Overview
Centrifugal fans are engineered for high-pressure applications, adeptly moving air against resistance. In contrast, axial fans are optimized for low-pressure environments, effectively managing substantial volumes of air. This article elucidates the operational mechanisms, performance metrics, and appropriate applications for each fan type, underscoring their unique advantages across various industrial and ventilation contexts.
Introduction
Centrifugal and axial fans serve essential functions in a range of industrial and commercial applications, each presenting distinct advantages tailored to meet specific requirements. Recognizing the differences between these two fan types is crucial for optimizing efficiency and performance in ventilation systems, cooling solutions, and beyond.
As technologies evolve and demands for energy efficiency escalate, engineers and designers face the challenge of selecting the appropriate fan for their unique applications.
This exploration examines the performance metrics, operational principles, and ideal use cases for centrifugal and axial fans, offering vital insights for informed decision-making.
Understand Centrifugal and Axial Fans
Centrifugal blowers, often referred to as radial blowers, leverage centrifugal force to transport air or gases with remarkable efficiency. By drawing air into the center of the fan and expelling it at a right angle through an outlet, these blowers are particularly effective in high-pressure applications. This design allows centrifugal blowers to generate significant static pressure, which is vital in environments such as pneumatic conveying and dust collection systems.
Conversely, axial blowers function by moving air parallel to the device’s axis. They intake air and discharge it in the same direction, enabling them to manage large volumes of air at lower pressures. This characteristic renders axial blowers ideal for ventilation and cooling applications across various sectors, including HVAC systems and expansive areas like cooling towers.
Recent advancements in ventilation technology have birthed IP55-rated centrifugal devices, which offer enhanced protection against moisture and temperature fluctuations. These devices are increasingly employed in cold storage and refrigeration units, ensuring reliable airflow while reducing the risks of condensation. Moreover, the growing demand for energy-efficient solutions has spurred manufacturers to innovate, resulting in devices that not only meet but exceed regulatory efficiency standards.
