Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of various thermal management products, meticulously examining their features, benefits, and limitations. It highlights the crucial distinction between active and passive solutions, underscoring the importance of this understanding for engineers tasked with selecting appropriate products. Effective temperature regulation in electronic devices is paramount, as overheating can lead to significant performance issues and product failures. By grasping these differences, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance device reliability and efficiency.
Introduction
Thermal management is integral to the performance and longevity of electronic devices. However, many engineers encounter challenges in selecting the most effective solutions. As the demand for high-performance electronics escalates, it becomes imperative to understand the features and benefits of various thermal management products. This understanding is essential for ensuring optimal functionality. Engineers must navigate the complexities of active versus passive solutions, prioritizing key criteria to make informed decisions that enhance both efficiency and reliability.
Understanding Thermal Management: Key Concepts and Importance
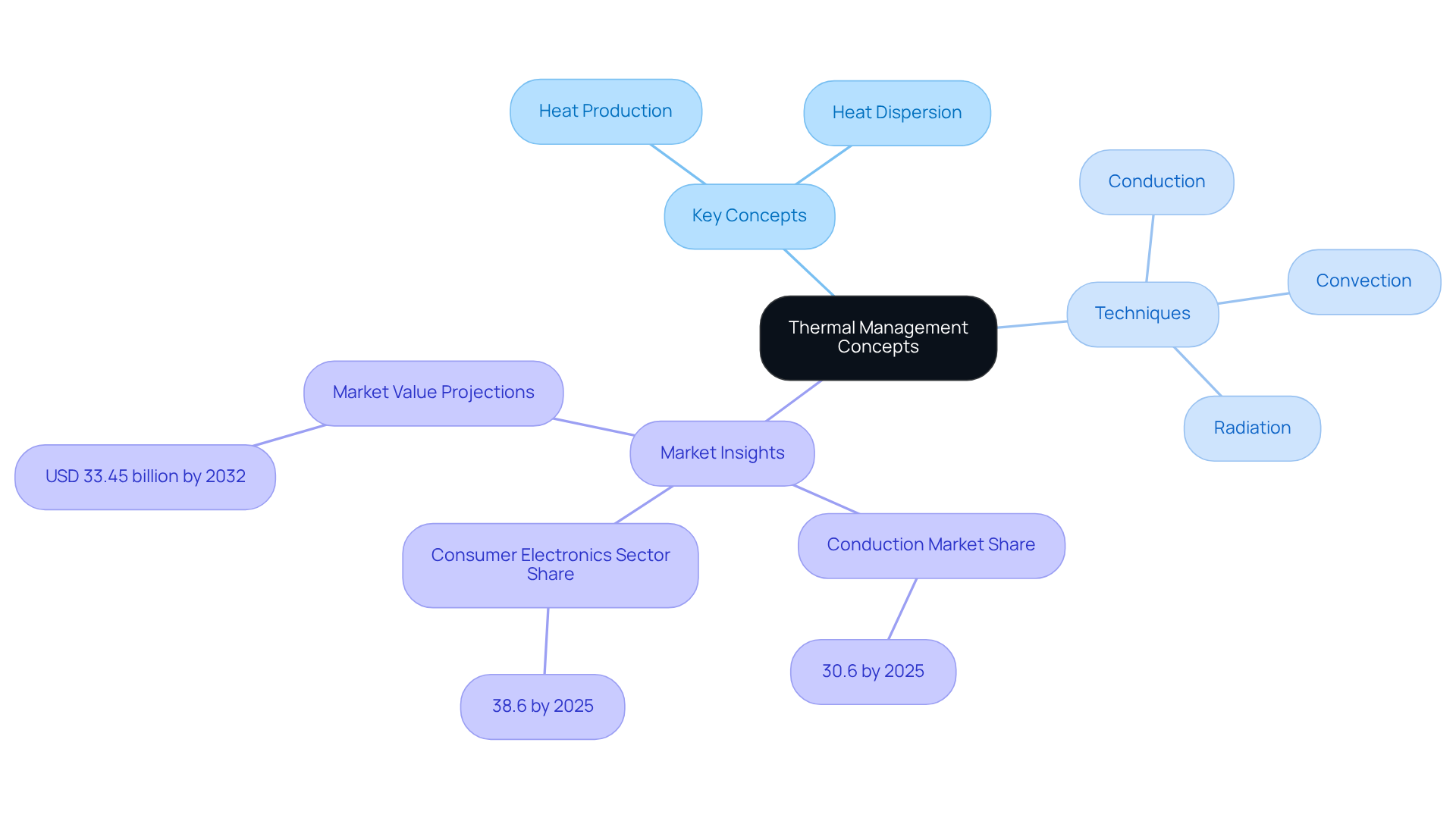
Thermal management products encompass the techniques and processes essential for regulating the temperature of electronic devices and systems. This regulation is critical for preventing overheating, which can impair performance, reduce component lifespan, and result in potential failures. Key concepts in temperature regulation include:
- Heat production
- Heat dispersion
- Various techniques employed to manage these processes, such as:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
Notably, conduction temperature regulation devices are projected to capture a 30.6% market share by 2025, underscoring their effectiveness in managing heat within consumer electronics. Furthermore, the consumer electronics sector is anticipated to account for 38.6% of the heat control market in 2025, emphasizing its pivotal role in driving demand for innovative refrigeration solutions.
