Overview
This article delves into the essential types of fans utilized in electronics engineering, underscoring their pivotal role in thermal management and system performance. Fans, including centrifugal and axial models, are indispensable for dissipating heat and ensuring optimal operating conditions. Key considerations such as airflow, efficiency, and noise levels are critical when selecting the appropriate fan for specific applications. Understanding these factors is vital for engineers aiming to enhance system reliability and performance.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of fans in electronics engineering underscores their pivotal role in maintaining optimal performance and reliability across various devices. As electronic systems evolve in complexity, the demand for efficient cooling solutions is surging, with market projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. However, engineers encounter the challenge of selecting the appropriate fan type—ranging from centrifugal to axial—to meet specific thermal management needs. Key factors must be considered to ensure that the chosen fan not only enhances performance but also aligns with energy efficiency and operational requirements.
Define Fans: Understanding Their Role in Electronics Engineering
In electronics engineering, fans serve as essential mechanical devices designed to produce airflow and regulate temperature within components and systems. Their primary function is to dissipate heat generated by electronic devices, a critical factor in preventing overheating and ensuring reliability. Effective thermal management is paramount for the performance and longevity of various applications, including computers, telecommunications equipment, and industrial machinery.
For instance, the electric cooling devices market was valued at approximately USD 8.125 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 16.75 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 6.5% from 2025 to 2033. This growth underscores the increasing demand for driven by the proliferation of digital devices and the necessity for advanced thermal management.
Moreover, the integration of intelligent technologies in ventilation systems, such as real-time monitoring capabilities, is becoming increasingly significant as industries prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability. The importance of airflow in electronic devices cannot be overstated; it is crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions and enhancing the overall performance of electronic systems.
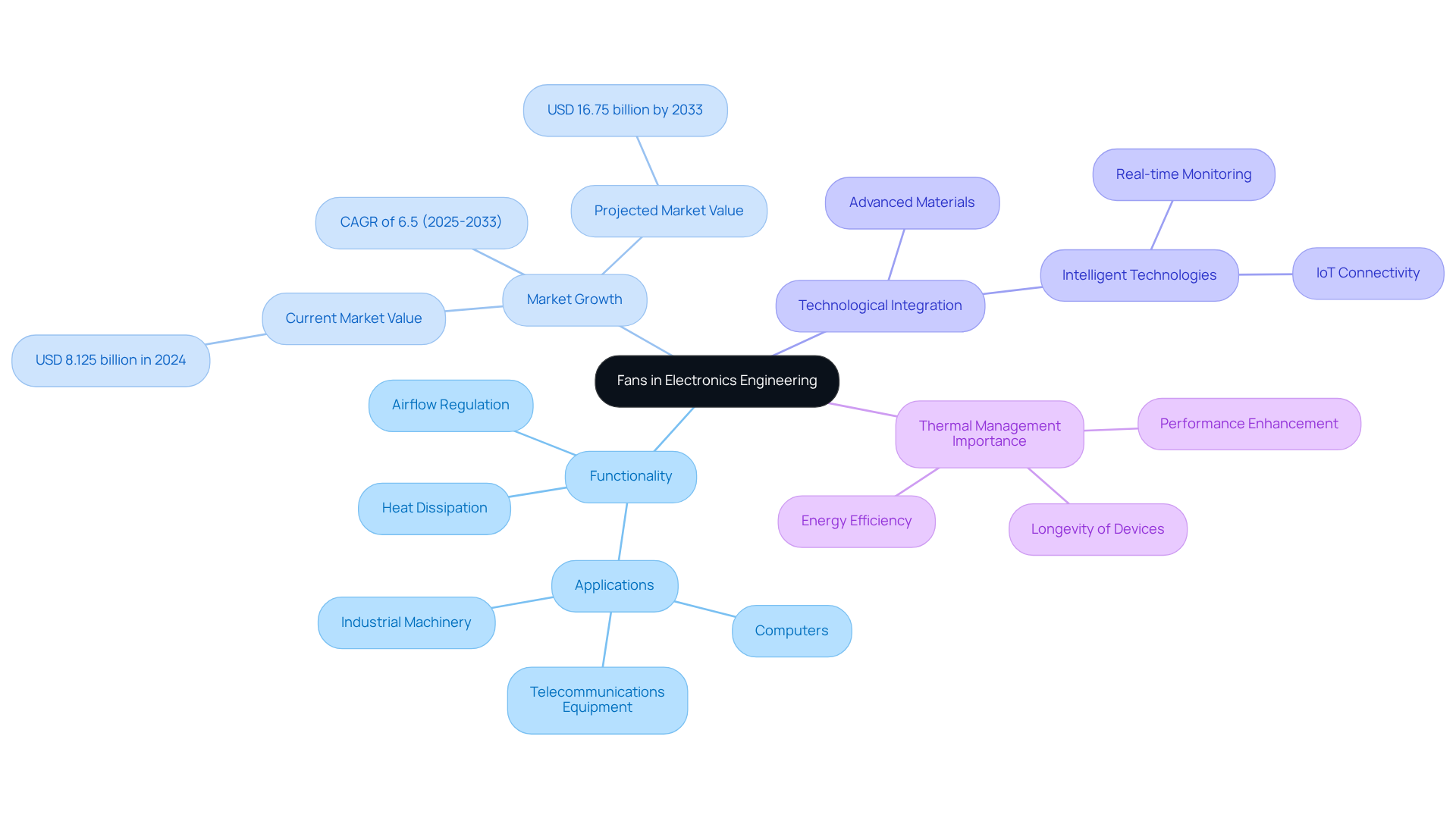
Explore Different Types of Fans: Centrifugal, Axial, and More
Supporters can be categorized into different kinds of fans, primarily featuring . Gagner-Toomey Associates, recognized as the world’s largest manufacturer of standard and custom air-movers, presents an extensive product line optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise.