Engineers have recognized the distinct advantages of [centrifugal vs axial fan](https://gagner-toomey.com/10-key-insights-on-axial-vs-centrifugal-fan-performance) types for various specific applications. For instance, when discussing centrifugal vs axial fan options, centrifugal blowers are preferred in scenarios requiring high-pressure airflow, while axial units excel in low-resistance environments where substantial air volumes are necessary. Understanding the is crucial for optimizing performance across diverse settings, ensuring the selection of the appropriate fan based on the specific airflow and pressure requirements of each application.
Explore How Centrifugal and Axial Fans Work
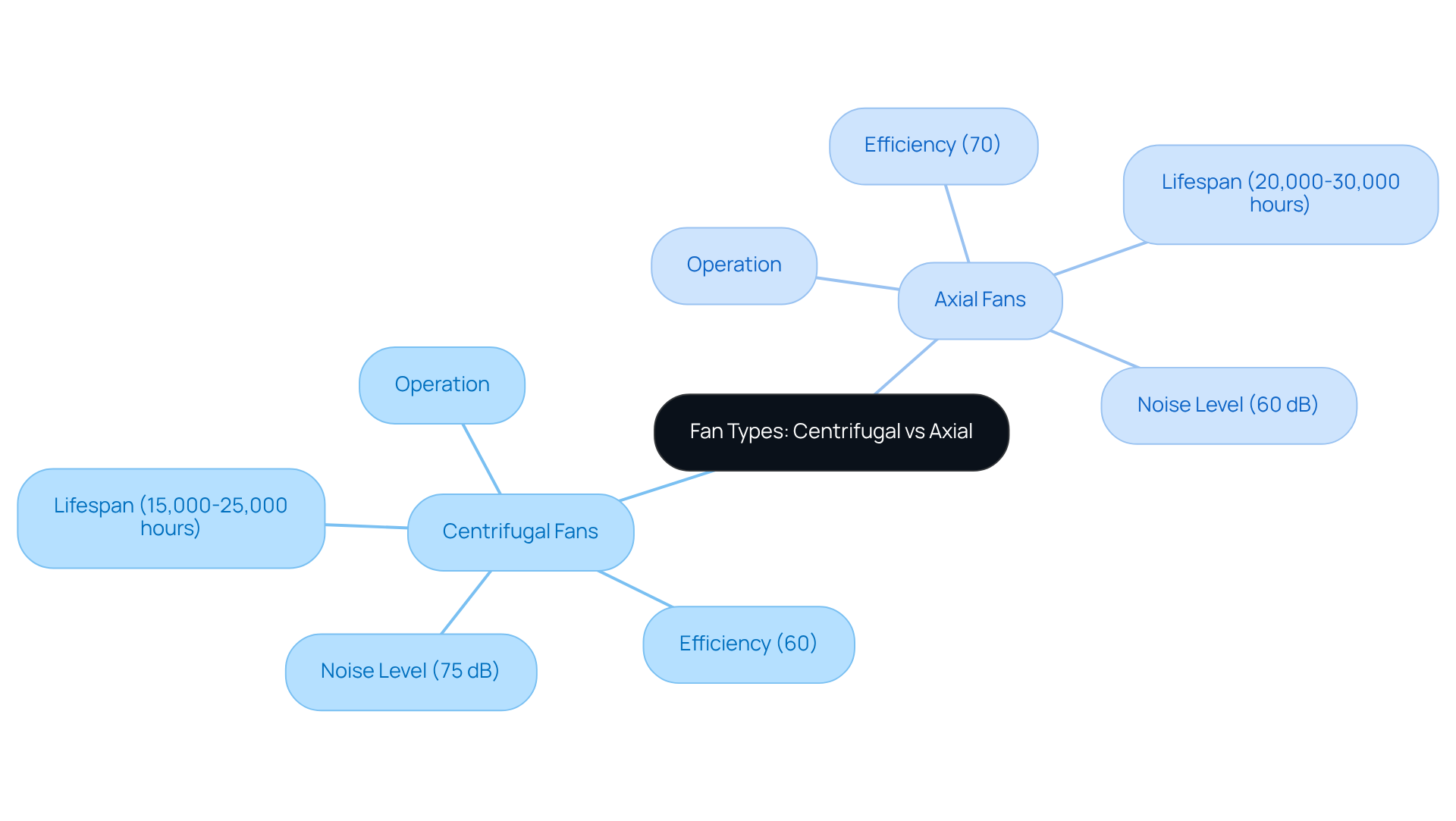
Centrifugal blowers are designed to efficiently pull air into their center through an inlet, illustrating the differences between centrifugal vs axial fan designs. The rotating impeller plays a crucial role by accelerating the air outward, which significantly increases its pressure as it exits through the fan housing. This innovative design enables centrifugal blowers to produce high static pressure, capable of reaching up to 10 inches of water gauge (inwg). Such capability makes them particularly effective in applications where airflow must overcome resistance, such as in duct systems.
In contrast, these blowers demonstrate the differences between centrifugal vs axial fan designs by utilizing blades that revolve around a central hub, generating a pressure difference that draws air in along the axis and releases it in the same direction. This mechanism proves highly efficient for , especially in open spaces where resistance is minimal. As of 2025, the efficiency ratings for centrifugal devices hover around 60%, while alternative types achieve approximately 70%. Notably, forward-curved blowers operate within an efficiency range of 60-70%, whereas backward-curved units can reach up to 90% efficiency.
Noise levels also present a significant consideration; centrifugal units can reach sound levels as high as 75 dB, while other types typically operate at around 60 dB. Furthermore, the projected lifespan of centrifugal units ranges from 15,000 to 25,000 hours, contrasting with 20,000 to 30,000 hours for other types. This difference in lifespan is a critical factor when evaluating long-term operational expenses.
