Overview
The article delineates four essential steps for engineers in selecting the appropriate cooling fan supplier. It underscores the significance of:
- Comprehending various fan types
- Evaluating product offerings
- Assessing supplier reliability
- Considering energy efficiency
Each step is bolstered by specific criteria, including:
- The necessity for customization
- Advancements in technology
- Adherence to industry standards
This structured approach ensures engineers can make informed decisions that not only meet their project requirements but also align with sustainability goals.
Introduction
Selecting the right cooling fan supplier is a critical task for engineers navigating the complexities of temperature regulation across various applications. An array of fan types is available, each designed for specific operational needs. Understanding the nuances of these options can significantly impact project success.
However, the challenge extends beyond merely identifying the appropriate fan type; it encompasses evaluating suppliers based on their product offerings, reliability, and commitment to energy efficiency.
How can engineers ensure they make informed choices that align with both performance requirements and sustainability goals?
Understand Different Types of Cooling Fans
Cooling fans are essential components in various applications, categorized into several types, each tailored for specific needs:
- Axial Blowers: These devices move air parallel to their axis, making them suitable for general cooling applications. Their effectiveness in low-pressure environments positions them as a popular option in electronic devices and data centers, where high airflow is critical for maintaining optimal temperatures.
- Centrifugal Blowers: Designed to draw air into the center and expel it at a right angle, centrifugal blowers excel in high-pressure applications. They are frequently employed in HVAC systems and industrial processes, where robust airflow management is essential to ensure system reliability and performance.
- Mixed-Flow Units: Combining the characteristics of both axial and centrifugal types, mixed-flow units offer versatility in managing a variety of pressures and airflow needs. This adaptability renders them suitable for various applications, including those that require both high efficiency and compact design.
- Cross-Flow Fans: These fans push air through a narrow channel, providing uniform airflow in compact spaces. Their design is particularly advantageous in scenarios where space is restricted, such as in consumer electronics and specialized temperature control systems.