Centrifugal blowers, commonly known as blowers, utilize a rotating impeller to draw air into the device and expel it at a right angle, rendering them ideal for high-pressure applications. Gagner-Toomey’s centrifugal blowers are available in sizes ranging from 15 to 225mm, effectively addressing diverse industrial requirements.
In contrast, axial blowers direct air parallel to the unit’s axis, typically employed for cooling applications where substantial air movement is essential at reduced pressures. Gagner-Toomey provides a comprehensive selection of DC input tube axial devices, with dimensions spanning from 15 to 280mm, aptly suited for electronics and automotive applications.
Furthermore, different kinds of fans include:
- Mixed-flow fans, which integrate features of both centrifugal and axial fans
- Blower fans designed for specific applications necessitating directed air movement
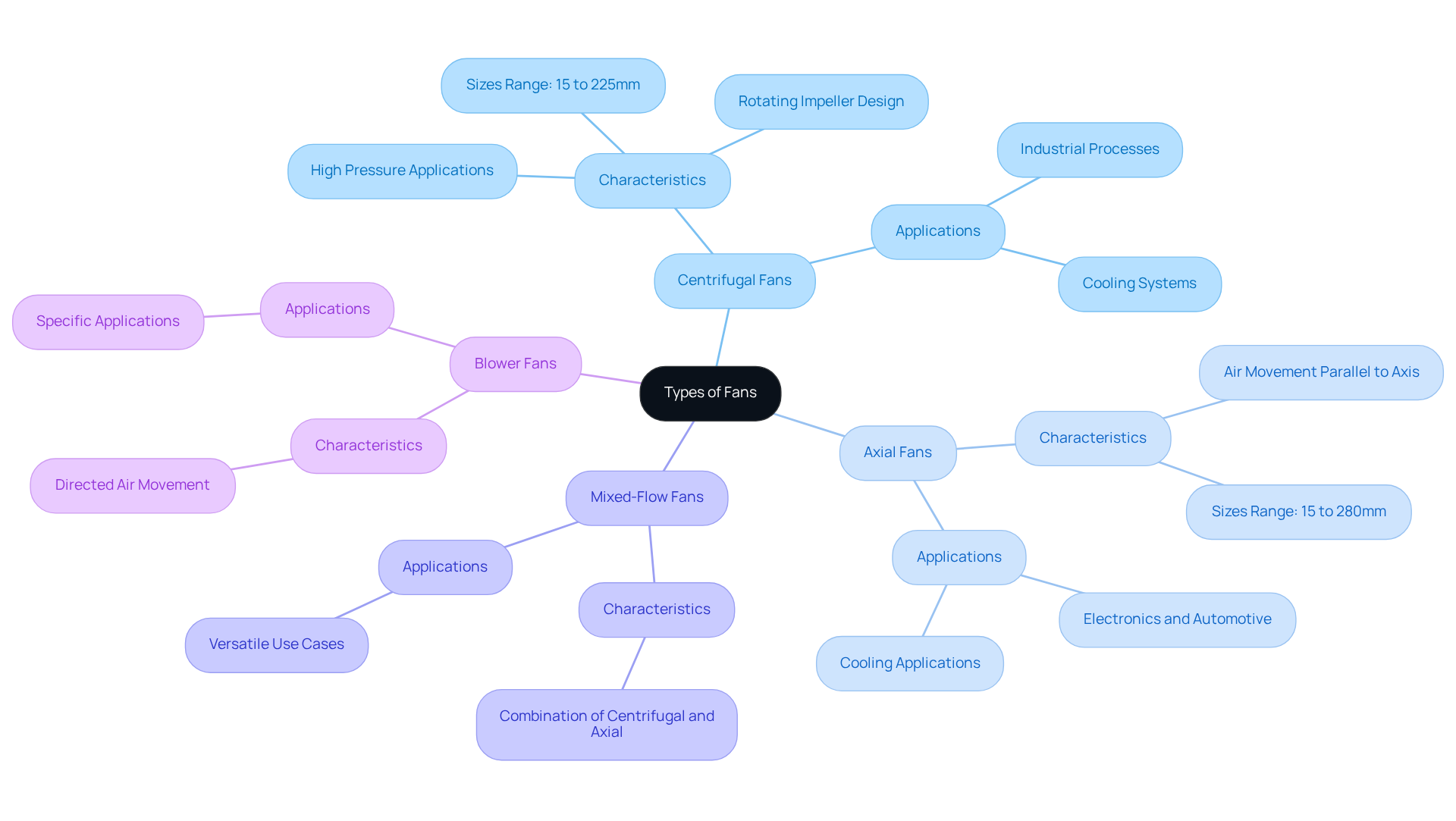
Analyze Fan Characteristics: Performance, Efficiency, and Suitability
Selecting the right fan for electronic applications requires a careful evaluation of different kinds of fans, focusing on several critical features: airflow, static pressure, efficiency, and noise levels.
- Airflow, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), indicates the volume of air a fan can move, which is vital for effective cooling and ventilation. For example, a warehouse measuring 25′ L x 50′ W x 75′ H necessitates between 14,000 to 15,000 CFM for optimal air circulation, whereas a garage of dimensions 25′ L x 30′ W x 20′ H requires at least 2,358 CFM. This illustrates the necessity of aligning fan capacity with room dimensions.
- Static pressure, defined as the resistance a fan must overcome in the airstream path, is especially pertinent in systems that involve ductwork. Understanding is essential for selecting devices capable of maintaining adequate airflow in complex configurations, thereby ensuring effective operation.
- Efficiency is paramount for reducing energy consumption, particularly in scenarios where multiple devices are in use. Research shows that facilities that incorporate blowers alongside air conditioning can reduce AC usage by up to 30%, leading to significant long-term savings. This efficiency is further enhanced by modern devices, which frequently feature high-efficiency motors designed for quiet operation and lower energy use.