Compare Performance Metrics: Airflow, Pressure, and Efficiency
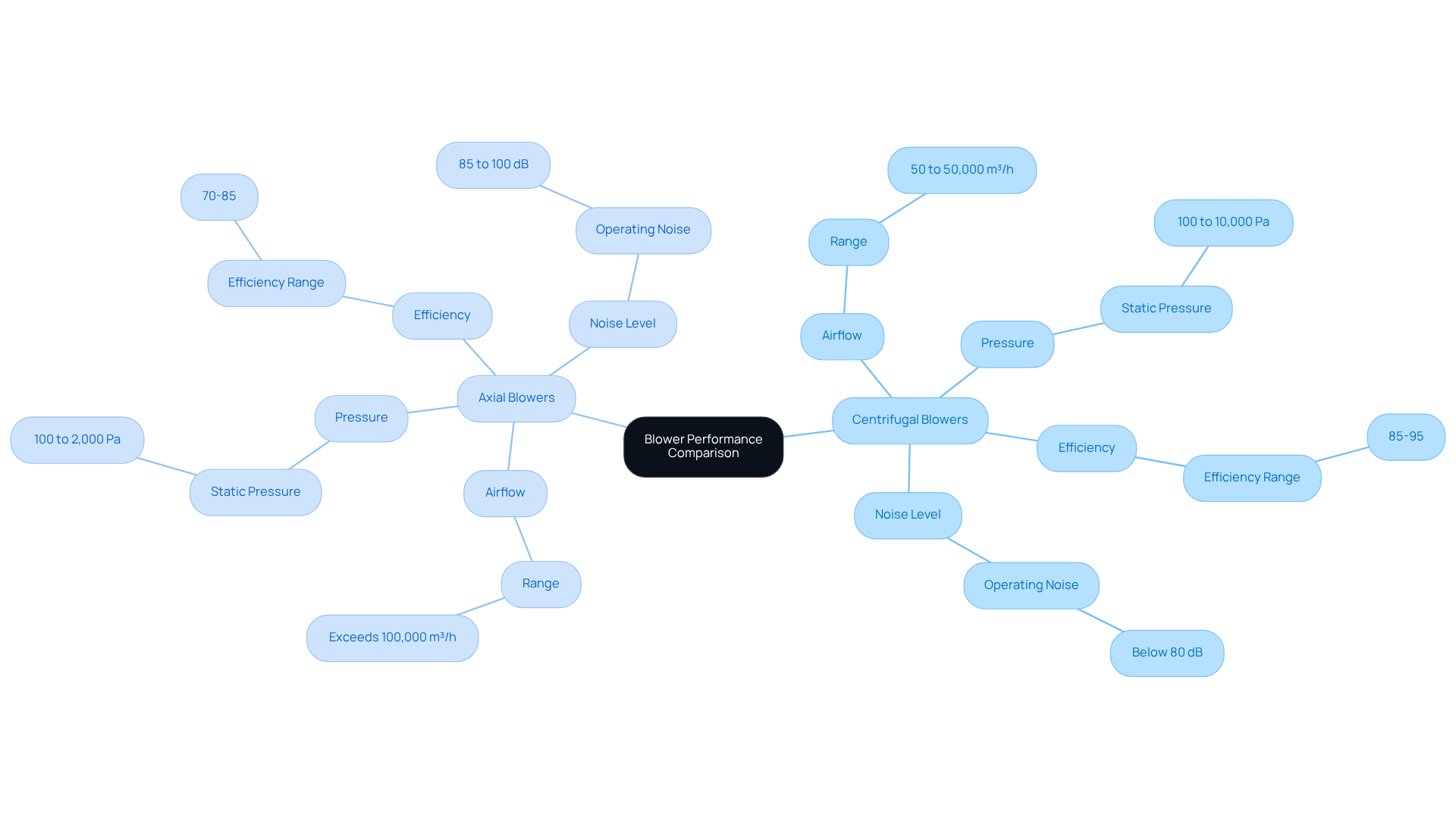
When evaluating airflow, centrifugal blowers typically provide ranging from 50 to 50,000 m³/h. In contrast, other blower types excel with high airflow rates, often exceeding 100,000 m³/h.
Regarding pressure, centrifugal blowers are capable of generating high static pressures, between 100 and 10,000 Pa, making them ideal for applications that require airflow against resistance, such as duct systems and industrial ventilation. Conversely, other blowers operate at lower pressures, generally between 100 and 2,000 Pa.
Efficiency metrics also differ significantly; centrifugal blowers can achieve efficiencies of 85-95%, while straight-flow units typically range from 70-85%. Furthermore, centrifugal blowers usually operate below 80 decibels, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments, whereas axial units produce noise levels between 85 and 100 decibels.
Centrifugal blowers are versatile for handling intricate materials and feature a robust design that enhances their efficiency in demanding settings. In contrast, axial blowers have a limited adjustment range of 50% to 100%, and excessive modifications can lead to performance issues.