Understanding these fan types is vital for engineers as they assess their provided by a cooling fan supplier. Factors such as airflow, pressure, and spatial constraints significantly influence the selection of the appropriate fan. The market for ventilation fans is evolving, with axial fans anticipated to maintain a substantial share due to their effectiveness and cost-efficiency, while centrifugal fans are preferred in high-pressure situations. As the demand for advanced temperature regulation solutions escalates, innovations in fan technology continue to enhance performance and energy efficiency across various sectors.
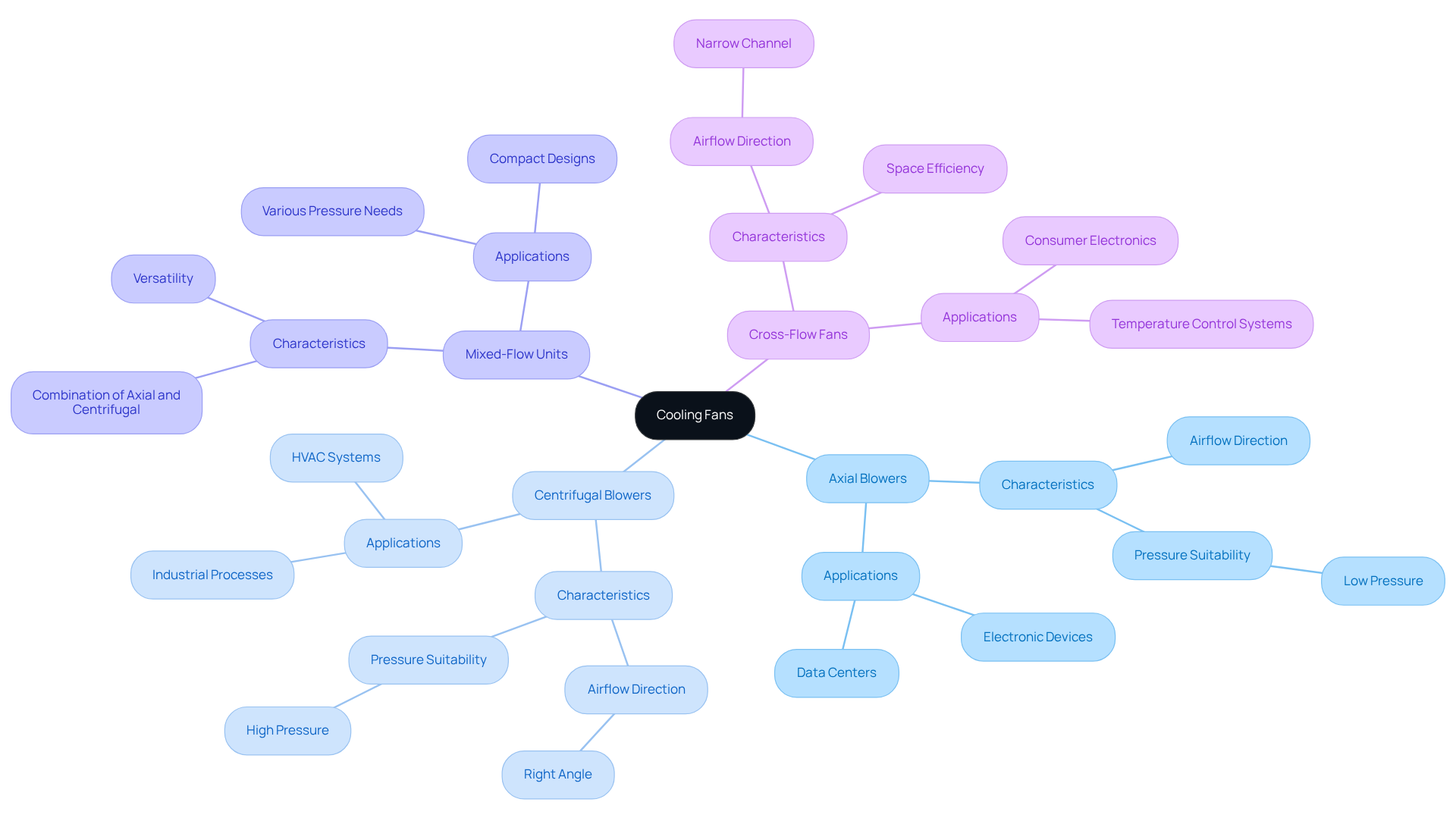
Evaluate Supplier Product Offerings and Capabilities
When assessing potential , engineers should focus on several key factors that will effectively guide their decision-making process.
- Product Range: Suppliers must provide a diverse selection of cooling fans, including axial, centrifugal, and mixed-flow options, to accommodate various applications. A broad product range is essential for ensuring that engineers can find the right solution for their specific needs.
- Customization Options: It is crucial to determine whether the provider offers customization capabilities to meet specific engineering requirements, such as tailored sizes, airflow specifications, and noise reduction features. This flexibility is vital, as contemporary applications frequently necessitate distinctive solutions that enhance performance and effectiveness.
- Technological Advancements: Suppliers that integrate cutting-edge technologies into their products should be prioritized. Innovations like energy-saving motors and intelligent control systems are increasingly significant, improving operational performance and decreasing energy use. This aligns with the industry’s movement toward sustainability. Notably, the integration of IoT and AI technologies is transforming operations and enhancing efficiency in fan applications.
- Certifications: Ensure that the products comply with relevant industry standards and certifications. This compliance serves as a strong indicator of reliability and performance, which is essential for maintaining operational stability in demanding environments.
- Case Studies: Examining case studies or testimonials from prior clients can provide valuable insights into the provider’s capability to deliver effective and tailored solutions. Successful implementations in similar applications can serve as a benchmark for evaluating potential partnerships. Highlighting particular instances of tailored fan solutions can further demonstrate the provider’s capabilities.
By concentrating on these elements, engineers can make informed choices when selecting a cooling fan supplier. This approach ensures they choose partners capable of meeting their specific needs and contributing to the success of their projects.
