Overview
Micro blowers demonstrate superior performance compared to traditional fans in applications that demand high-pressure airflow within compact spaces. This characteristic makes them particularly well-suited for portable electronics and medical devices.
The advanced design of micro blowers not only enhances energy efficiency but also facilitates effective thermal management. In contrast, traditional fans excel in larger environments where substantial air volume circulation is essential.
This distinction highlights the importance of selecting the appropriate airflow solution based on specific application requirements.
Introduction
In the realm of cooling technologies, the choice between micro blowers and traditional fans significantly impacts efficiency and performance across various applications. Micro blowers, characterized by their compact design and capability to generate high-pressure airflow, are revolutionizing the cooling of sensitive electronic devices. In contrast, traditional fans continue to dominate larger spaces with their high-volume air movement.
As industries evolve and the demand for effective thermal management intensifies, understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each technology becomes essential for engineers and decision-makers. This exploration delves into the distinct characteristics, applications, and performance metrics of micro blowers and traditional fans, illuminating the path toward optimal cooling solutions in an increasingly complex technological landscape.
Understand Micro Blowers and Traditional Fans
Micro blowers are a cutting-edge solution in airflow technology, specifically designed to provide high-pressure airflow while maintaining low volumes. These compact devices often utilize advanced innovations such as Axial Air-Gap Technology to optimize efficiency. Micro blowers have unique features that make them ideal for applications with stringent space constraints, particularly in portable electronics and medical devices.
In contrast, traditional devices, encompassing both axial and centrifugal types, are engineered to circulate larger volumes of air at lower pressures. These devices are extensively employed in HVAC systems, industrial environments, and .
The fundamental difference between these two technologies is rooted in their airflow characteristics:
- Micro blowers excel in producing high-pressure airflow,
- Conventional fans are tailored for volume, thus addressing diverse operational requirements across various industries.
Explore Applications in Electronics
Micro blowers are becoming increasingly vital in such as smartphones, laptops, and medical equipment, where effective thermal management is paramount. The compact design and high-pressure output of micro blowers facilitate efficient temperature regulation of sensitive components without occupying significant space. Furthermore, the user-friendly features of micro blowers, including intuitive controls, significantly enhance workflow efficiency in electronics projects. This is exemplified in the Jindal BOPP Slitter Rewinder case study, which showcased notable increases in operational productivity.
Conversely, conventional fans are predominantly employed in larger environments like data centers, industrial machinery, and residential HVAC systems, where they ensure efficient temperature regulation across expansive areas or equipment. Passive temperature regulation, which operates silently, is particularly advantageous in noise-sensitive environments.
Understanding these distinct applications, alongside the importance of safety protocols in compact fan products, is crucial for selecting the appropriate temperature control solution tailored to the specific needs of electronic devices or systems. As Johan Enslin from ARPA-E emphasized, energy absorption is a critical factor in temperature regulation technologies, underscoring the need for efficient solutions.
Compare Performance and Efficiency
Engineered to deliver enhanced static pressure with reduced airflow, micro blowers are particularly efficient for applications that require focused airflow, such as the maintenance of high-density electronic components. As Sam Pelonis observes, in a specific direction, while ventilators circulate air throughout a defined space.” In contrast, traditional fans are designed to move larger volumes of air, making them suitable for general temperature regulation purposes.