Recent advancements in heat regulation technologies, including microchannel heat exchange and advanced adhesive materials, are fostering innovation in the field, particularly as the demand for high-performance electronic devices continues to rise. The significance of temperature regulation, which can be effectively managed through thermal management products, is further underscored by its impact on energy efficiency, safety, and the operational lifespan of electronic devices.
With the expected to reach USD 33.45 billion by 2032, propelled by the increasing need for advanced cooling systems across various sectors, understanding these principles is vital for engineers and designers to ensure their products operate reliably under diverse conditions. Additionally, the Asia-Pacific region accounts for over 40% of the global temperature control market share, indicating substantial growth opportunities in this domain.
Types of Thermal Management Products: Active vs. Passive Solutions
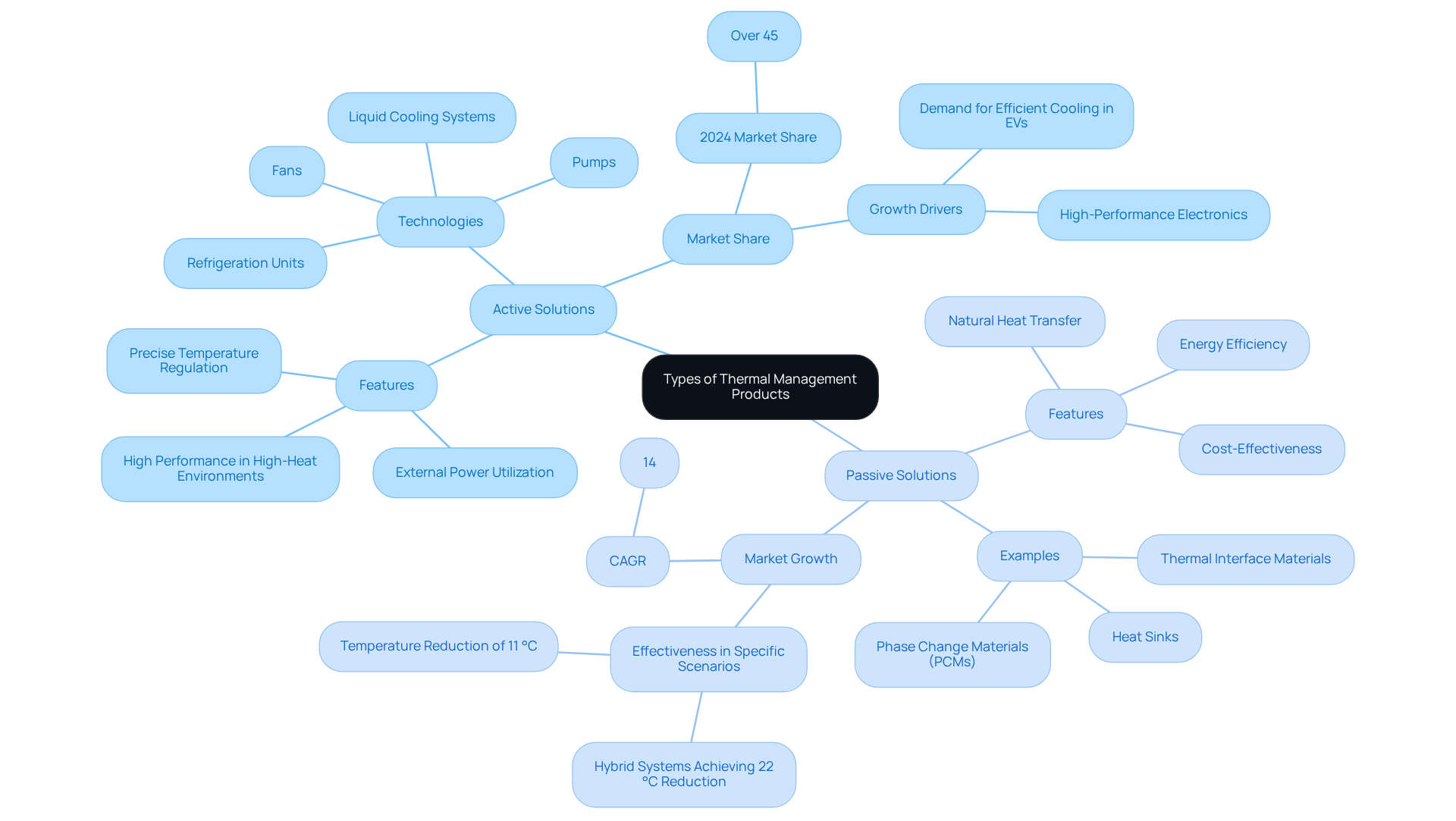
Thermal management products are primarily divided into active and passive solutions, each possessing distinct features and applications. Active thermal management solutions utilize external power sources to improve heat dissipation, employing technologies such as fans, pumps, and refrigeration units. These systems excel in high-heat environments, providing precise temperature regulation and enhanced performance. For example, recent innovations in active cooling technologies, such as Mahle’s bionic battery cooling plate developed in August 2023, have showcased significant efficiency improvements, with certain systems achieving over 20% better performance compared to traditional methods.
Conversely, passive temperature management relies on natural heat transfer processes, including conduction and convection, without the need for additional energy input. Common examples encompass heat sinks, thermal interface materials, and phase change materials (PCMs). While passive solutions generally offer greater energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness, they may not match the performance of active systems in demanding applications. Research indicates that optimal configurations of standalone PCMs can reduce maximum cell temperatures by as much as 11 °C, whereas ideal designs of hybrid temperature control setups can achieve reductions of 22 °C, demonstrating their effectiveness in specific scenarios.
The market for thermal management products is evolving, with active solutions accounting for over 45% of the market share in 2024, driven by the increasing demand for efficient cooling options in electric vehicles and high-performance electronics. Industry leaders emphasize the importance of selecting the appropriate thermal management products based on application requirements, as 55% of product failures are attributed to overheating. As technology advances, the integration of intelligent heat control solutions is becoming increasingly prevalent, enhancing the capabilities of both active and passive approaches. Furthermore, the passive system segment is anticipated to grow at a 14% CAGR, while the liquid cooling and heating category is projected to experience the highest CAGR of 29.2% during the forecast period. Understanding the advantages and limitations of each category is essential for engineers to make informed decisions when selecting for heat control solutions.