This performance comparison highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each fan type across various operational contexts, thereby assisting engineers in selecting the most suitable solution for specific applications.
Assess Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Fan Type
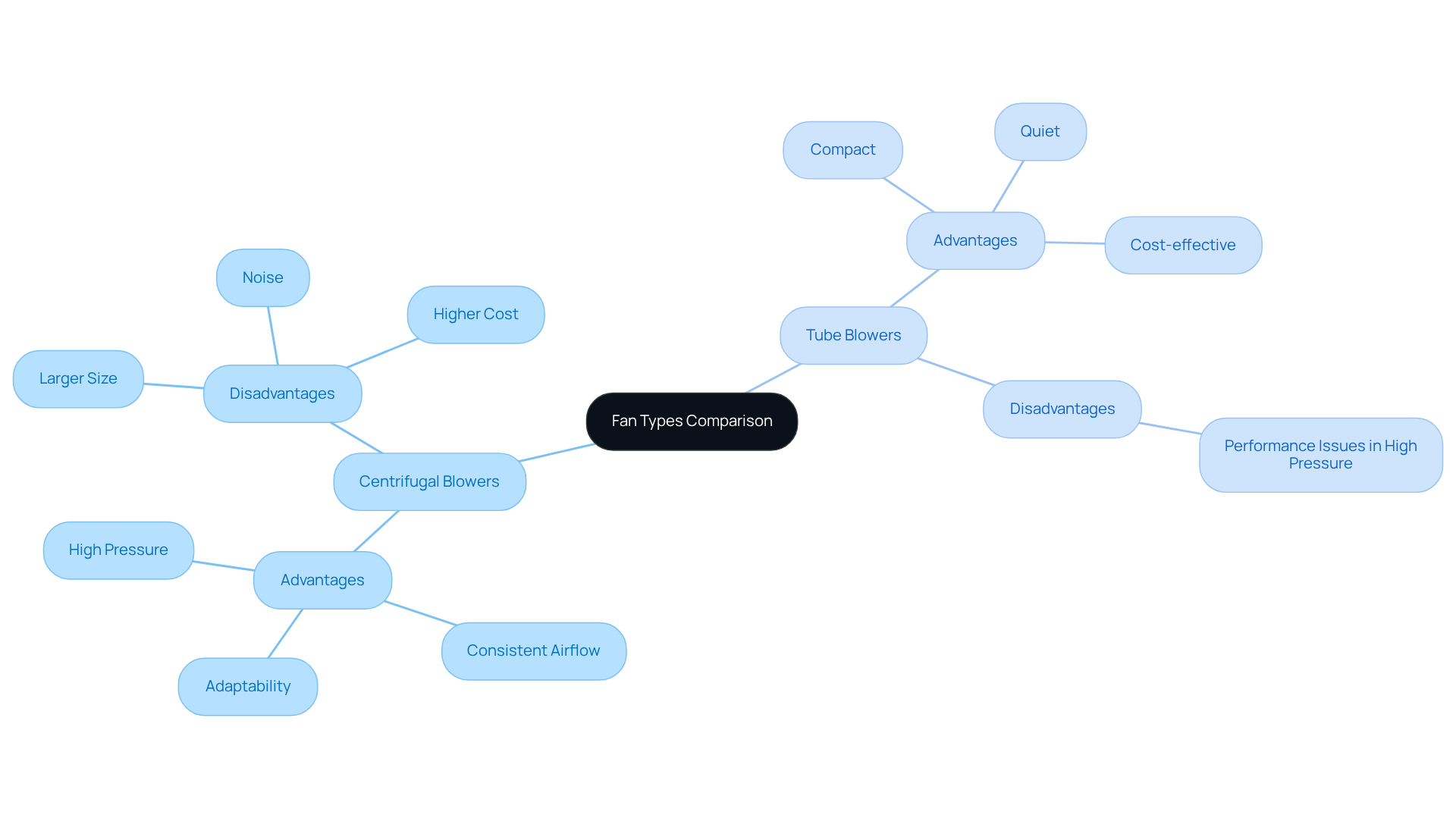
[Centrifugal blowers](https://gagner-toomey.com/10-essential-insights-on-electric-blower-fans-for-engineers) are distinguished by their high-pressure capabilities, providing consistent airflow and adaptability across diverse environments. They are particularly effective in applications requiring airflow through ducts or against resistance, making them essential in industrial settings.
