Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison between ball bearings and sleeve bearings, focusing on their performance, cost, and efficiency. It highlights the suitability of each type for various applications.
Specifically, sleeve bearings are identified as more cost-effective and quieter options for low-speed operations. In contrast, ball bearings are recognized for their superior durability and efficiency in high-speed applications.
Ultimately, the choice between these two types of bearings is contingent upon specific engineering requirements, underscoring the importance of tailored solutions in engineering design.
Introduction
The choice between ball bearings and sleeve bearings represents a pivotal consideration for engineers, significantly influencing both machinery performance and the overall cost and efficiency of operations. Each bearing type offers unique advantages and challenges; for instance, sleeve supports operate with whisper-quiet efficiency in low-speed applications, whereas ball bearings exhibit high-speed durability in demanding environments.
As industries evolve and the demand for optimized performance escalates, understanding the intricate balance of efficiency, lifespan, and cost-effectiveness becomes essential.
- Which bearing type will ultimately prove most suitable for specific applications?
- How can engineers effectively navigate the complexities of this decision?
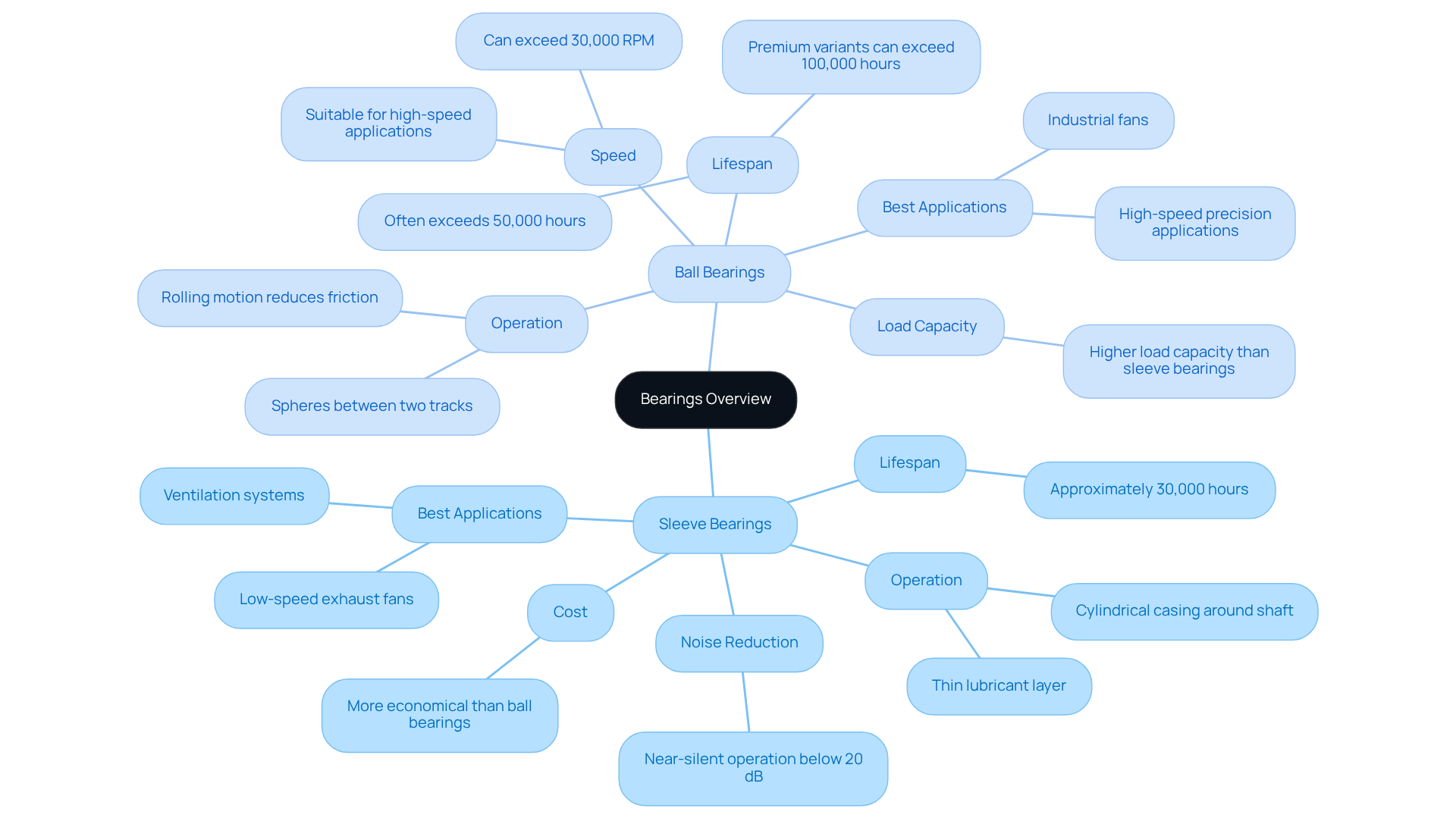
Understand Sleeve and Ball Bearings
Sleeve supports, often referred to as plain supports, consist of a cylindrical casing that encases a rotating shaft. Their operation relies on maintaining a thin layer of lubricant between the shaft and the surface, which minimizes friction and facilitates smooth functionality. This design proves