Overview
The article delves into the intricate workings of backward inclined centrifugal fans, elucidating their fundamental principles, notable advantages, and diverse applications across various industries. It asserts that these fans operate with remarkable efficiency by harnessing centrifugal force and fluid dynamics, positioning them as optimal choices for HVAC systems, industrial exhaust, and cooling towers. Furthermore, the discussion underscores their quiet operation and adaptability to fluctuating air volumes, ultimately establishing their significance in contemporary engineering solutions.
Introduction
Backward inclined centrifugal fans represent the pinnacle of modern ventilation technology, delivering an exceptional combination of efficiency and adaptability. Their innovative design effectively minimizes turbulence while maximizing airflow, rendering them indispensable across a spectrum of industrial applications—from HVAC systems to dust collection.
Yet, with a plethora of specifications and operational principles to navigate, how can one identify the ideal fan for specific requirements? This article explores the fundamental mechanics, advantages, and applications of backward inclined centrifugal fans, offering insights that empower readers to make informed decisions regarding their selection and implementation.
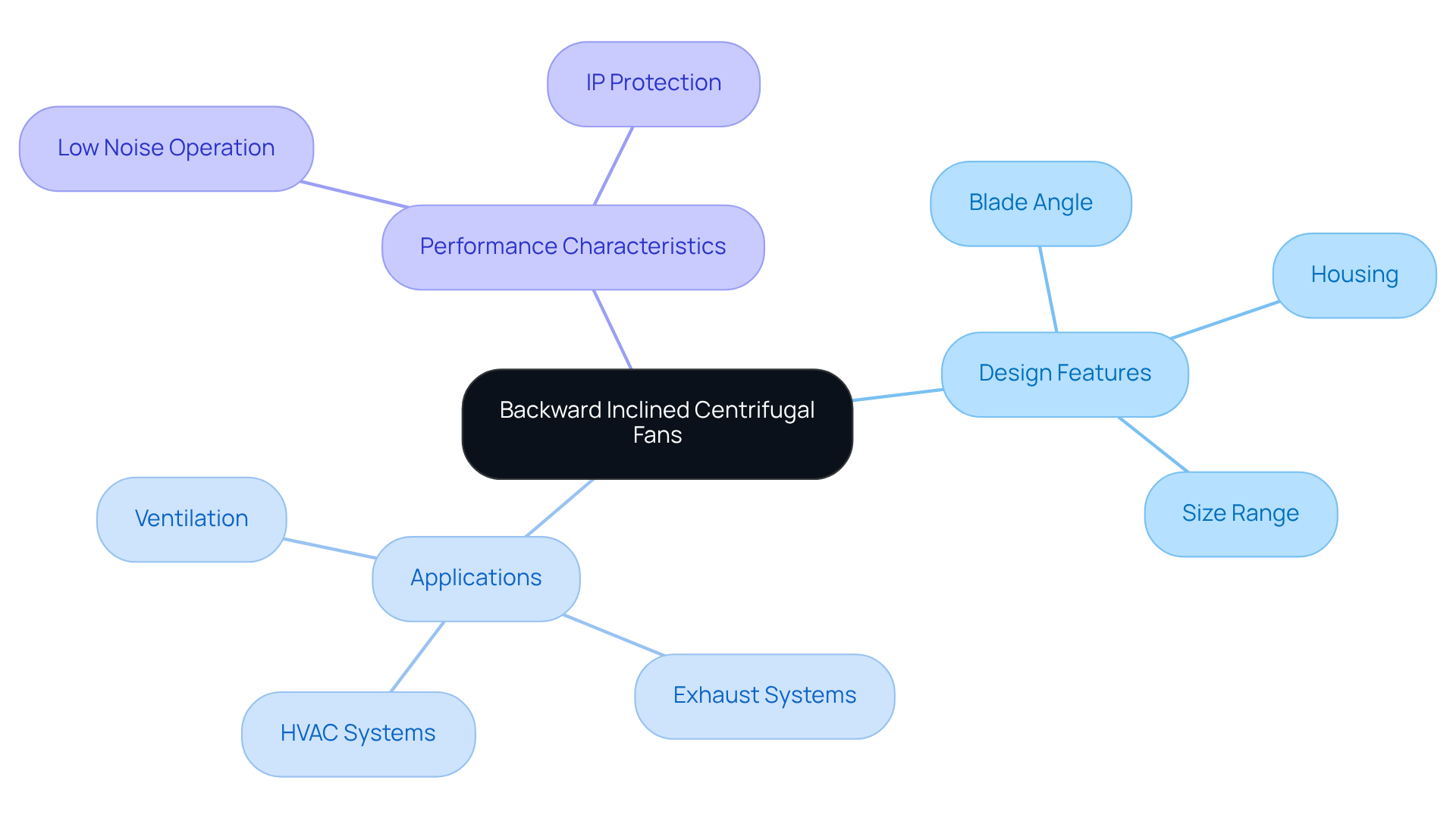
Define Backward Inclined Centrifugal Fans
Backward inclined rotary blowers represent a sophisticated solution characterized by blades angled backward relative to the direction of rotation. This innovative design facilitates effective ventilation and minimizes turbulence, making these devices ideal for a variety of industrial applications.