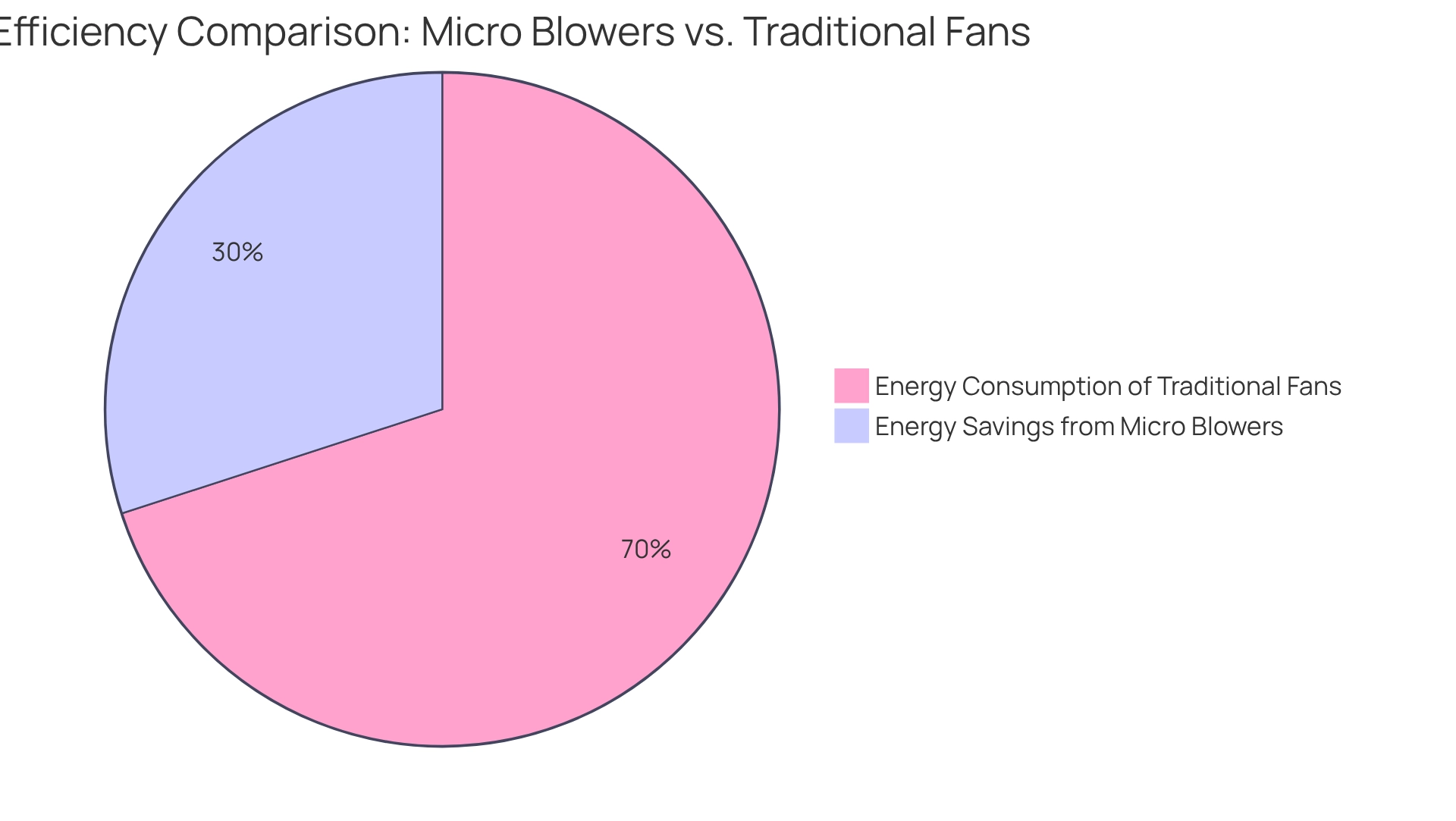
In terms of energy efficiency, micro blowers typically consume less power because of their advanced design characteristics. This reduced energy consumption can yield substantial cost savings over time, particularly in environments with high cooling demands. Research indicates that micro devices can achieve energy savings of up to 30% compared to conventional units, underscoring their potential for long-term operational efficiency.
Furthermore, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as the largest market for ventilation devices, indicating significant demand and growth potential in this sector. As the market evolves, performance evaluations between these two technologies consistently highlight the advantages of micro devices in specialized applications, while conventional fans remain a reliable choice for broader cooling requirements.