Comparison Criteria: Evaluating Thermal Management Solutions for Your Project
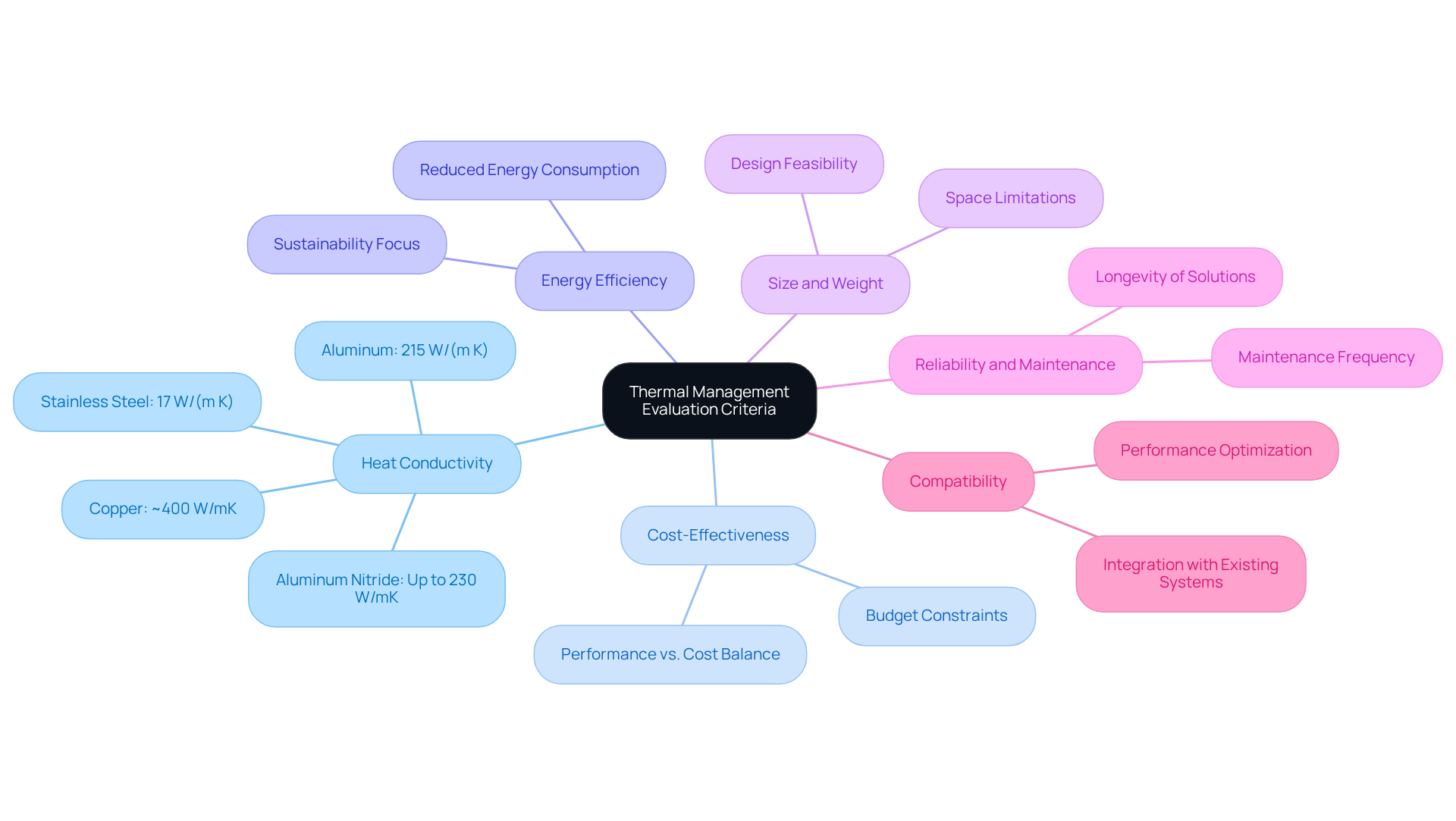
When assessing heat control options, it is imperative to consider several factors to ensure the selected product meets project specifications. The key factors include:
- Heat Conductivity: The ability of a substance to transfer heat is crucial for effective heat control. Materials with higher heat conductivity can disperse warmth more efficiently, which is essential for effective thermal management products.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Budget constraints often play a significant role in the selection of heat control solutions. It is essential to strike a balance between performance and cost to attain the best value for the investment.
- Energy Efficiency: Solutions that reduce energy consumption while delivering sufficient cooling are increasingly vital, particularly in designs that prioritize environmental sustainability.
- Size and Weight: In environments where space is limited, the physical dimensions and weight of heat control products can significantly impact design feasibility and practicality.
- : The longevity of heat regulation solutions and the frequency of required maintenance can affect long-term operational costs and the reliability of performance.
- Compatibility: Ensuring that the heat regulation solution integrates seamlessly with existing systems and components is essential for achieving peak performance.
By taking these criteria into account, engineers can make informed decisions about thermal management products that align with their project objectives.