- Noise levels are also a significant consideration in fan selection, particularly in environments sensitive to sound, such as consumer electronics or office spaces. For instance, a logistics center that transitioned to whisper-quiet fan models reported enhancements in airflow and a reduction in background noise, thereby improving communication and employee satisfaction.
In conclusion, understanding these characteristics—airflow, static pressure, efficiency, and noise levels—enables engineers to select different kinds of fans that not only meet performance criteria but also enhance energy efficiency and user comfort in electronic applications.
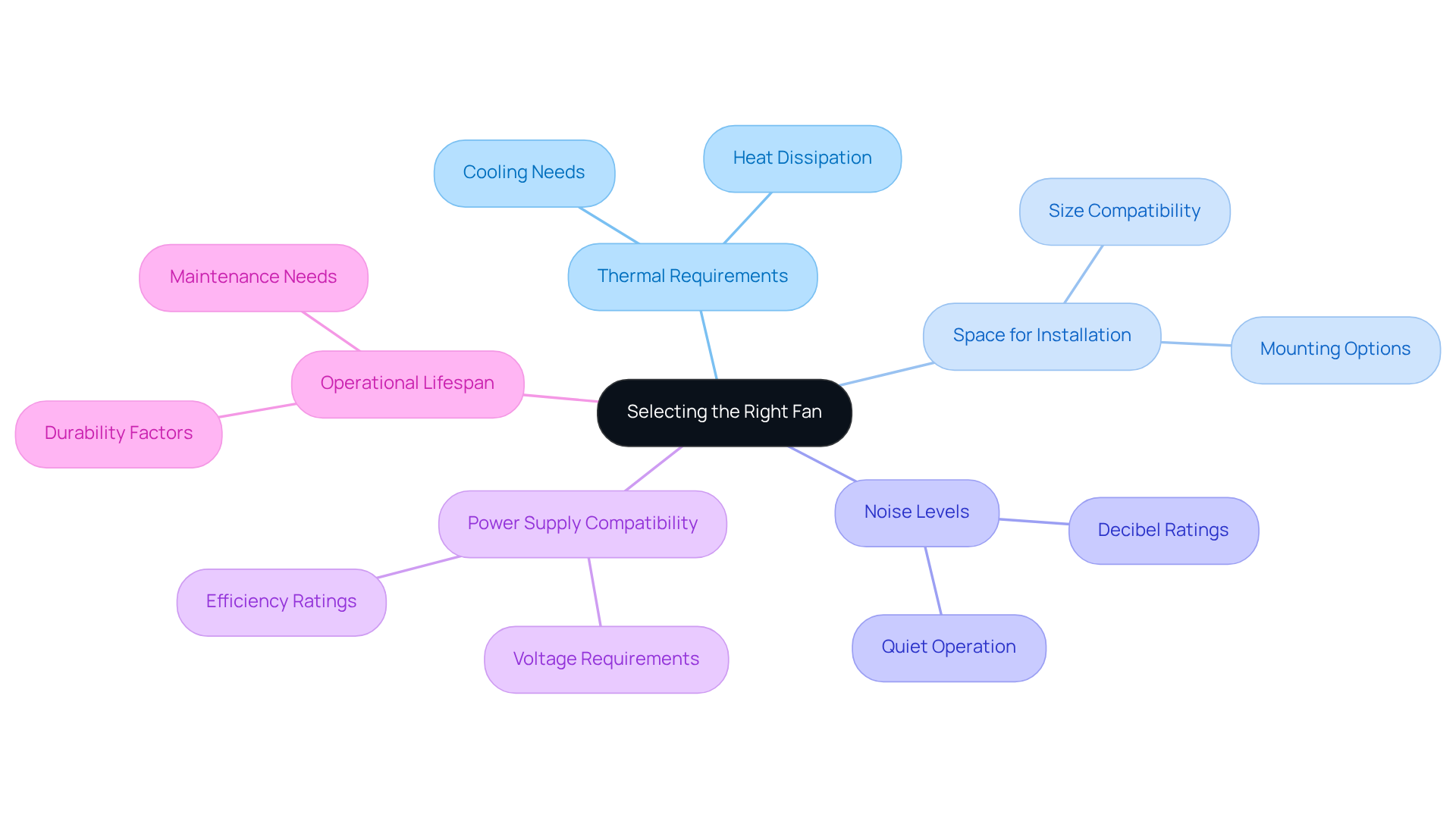
Select the Right Fan: Considerations for Electronics Engineering Applications
Selecting the right for an electronics engineering project is a critical undertaking that requires careful consideration. Engineers must thoroughly assess the thermal requirements of the system, evaluate the available space for fan installation, and determine the acceptable noise levels. Furthermore, compatibility with power supply specifications and the fan’s operational lifespan are essential factors that cannot be overlooked.
For example, in high-performance computing environments:
- High static pressure fans are often necessary to ensure effective cooling.
- Conversely, quieter axial fans are typically favored in consumer electronics.
By understanding the specific needs of the application, engineers can make informed decisions regarding different kinds of fans to ultimately enhance system performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the various kinds of fans in electronics engineering is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability of electronic systems. Fans play a pivotal role in managing heat and maintaining airflow, directly influencing the longevity and efficiency of devices. Recognizing the importance of these mechanical devices empowers engineers to make informed decisions that enhance system performance and energy efficiency.