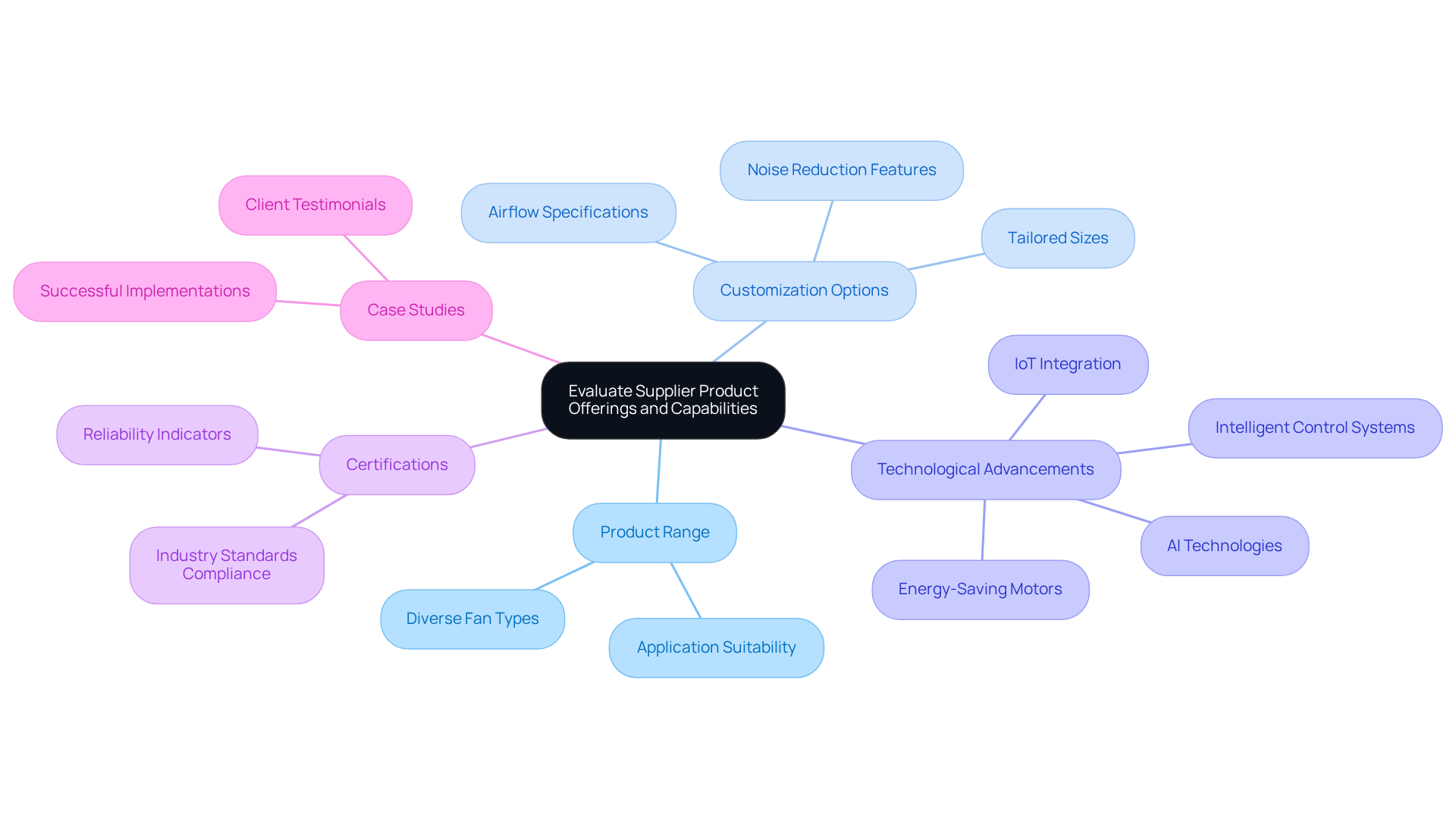
Assess Supplier Reliability and Customer Support
To evaluate the reliability and customer support of potential cooling fan suppliers, consider the following key factors:
- Reputation: Investigate the provider’s standing within the industry by examining reviews, ratings, and feedback from fellow engineers and companies. A strong reputation often correlates with consistent quality and service.
- Response Time: Evaluate the provider’s responsiveness to inquiries and requests for information. Industry benchmarks indicate that providers should aim for a first response time of under one hour for emails and 15 minutes for social media messages. Notably, 90% of customers expect an immediate response to inquiries, underscoring the urgency of prompt customer support. A quick response is indicative of effective customer service and commitment to client needs.
- Technical Support: Confirm that the vendor provides comprehensive technical support, including installation guidance, troubleshooting assistance, and access to knowledgeable staff. Engineers often emphasize the importance of having reliable support to address complex issues swiftly. As one engineer noted, “Having a responsive support team can make all the difference when troubleshooting unexpected problems.”
- Warranty and Return Policies: Scrutinize the to gauge the provider’s dedication to product quality and customer satisfaction. Clear and fair policies can significantly enhance the purchasing experience and foster trust.