Gagner-Toomey Associates, recognized as the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offers a comprehensive range of backward inclined centrifugal fans that are meticulously optimized for performance and efficiency.
Backward inclined centrifugal fans are commonly employed in HVAC systems, exhaust systems, and other ventilation scenarios where consistent airflow is paramount. Their construction typically features a robust housing that supports the fan blades, ensuring durability and reliable performance across diverse operational conditions.
With sizes ranging from 15 to 225mm, these devices are engineered for and include IP protection in most models upon request, thus providing tailored solutions to meet the specific demands of electronics and automotive applications.
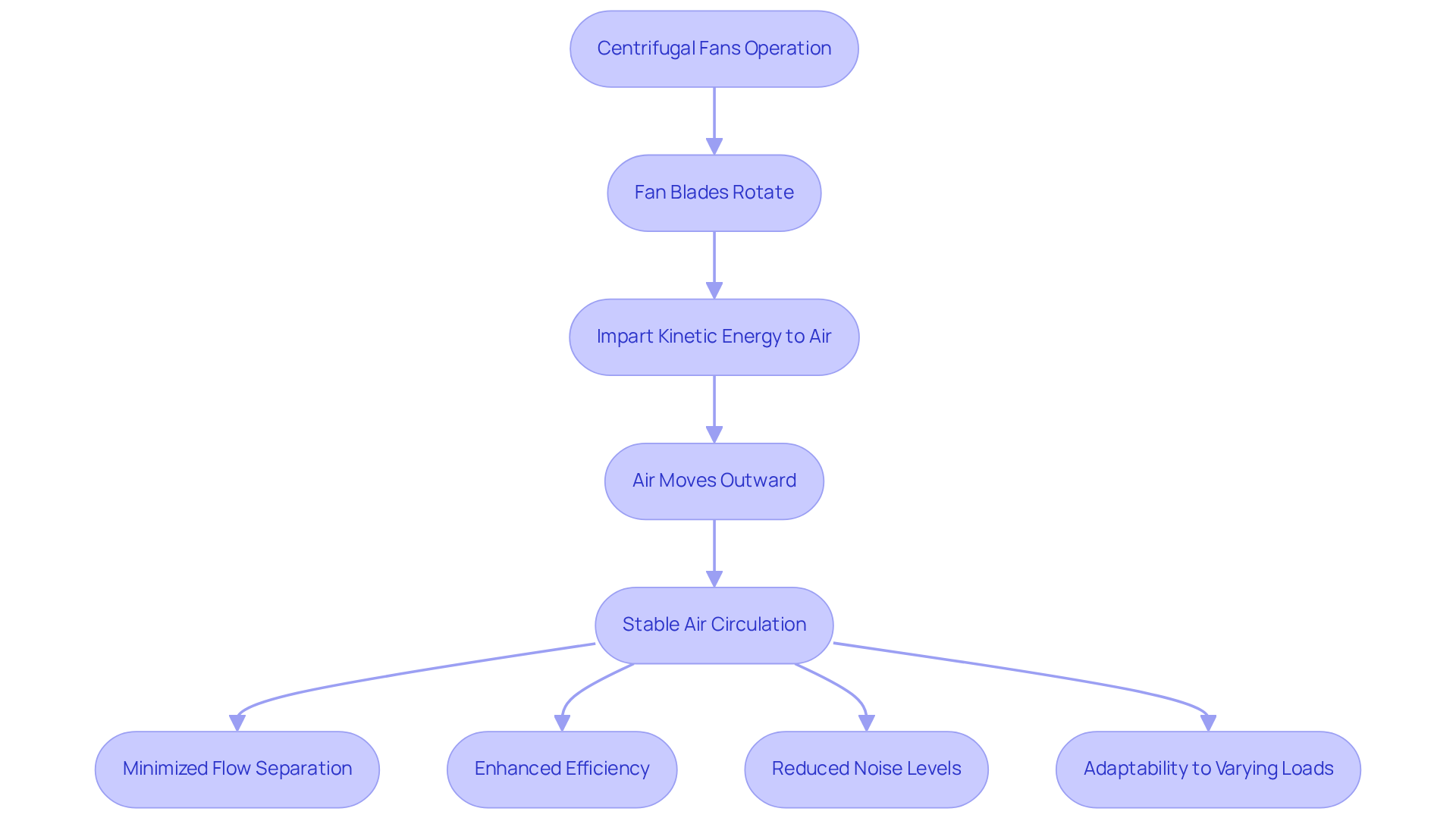
Explain Operational Principles
Backward inclined centrifugal fans operate on the fundamental principles of centrifugal force and fluid dynamics. As the fan blades rotate, they impart kinetic energy to the air, prompting it to move outward from the center of the fan. The design of the backward inclined centrifugal fan, with its tilted blades, significantly minimizes the risk of flow separation, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing noise levels. This design fosters a stable air circulation pattern, making the backward inclined centrifugal fan particularly suitable for applications that demand . Furthermore, these devices are capable of managing varying loads without substantial performance degradation, rendering them highly adaptable across different operational settings.
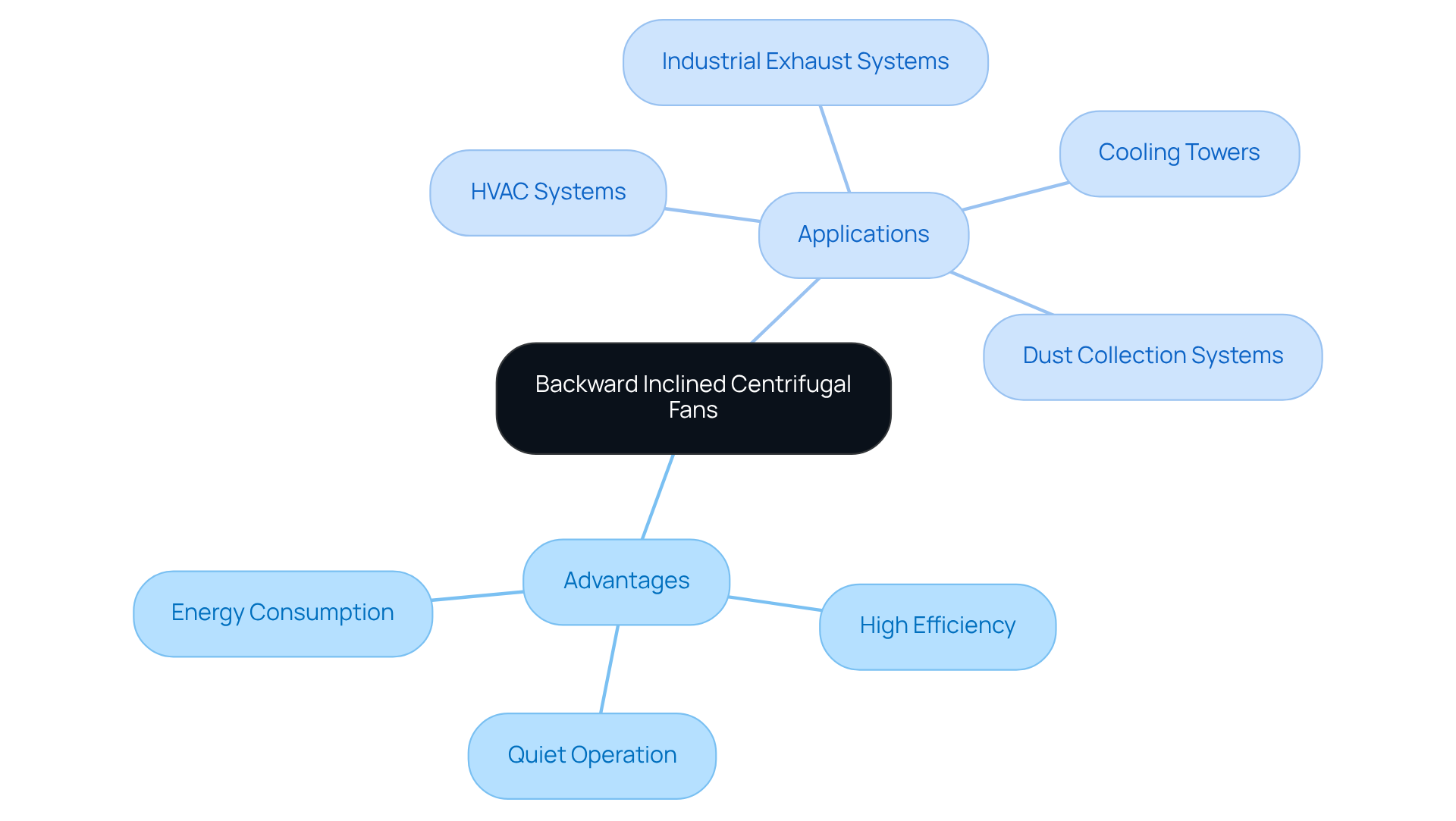