particularly advantageous in environments where noise reduction is paramount, as cylindrical supports can achieve near-silent operation below 20 dB. Furthermore, sleeve supports are typically more economical than sphere supports, rendering them a cost-effective choice for engineers. They excel in unclean environments, often outlasting spherical supports as impurities settle harmlessly within the bronze material. However, they may face limitations regarding load capacity and speed, generally offering a lifespan of approximately 30,000 hours.
Conversely, spherical elements feature a series of spheres positioned between two tracks, significantly reducing friction and enhancing load capacity. The rolling motion of the spheres diminishes wear and heat generation, making them suitable for high-speed applications, with lifespans frequently exceeding 50,000 hours and capable of reaching over 100,000 hours in premium variants. This characteristic renders spherical rollers particularly well-suited for environments that demand high reliability and performance.
Understanding these fundamental is essential for selecting the appropriate type of support for specific engineering needs. For instance, shaft supports are optimal in situations involving frequent starts and stops, as they do not suffer from false brinelling damage, while sphere supports are preferred in high-speed precision applications. Practical applications of journal supports are evident in various electronic devices, such as low-speed exhaust fans and ventilation systems, where their quieter operation and cost efficiency make them a favored choice for residential and office machinery. As engineers assess their options, the decision regarding ball bearing vs sleeve bearing should consider speed requirements, load characteristics, noise limitations, and maintenance capabilities.