Evaluate Pros and Cons
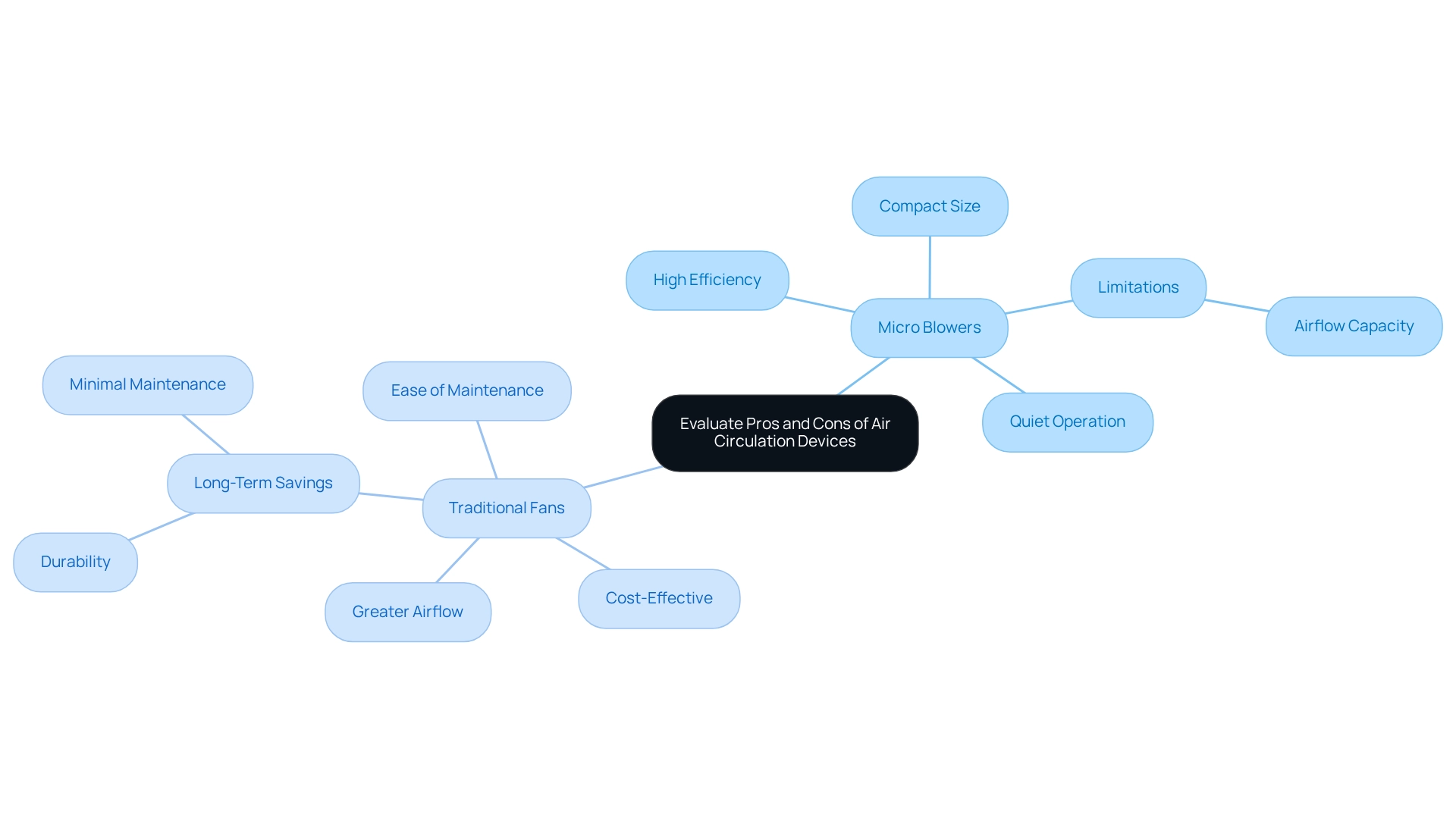
Micro blowers offer several distinct advantages that make them appealing for specific applications. Their compact size is particularly beneficial in environments where space is limited. Additionally, they demonstrate high efficiency, functioning effectively even in tight quarters, and their quiet operation minimizes noise, which is advantageous in sensitive applications.