Product Comparison: Features, Benefits, and Limitations of Leading Thermal Management Solutions
In this section, we compare several leading thermal management solutions based on their features, benefits, and limitations:
-
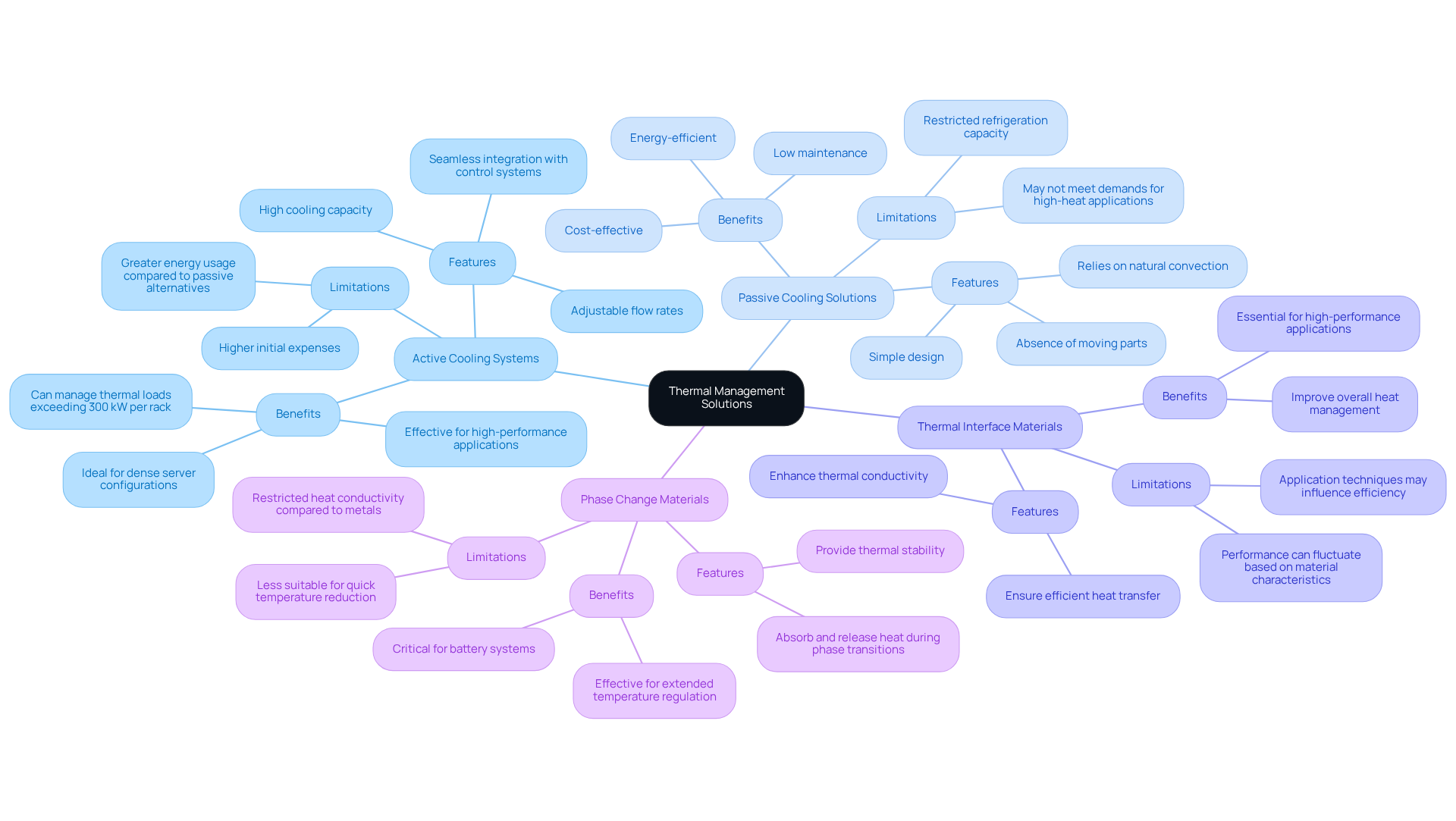
Active Cooling Systems (e.g., Liquid Cooling Solutions):
- Features: High cooling capacity, adjustable flow rates, and seamless integration with control systems.
- Benefits: Particularly effective for high-performance applications, such as data centers and electric vehicles, where significant heat generation occurs. Liquid temperature regulation technologies, such as those introduced by Aligned, can manage thermal loads exceeding 300 kW per rack, making them ideal for environments with dense server configurations. In 2023, data centers utilized 7.4 Gigawatts of power, underscoring the essential requirement for efficient temperature management in these environments.
- Limitations: While providing enhanced temperature regulation, these setups often involve higher initial expenses and greater energy usage compared to passive alternatives.