Compare Performance Metrics: Efficiency, Noise, and Lifespan
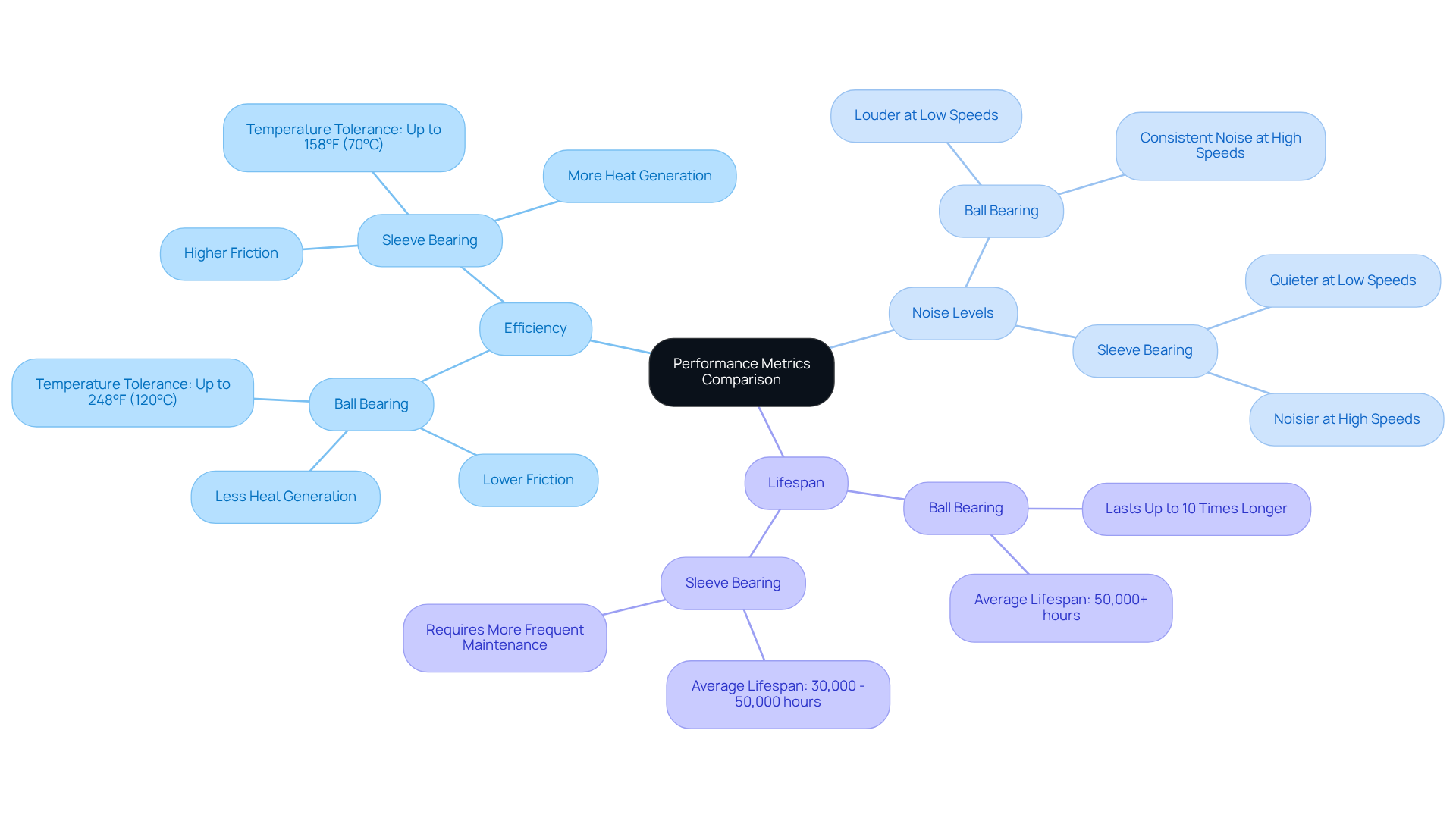
In terms of efficiency, the comparison of ball bearing vs sleeve bearing indicates that ball components generally outperform cylindrical supports due to their lower frictional resistance, which leads to reduced energy consumption and heat generation. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in electronic applications, where effective thermal management is crucial.
Regarding noise levels, cylindrical supports operate more quietly at lower speeds; however, as speed increases, they can become significantly noisier because of heightened friction. For instance, tubular supports are known to generate more noise at elevated velocities, while spherical supports, although typically louder at lower speeds, maintain a consistent noise level at higher speeds due to their rolling motion that minimizes friction.
Lifespan is another critical factor; under optimal conditions, spherical rollers can last up to ten times longer than cylindrical supports, which is an important aspect in the debate of ball bearing vs sleeve bearing, as noted by the University of Michigan. In contrast, when considering ball bearing vs sleeve bearing, journal supports typically last between 30,000 and 50,000 hours on average and may necessitate more frequent maintenance and replacement, especially in high-load scenarios, making them less suitable for demanding applications.
Furthermore, spherical rollers can withstand temperatures as high as 248°F (120°C) or more, whereas cylindrical supports function efficiently only up to approximately 158°F (70°C). This temperature tolerance further underscores the for high-performance applications.