Nevertheless, micro blowers may encounter limitations regarding airflow capacity, rendering them less suitable for larger-scale operations. In contrast, traditional fans offer significant benefits, including greater airflow, making them more appropriate for extensive cooling requirements. They also tend to be cost-effective, often proving to be more economical for larger applications, and their straightforward design facilitates ease of maintenance, thereby contributing to lower upkeep costs.
For example, large industrial blowers, despite necessitating a higher initial investment, are engineered for durability and demand minimal maintenance compared to complex HVAC systems. This results in long-term savings through decreased operational hours and reduced maintenance expenses, thereby enhancing their cost-efficiency in extensive applications.
When evaluating the cost-efficiency of air circulation methods in 2025, conventional devices continue to exhibit considerable advantages, particularly in scenarios where robust airflow is essential. Industry specialists note that while traditional air movers may be more cost-effective, micro blowers are advantageous in compact settings despite their elevated price per unit of airflow. Furthermore, ECMs () are acknowledged as the most efficient type of motor utilized in Air Circulation Fans (ACFs), underscoring the efficiency aspects of cooling solutions.
Regulatory considerations also play a role; as noted by AHRI, an energy conservation standard is deemed unnecessary for blowers, as all states must comply with ASHRAE 90.1. This underscores the importance of understanding industry standards when making informed choices between traditional fans and micro blowers, as the decision ultimately rests on specific application requirements, including space constraints, cooling demands, and budget considerations. A thorough understanding of these factors is vital for engineers striving for optimal solutions within the electronics industry.
Conclusion
The comparison between micro blowers and traditional fans underscores the distinct advantages and applications inherent to each cooling technology. Micro blowers, characterized by their compact design and capability to generate high-pressure airflow, are particularly well-suited for space-constrained environments, such as portable electronics and medical devices. Their efficiency and quiet operation render them a valuable choice for applications necessitating precise thermal management. Conversely, traditional fans excel in larger settings, providing high airflow capabilities and cost-effectiveness for extensive cooling needs across both industrial and residential applications.
As the demand for effective thermal management escalates, grasping the performance metrics and efficiency of both micro blowers and traditional fans becomes essential. Micro blowers exhibit significant energy savings and are tailored for specialized tasks, while traditional fans remain a reliable option for broader cooling solutions. A thorough evaluation of the pros and cons of each technology reveals that the ultimate choice hinges on specific application requirements, encompassing space limitations, cooling demands, and budget constraints.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate cooling solution necessitates careful consideration of the unique characteristics of micro blowers and traditional fans. By aligning the right technology with operational needs, engineers and decision-makers can ensure optimal performance and efficiency within an increasingly complex technological landscape. The ongoing evolution of cooling technologies will undoubtedly shape future innovations, making it imperative to stay informed about these advancements for the benefit of various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are micro blowers and what is their primary function?
Micro blowers are compact devices designed to provide high-pressure airflow while maintaining low volumes, making them ideal for applications with stringent space constraints.
What technology do micro blowers utilize to enhance their efficiency?
Micro blowers often use advanced innovations such as Axial Air-Gap Technology to optimize their efficiency.
In what applications are micro blowers typically used?
Micro blowers are particularly suited for portable electronics and medical devices due to their small size and high-pressure airflow capabilities.
How do micro blowers differ from traditional airflow devices?
Micro blowers excel in producing high-pressure airflow, whereas traditional devices, including axial and centrifugal fans, are designed to circulate larger volumes of air at lower pressures.
Where are traditional airflow devices commonly used?
Traditional airflow devices are extensively employed in HVAC systems, industrial environments, and general cooling applications.
What is the fundamental difference between micro blowers and conventional fans?
The fundamental difference lies in their airflow characteristics: micro blowers focus on high-pressure airflow, while conventional fans are tailored for moving larger volumes of air.