This article highlights the different types of fans, including centrifugal and axial models, each with unique applications and characteristics. Key factors such as airflow, static pressure, efficiency, and noise levels are vital considerations when selecting the appropriate fan for specific electronic applications. By understanding these parameters, engineers can tailor solutions that meet both performance requirements and user comfort.
Ultimately, the significance of fans in electronics engineering cannot be overstated. As technology advances and the demand for efficient cooling solutions grows, prioritizing the selection of the right fan becomes imperative. By embracing the insights shared in this article, engineers can contribute to the development of more reliable, efficient, and sustainable electronic systems, ensuring that they meet the ever-evolving needs of the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of fans in electronics engineering?
The primary function of fans in electronics engineering is to produce airflow and regulate temperature within components and systems, helping to dissipate heat generated by electronic devices.
Why is thermal management important in electronic devices?
Thermal management is important because it prevents overheating and ensures the reliability and longevity of various applications, including computers, telecommunications equipment, and industrial machinery.
What is the projected growth of the electric cooling devices market from 2024 to 2033?
The electric cooling devices market was valued at approximately USD 8.125 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 16.75 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 6.5% from 2025 to 2033.
What factors are driving the demand for efficient cooling solutions?
The demand for efficient cooling solutions is driven by the proliferation of digital devices and the necessity for advanced thermal management.
How are intelligent technologies impacting ventilation systems in industries?
Intelligent technologies are becoming increasingly significant in ventilation systems due to their real-time monitoring capabilities, which help industries prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability.
What is the significance of airflow in electronic devices?
Airflow is crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions and enhancing the overall performance of electronic systems.