Evaluate Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Considerations
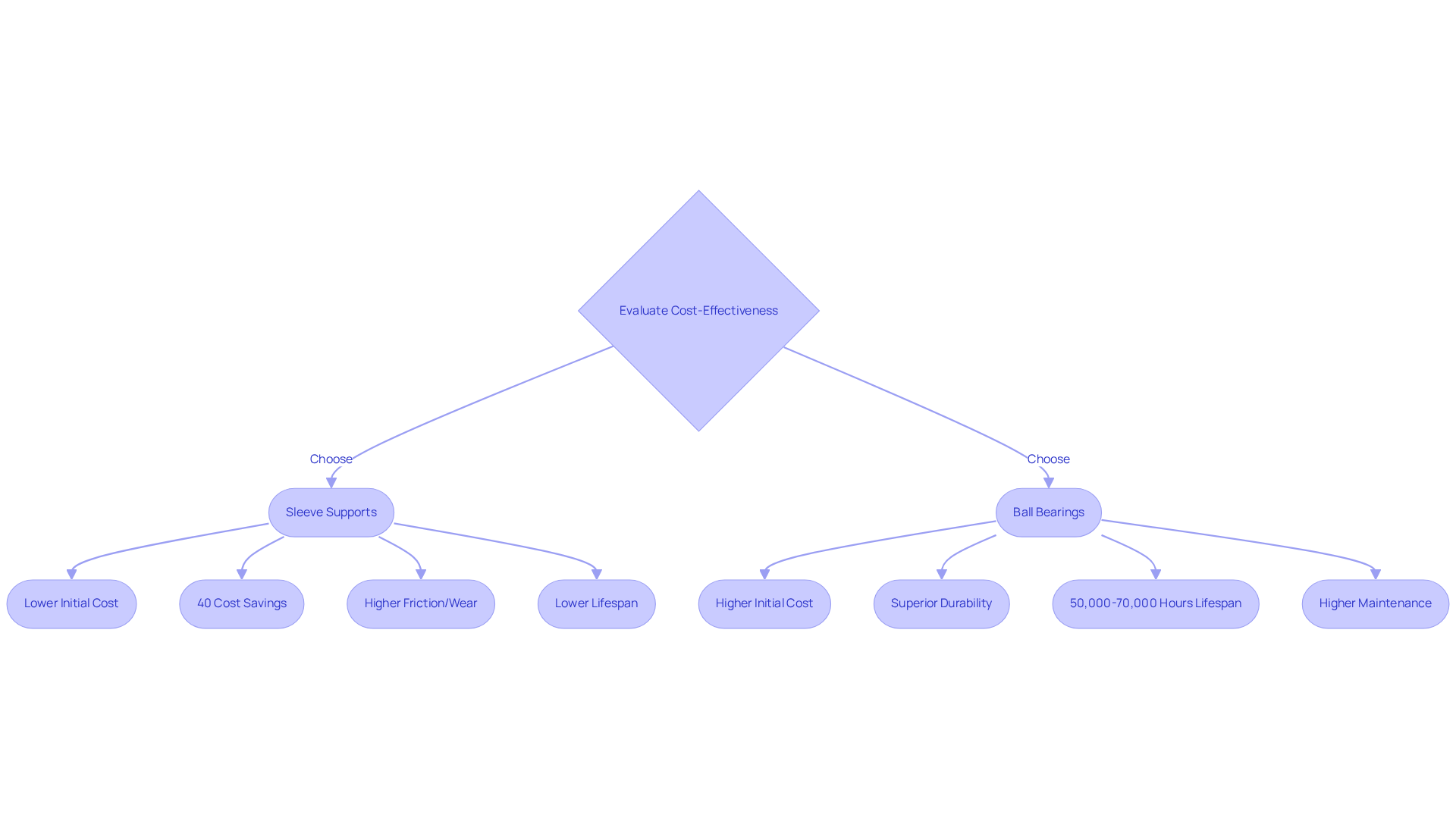
When assessing the cost-effectiveness of sleeve supports in the context of ball bearing vs sleeve bearing, initial investment plays a significant role. Sleeve supports typically carry a lower price tag, making them appealing for budget-conscious projects. They can reduce expenses by 40% compared to roller components, contributing to their initial cost-efficiency. However, it is crucial to consider the long-term financial implications of using ball bearing vs sleeve bearing. While sleeve supports may save money initially, their can lead to increased maintenance and replacement costs over time. Sleeve supports are frequently utilized for low-speed applications due to their lower upkeep requirements compared to other support types, which can be advantageous in specific projects.
In contrast, spherical components, despite their higher initial cost, often deliver superior durability and efficiency, resulting in reduced operational expenses and minimized downtime. For instance, dual roller fans can endure between 50,000 to 70,000 hours at 40°C, significantly surpassing the 10,000 to 20,000 hours lifespan of typical bushing fans. Financial analysts frequently emphasize that while some components may appear economical at first glance, the total value of spherical alternatives, particularly in the discussion of ball bearing vs sleeve bearing, becomes evident in scenarios demanding high performance and durability. Furthermore, ball rollers are more susceptible to contamination, complicating their maintenance compared to sleeve rollers. Therefore, careful consideration of both upfront costs and long-term maintenance expenses is essential for making informed selection decisions.