For example, centrifugal blowers are frequently employed in laptops due to their low profile, which is vital for compact electronic designs. However, their larger dimensions, increased noise levels, and higher costs compared to similar devices can present challenges.
Conversely, tube blowers are typically more compact, quieter, and more cost-effective, making them suitable for high-volume, low-pressure applications such as cooling electronic devices. Their availability in virtually any size further emphasizes their versatility.
Despite these benefits, axial units encounter difficulties in high-pressure scenarios, where their performance may diminish, and they can generate significant noise at elevated speeds.
Centrifugal blowers are particularly well-suited for applications that demand moderate to high pressure, such as air conditioning systems and industrial ventilation. Understanding the is critical for engineers when selecting the appropriate fan type based on specific performance metrics and usage requirements.
Furthermore, it is important to recognize that centrifugal blowers generally exhibit greater efficiency at higher pressures, which is a key consideration for engineers. Insights from industry specialists underscore the importance of selecting the right fan according to specific needs and environmental conditions. A balanced comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of centrifugal vs axial fan types is essential for informed decision-making.
Identify Suitable Applications for Centrifugal and Axial Fans
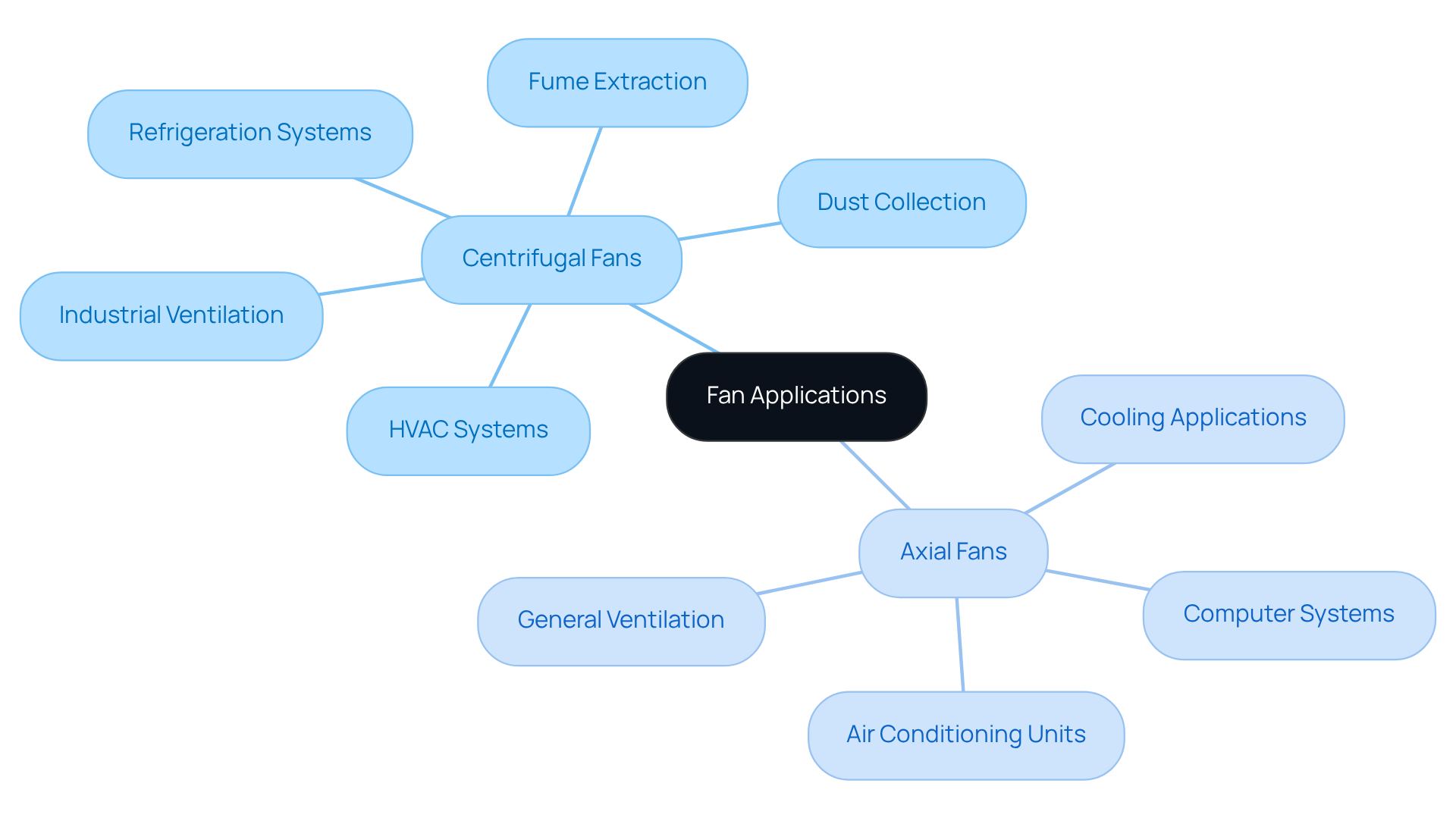
Centrifugal blowers serve a critical role in HVAC systems, industrial ventilation, and applications requiring high-pressure airflow, such as dust collection and fume extraction. Their importance extends to refrigeration systems, where . Conversely, axial fans excel in cooling applications, including computer systems, air conditioning units, and general ventilation, where the efficient movement of large air volumes is essential. Their design is particularly advantageous in open environments where spatial constraints are minimal. By understanding these distinct applications, engineers and designers can make informed decisions in selecting the appropriate fan type to meet their specific operational requirements.
Conclusion
Centrifugal and axial fans present distinct advantages tailored to specific applications, rendering them indispensable across various industries. A thorough understanding of their operational principles and performance metrics is crucial for selecting the appropriate fan type to optimize airflow and pressure requirements. Recognizing these differences is vital for enhancing efficiency and effectiveness in diverse settings.