Discuss Advantages and Applications
Backward inclined centrifugal fans provide significant advantages, such as high efficiency, quiet operation, and the capability to manage varying air volumes. Their innovative design not only minimizes energy consumption but also maximizes airflow, positioning them as an environmentally friendly option. The following applications illustrate their versatility:
- HVAC Systems: Essential for air circulation and ventilation in both commercial and residential settings.
- Industrial Exhaust Systems: Highly effective in eliminating fumes and contaminants generated during manufacturing processes.
- Cooling Towers: Crucial for improving cooling efficiency in power plants and industrial facilities.
- Dust Collection Systems: Vital in woodworking and manufacturing environments to uphold air quality by removing particulate matter.
These applications highlight the of backward inclined centrifugal fans, establishing them as a compelling choice for various industries.
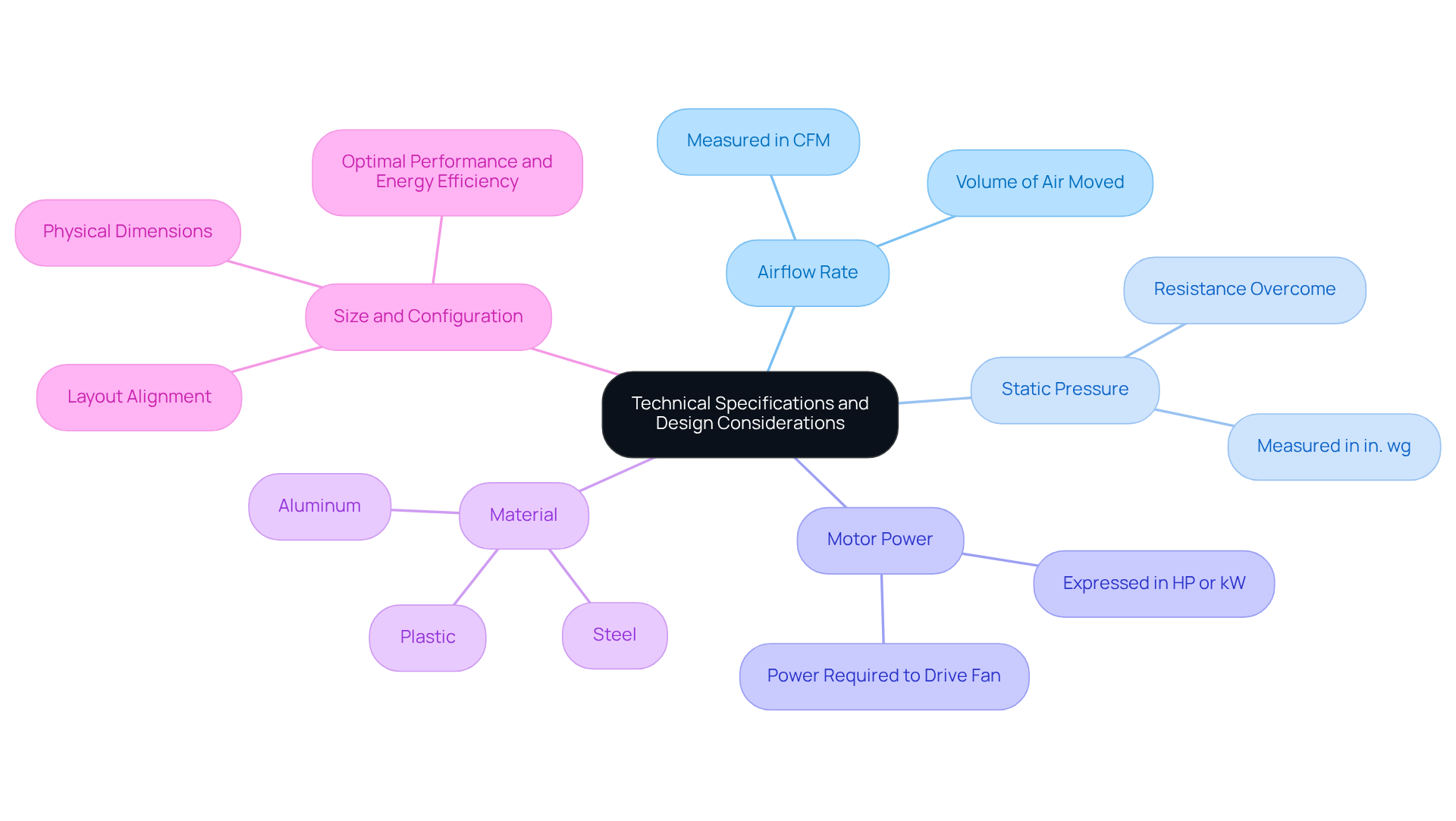
Outline Technical Specifications and Design Considerations
When selecting a backward inclined centrifugal fan, several critical technical specifications and design considerations must be taken into account:
- Airflow Rate: Measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), this metric indicates the volume of air the fan can effectively move.
- Static Pressure: This refers to the resistance the fan can overcome, typically measured in inches of water gauge (in. wg).
- Motor Power: The power required to drive the fan is usually expressed in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW).