- Long-term Relationships: Prefer vendors that have developed long-term connections with their clients, as this frequently indicates reliability and trustworthiness. Engineers frequently cite the value of ongoing support and partnership with a cooling fan supplier in achieving successful project outcomes. For instance, a case study highlighted how a supplier’s consistent support led to a successful project completion, reinforcing the importance of strong supplier relationships.
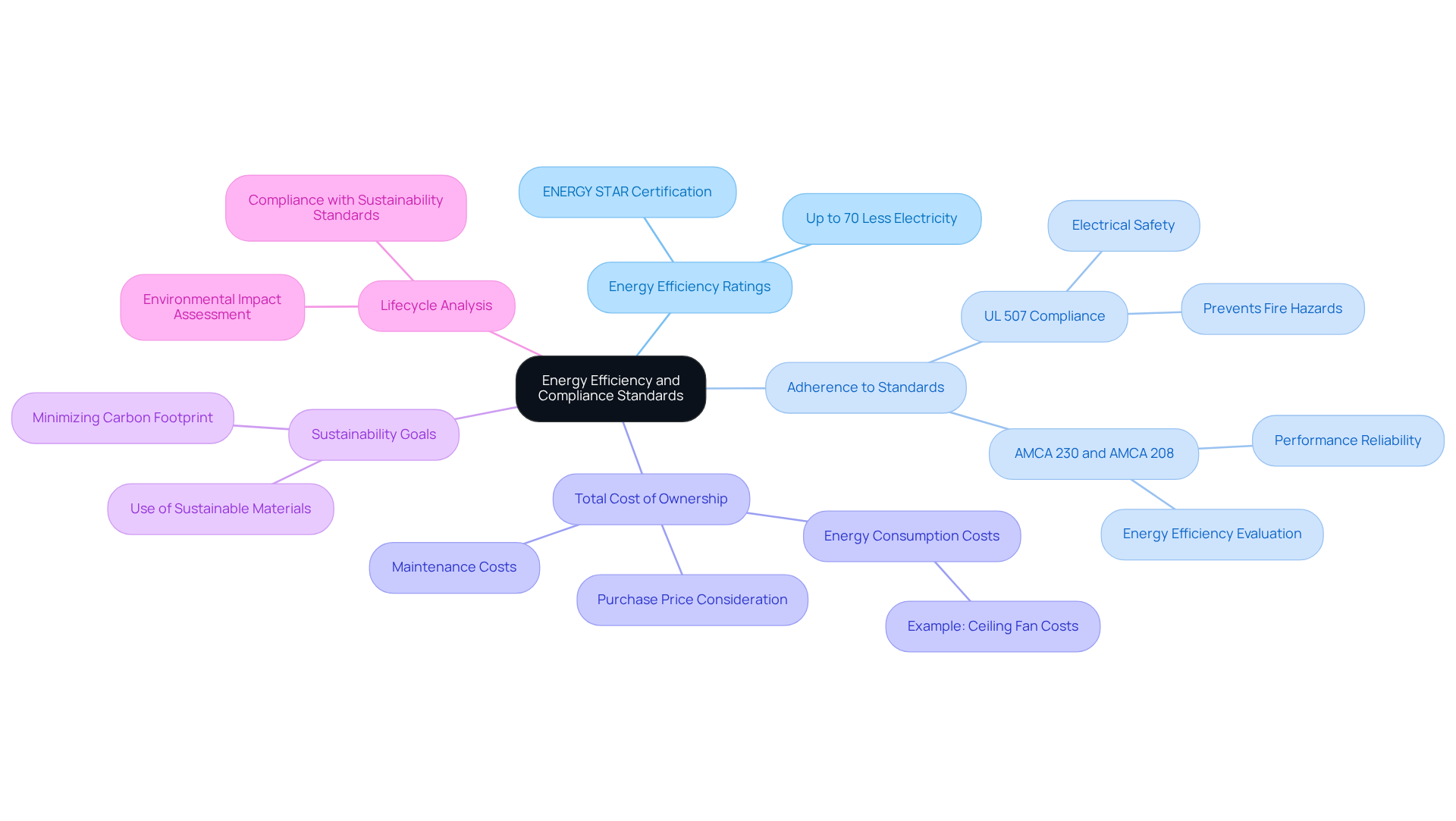
Consider Energy Efficiency and Compliance Standards
When evaluating energy efficiency and compliance standards for cooling fans, engineers should prioritize several key aspects:
- Energy Efficiency Ratings: Devices with high energy efficiency ratings should be sought, particularly those certified by ENERGY STAR. Such certifications not only signify reduced operational expenses but also support sustainability initiatives, as ENERGY STAR-rated units can consume up to 70% less electricity than traditional models.
