?
Mini fans are essential in high-performance computing environments for managing heat generated by CPUs and GPUs, which produce significant amounts of heat during operation.
What factors should engineers consider when selecting a mini fan?
Engineers should consider performance metrics such as airflow (measured in CFM), static pressure (inH2O), noise levels (dB), and the specific capabilities of the mini fans.
What challenges may arise with small ventilation devices?
Potential challenges include the need for expert assembly and maintenance to avoid issues such as imbalance and increased noise.
How do small ventilators contribute to the reliability of electronic devices?
Incorporating small ventilators enhances thermal regulation, which boosts the reliability and longevity of electronic devices.