Application Suitability: When to Choose Each Bearing Type
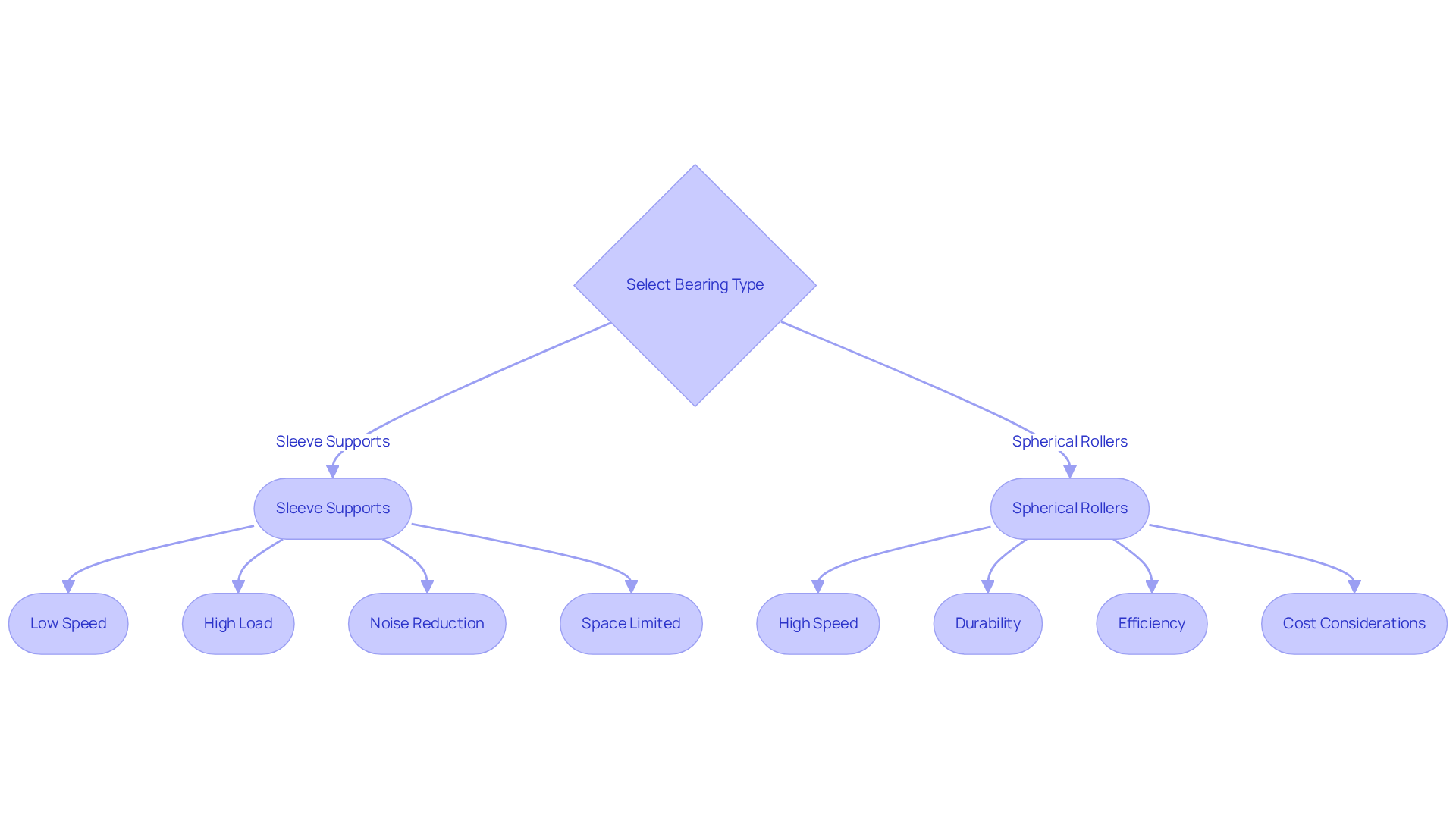
Selecting the appropriate type of support hinges on the specific application requirements. Sleeve supports are often favored in low-speed, high-load scenarios where noise reduction is paramount, such as in fans and pumps. Their straightforward design facilitates compact configurations, making them particularly suitable for space-limited environments. In consumer electronics, for instance, sleeve supports provide silent operation, which is vital for user comfort. They typically operate 10-15 decibels quieter than comparable components, making them ideal for low-noise applications.