- Adherence to Standards: It is essential to confirm that the units meet critical industry criteria such as UL 507, AMCA 230, and AMCA 208. Compliance with these standards guarantees safety, performance reliability, and energy efficiency, which are vital for meeting regulatory requirements and enhancing product reliability. For instance, UL 507 ensures that the fan is constructed and wired to prevent fire hazards, electrical shocks, and mechanical failures.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Assessing the total cost of ownership involves considering not just the purchase price, but also energy consumption and maintenance costs. For example, a ceiling fan typically operates between 50 to 100 watts, translating to an average monthly cost of approximately $2.70 when used for 10 hours a day at an electricity rate of $0.12 per kWh. Understanding these costs can lead to over time.
- Sustainability Goals: It is important to align fan selection with the organization’s sustainability objectives. Opting for energy-efficient models not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes the carbon footprint, supporting broader environmental goals. Additionally, selecting fans made from sustainable materials further reinforces this commitment.
- Lifecycle Analysis: Conducting a lifecycle analysis is crucial to evaluate the environmental impact of the fan throughout its operational life, from production to disposal. This analysis aids in selecting products that are not only efficient but also environmentally responsible, ensuring compliance with sustainability standards.
By concentrating on these factors, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance both performance and sustainability in solutions provided by their cooling fan supplier.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate cooling fan supplier is a pivotal decision that can profoundly influence the performance and efficiency of engineering projects. By comprehensively understanding the diverse types of cooling fans and their specific applications, engineers can effectively align their needs with the offerings of suitable suppliers. This strategic alignment not only guarantees optimal temperature regulation but also significantly enhances overall system reliability and effectiveness.
This article delineates essential criteria for the selection of a cooling fan supplier, including:
- An evaluation of product offerings
- Customization capabilities
- Technological advancements
- Supplier reliability
Key factors such as energy efficiency ratings and compliance with industry standards further underscore the necessity of making informed choices. By prioritizing these elements, engineers can cultivate partnerships that not only satisfy immediate project requirements but also contribute to long-term sustainability objectives.
Ultimately, the selection of a cooling fan supplier transcends mere purchasing; it represents a strategic initiative that can impact energy consumption, operational costs, and environmental consequences. Engineers are urged to adopt a comprehensive approach to supplier evaluation, ensuring that their selections align with both technical specifications and broader organizational goals. By doing so, they can foster successful collaborations that propel innovation and efficiency in their engineering pursuits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of cooling fans?
The main types of cooling fans are Axial Blowers, Centrifugal Blowers, Mixed-Flow Units, and Cross-Flow Fans.
How do Axial Blowers work and where are they commonly used?
Axial Blowers move air parallel to their axis and are suitable for general cooling applications. They are commonly used in electronic devices and data centers where high airflow is critical.
What distinguishes Centrifugal Blowers from other types of fans?
Centrifugal Blowers draw air into the center and expel it at a right angle, excelling in high-pressure applications. They are frequently used in HVAC systems and industrial processes.
What are Mixed-Flow Units and their advantages?
Mixed-Flow Units combine characteristics of both axial and centrifugal fans, offering versatility in managing various pressures and airflow needs. They are suitable for applications requiring high efficiency and compact design.
In what scenarios are Cross-Flow Fans beneficial?
Cross-Flow Fans push air through a narrow channel, providing uniform airflow in compact spaces. They are particularly advantageous in consumer electronics and specialized temperature control systems.
Why is understanding different fan types important for engineers?
Understanding different fan types is vital for engineers to assess their temperature regulation needs, as factors like airflow, pressure, and spatial constraints significantly influence the selection of the appropriate fan.
What trends are observed in the market for ventilation fans?
The market for ventilation fans is evolving, with axial fans expected to maintain a substantial share due to their effectiveness and cost-efficiency, while centrifugal fans are preferred in high-pressure situations. Innovations in fan technology are enhancing performance and energy efficiency across various sectors.