- Material: Fans can be constructed from various materials, including steel, aluminum, or plastic, depending on the specific application and environmental conditions.
- Size and Configuration: The physical dimensions and layout of the fan must align with the installation space and airflow requirements. Proper sizing is essential to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Backward inclined centrifugal fans play a crucial role in enhancing ventilation systems across various industries. Their distinct design, featuring backward-angled blades, not only optimizes airflow but also reduces turbulence and noise, making them an ideal choice for applications that demand consistent air movement. A comprehensive understanding of the principles and characteristics of these fans is vital for fully leveraging their potential in both industrial and commercial settings.
This article explores the operational principles that enable backward inclined centrifugal fans to function effectively. It highlights key advantages such as:
- High efficiency
- Quiet operation
- Adaptability to varying loads
Alongside a diverse range of applications from HVAC systems to dust collection. Furthermore, it discusses the technical specifications and design considerations essential for selecting the appropriate fan, emphasizing critical factors like airflow rate, static pressure, and material choice.
In conclusion, backward inclined centrifugal fans embody a sophisticated solution for efficient ventilation and air management. Their extensive applications and operational benefits underscore their importance in maintaining air quality and energy efficiency across varied environments. For industries aiming to enhance their airflow systems, investing in these fans represents a strategic decision that promises improved performance and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are backward inclined centrifugal fans?
Backward inclined centrifugal fans are ventilation devices characterized by blades angled backward relative to the direction of rotation. This design minimizes turbulence and enhances effective ventilation.
Who is a leading producer of backward inclined centrifugal fans?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is recognized as the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, offering a wide range of backward inclined centrifugal fans.
Where are backward inclined centrifugal fans commonly used?
They are commonly employed in HVAC systems, exhaust systems, and other ventilation applications where consistent airflow is essential.
What features are typical of backward inclined centrifugal fans?
These fans typically have a robust housing that supports the fan blades, ensuring durability and reliable performance in various operational conditions.
What sizes do backward inclined centrifugal fans come in?
Backward inclined centrifugal fans are available in sizes ranging from 15 to 225mm.
Are backward inclined centrifugal fans designed for quiet operation?
Yes, these fans are engineered for low noise operation.
Do backward inclined centrifugal fans offer any protection features?
Many models include IP protection upon request, providing tailored solutions for specific applications, especially in electronics and automotive sectors.