Conversely, spherical rollers excel in high-speed applications, including engines and robotics, where efficiency and durability are critical. These supports can handle speeds exceeding 30,000 RPM, significantly outpacing traditional supports that max out around 3,000 RPM. This capability is crucial in industrial machinery, where spherical elements play a fundamental role in the operation of conveyors, pumps, and gear systems. A case study on fan durability indicates that roller fans can last up to 50% longer than bushing fans in moderate temperature conditions, establishing them as the preferred choice for high-temperature environments.
Cost considerations also significantly influence the selection process. While cylindrical supports are generally less expensive upfront, spherical rollers provide due to their enhanced durability and reliability. Engineers frequently emphasize the importance of selecting components tailored to specific applications. As industry experts assert, the decision should factor in elements such as load type, speed, and environmental conditions. For example, although journal supports excel in low-speed, high-load situations, the comparison of ball bearing vs sleeve bearing shows that spherical rollers are more suitable for high-speed, high-load conditions, ensuring optimal efficiency and reliability. Additionally, it is noteworthy that ball fans can be installed in any orientation without affecting their lifespan, whereas sleeve fans function best when installed vertically.
Ultimately, the decision must align with the operational demands and budgetary constraints of the project, ensuring that the selected component meets both performance and cost-effectiveness standards. As Jenny Wang, an industry expert, remarked, “Your accurate description of where each bearing type excels will undoubtedly help engineers avoid common pitfalls.
Conclusion
Selecting between ball bearings and sleeve bearings necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their distinct characteristics and performance metrics. Sleeve bearings provide cost-effective solutions with quieter operation in low-speed applications, while ball bearings excel in high-speed, high-load scenarios due to their superior efficiency and longevity. The right choice is contingent upon specific project requirements, necessitating a careful balance between initial costs and long-term performance and maintenance considerations.
Key differentiators such as efficiency, noise levels, lifespan, and application suitability are critical in this decision-making process. Ball bearings typically offer lower friction and extended lifespans, rendering them ideal for demanding environments. In contrast, sleeve bearings are particularly effective in quieter, less intensive applications. By grasping these nuances, engineers can make informed decisions that align with operational demands and budget constraints.
Ultimately, the decision between ball bearings and sleeve bearings should be guided by a thorough evaluation of performance needs and cost implications. As technology continues to advance, remaining informed about the latest trends in bearing efficiency and cost-effectiveness will be essential for optimizing engineering solutions. Choosing the right bearing type not only influences immediate project outcomes but also plays a pivotal role in ensuring long-term operational success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are sleeve bearings and how do they operate?
Sleeve bearings, also known as plain supports, consist of a cylindrical casing that encases a rotating shaft. They operate by maintaining a thin layer of lubricant between the shaft and the surface, which minimizes friction and ensures smooth functionality.
What are the advantages of sleeve bearings?
Sleeve bearings are advantageous in environments requiring noise reduction, achieving near-silent operation below 20 dB. They are also more economical than spherical supports and excel in unclean environments, often outlasting spherical supports as impurities settle within the bronze material.
What are the limitations of sleeve bearings?
Sleeve bearings may have limitations regarding load capacity and speed, generally offering a lifespan of approximately 30,000 hours.
How do spherical bearings differ from sleeve bearings?
Spherical bearings feature a series of spheres positioned between two tracks, which significantly reduces friction and enhances load capacity. They are suitable for high-speed applications and can have lifespans exceeding 50,000 hours, with premium variants reaching over 100,000 hours.
In what applications are sleeve bearings typically used?
Sleeve bearings are commonly used in low-speed applications such as exhaust fans and ventilation systems, where their quieter operation and cost efficiency are beneficial for residential and office machinery.
When should engineers choose sleeve bearings over spherical bearings?
Engineers should choose sleeve bearings for applications involving frequent starts and stops, as they do not suffer from false brinelling damage. Spherical bearings are preferred for high-speed precision applications.
What factors should be considered when selecting between ball bearings and sleeve bearings?
When selecting between ball bearings and sleeve bearings, engineers should consider speed requirements, load characteristics, noise limitations, and maintenance capabilities.