-
Passive Cooling Solutions (e.g., Heat Sinks):
- Features: Simple design, absence of moving parts, and reliance on natural convection for heat dissipation.
- Benefits: Cost-effective, low maintenance, and energy-efficient, making them suitable for consumer electronics and low-power applications. Their simplicity allows for easy integration into various designs without the need for complex control systems.
- Limitations: Their refrigeration capacity is restricted, which may not meet the demands for high-heat applications, especially in settings where heat production is considerable. This limitation is critical as high-density racks and compute-intensive workloads exacerbate .
-
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs):
- Features: Enhance thermal conductivity between components and heat sinks, ensuring efficient heat transfer.
- Benefits: Improve overall heat management and reliability of electronic devices, essential for preserving optimal operating conditions in high-performance applications.
- Limitations: Performance can fluctuate greatly depending on material characteristics and application techniques, which may influence the overall efficiency of the temperature control solution.
-
Phase Change Materials (PCMs):
- Features: Absorb and release heat during phase transitions, providing thermal stability across varying conditions.
- Benefits: Effective for applications requiring temperature regulation over extended periods, such as battery systems, where maintaining a stable temperature is critical for performance and longevity.
- Limitations: Restricted heat conductivity in comparison to metals can influence response times, rendering them less appropriate for quick temperature reduction requirements.
By analyzing these thermal management products, engineers can identify the most suitable solution for their specific applications, balancing performance, cost, and efficiency. The growing demand for efficient cooling solutions is underscored by the projected growth of the data center cooling market, which is expected to reach USD 25.12 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 15.11%, driven by the increasing computational needs of AI and media applications.
Conclusion
Thermal management stands as a pivotal component in the design of electronic devices, ensuring optimal performance and longevity through effective temperature regulation. The array of thermal management products available today—both active and passive—fulfills distinct roles, addressing various industry needs. A comprehensive understanding of the features, benefits, and limitations of these solutions empowers engineers and designers to make informed choices that bolster the reliability and efficiency of their projects.
This article has delved into key concepts such as heat production, dispersion, and the technologies utilized in thermal management. Active solutions, exemplified by liquid cooling systems, deliver superior performance in demanding environments, whereas passive solutions like heat sinks present cost-effective and energy-efficient alternatives. The critical evaluation of factors such as heat conductivity, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility is paramount, as these criteria directly impact the success of thermal management strategies.
As the demand for advanced cooling systems escalates—driven by innovations and the growing complexity of electronic devices—the importance of effective thermal management becomes increasingly evident. Engineers and designers are urged to remain informed about the latest advancements in thermal management technologies and to meticulously assess their options. This diligence ensures that their products not only meet performance standards but also contribute to sustainability and energy efficiency. Ultimately, making the right choice in thermal management products can lead to enhanced product performance and diminished failure rates, underscoring the essential role these solutions play in contemporary engineering.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is thermal management?
Thermal management refers to the techniques and processes used to regulate the temperature of electronic devices and systems to prevent overheating, which can impair performance and reduce component lifespan.
Why is temperature regulation important?
Temperature regulation is crucial for preventing overheating, which can lead to performance issues, reduced lifespan of components, and potential failures in electronic devices.
What are the key concepts in temperature regulation?
The key concepts in temperature regulation include heat production, heat dispersion, and various techniques such as conduction, convection, and radiation.
What is the projected market share for conduction temperature regulation devices by 2025?
Conduction temperature regulation devices are projected to capture a 30.6% market share by 2025.
What role does the consumer electronics sector play in the heat control market?
The consumer electronics sector is anticipated to account for 38.6% of the heat control market in 2025, highlighting its importance in driving demand for innovative refrigeration solutions.
What advancements are being made in heat regulation technologies?
Recent advancements include microchannel heat exchange and advanced adhesive materials, which are fostering innovation in thermal management as the demand for high-performance electronic devices increases.
How does thermal management impact energy efficiency and safety?
Effective thermal management enhances energy efficiency, ensures safety, and extends the operational lifespan of electronic devices.
What is the expected market value of the heat control solutions market by 2032?
The heat control solutions market is expected to reach USD 33.45 billion by 2032, driven by the increasing need for advanced cooling systems across various sectors.
Which region accounts for a significant share of the global temperature control market?
The Asia-Pacific region accounts for over 40% of the global temperature control market share, indicating substantial growth opportunities in this area.