This article explores the mechanics of centrifugal and axial fans, demonstrating how centrifugal blowers excel in high-pressure scenarios, while axial fans adeptly manage large volumes of air at lower pressures. The discussion highlights their respective efficiencies, noise levels, and suitable applications, offering a comprehensive overview that empowers engineers and designers to make informed decisions. By examining factors such as airflow rates, pressure capabilities, and operational costs, this comparison underscores the necessity of aligning fan selection with specific operational needs.
In conclusion, the insights presented reinforce the importance of understanding centrifugal versus axial fan dynamics in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape. As industries increasingly pursue energy-efficient solutions, making informed choices based on performance metrics and application requirements is essential. Embracing this knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to sustainable practices across various sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between centrifugal and axial fans?
Centrifugal fans, or blowers, move air using centrifugal force, drawing air into the center and expelling it at a right angle, making them effective in high-pressure applications. Axial fans move air parallel to their axis, taking in and discharging air in the same direction, which is ideal for managing large volumes of air at lower pressures.
In what applications are centrifugal fans typically used?
Centrifugal fans are particularly effective in high-pressure applications such as pneumatic conveying and dust collection systems.
What applications are best suited for axial fans?
Axial fans are ideal for ventilation and cooling applications, commonly used in HVAC systems and large areas like cooling towers.
What advancements have been made in centrifugal fan technology?
Recent advancements include the development of IP55-rated centrifugal devices, which offer enhanced protection against moisture and temperature fluctuations, making them suitable for cold storage and refrigeration units.
How do centrifugal and axial fans differ in terms of airflow and pressure?
Centrifugal fans are preferred for high-pressure airflow scenarios, while axial fans excel in low-resistance environments where large air volumes are needed.
What is the efficiency range for centrifugal and axial fans?
As of 2025, centrifugal fan efficiency is around 60%, while axial fans achieve approximately 70%. Forward-curved blowers operate within a 60-70% efficiency range, and backward-curved units can reach up to 90% efficiency.
How do noise levels compare between centrifugal and axial fans?
Centrifugal fans can reach sound levels as high as 75 dB, while axial fans typically operate at around 60 dB.
What is the expected lifespan of centrifugal and axial fans?
The projected lifespan of centrifugal fans ranges from 15,000 to 25,000 hours, whereas axial fans generally last between 20,000 to 30,000 hours.

