Overview
This article examines the numerous benefits, diverse applications, and comparative advantages of Electronically Commutated (EC) fan motors. It underscores their remarkable efficiency, with performance metrics exceeding 90%, which leads to substantial reductions in energy consumption and maintenance costs when juxtaposed with traditional AC and DC motors. Consequently, EC motors are becoming an increasingly favored choice across various sectors, including HVAC, refrigeration, and automotive. The insights provided herein aim to guide professionals in making informed decisions regarding the adoption of EC technology in their engineering applications.
Introduction
Electronically Commutated (EC) fan motors are transforming the energy efficiency and performance landscape across various industries. Their advanced technology, which eliminates the need for traditional brushes, not only delivers remarkable efficiency—often exceeding 90%—but also promises substantial cost savings and reduced maintenance.
As the demand for sustainable solutions escalates, it is essential to evaluate how EC motors compare to their AC and DC counterparts regarding reliability, operational costs, and versatility.
This article explores the extensive benefits, applications, and comparisons of EC fan motors, elucidating why they are increasingly becoming the preferred choice in modern engineering solutions.
Define Electronically Commutated (EC) Motors
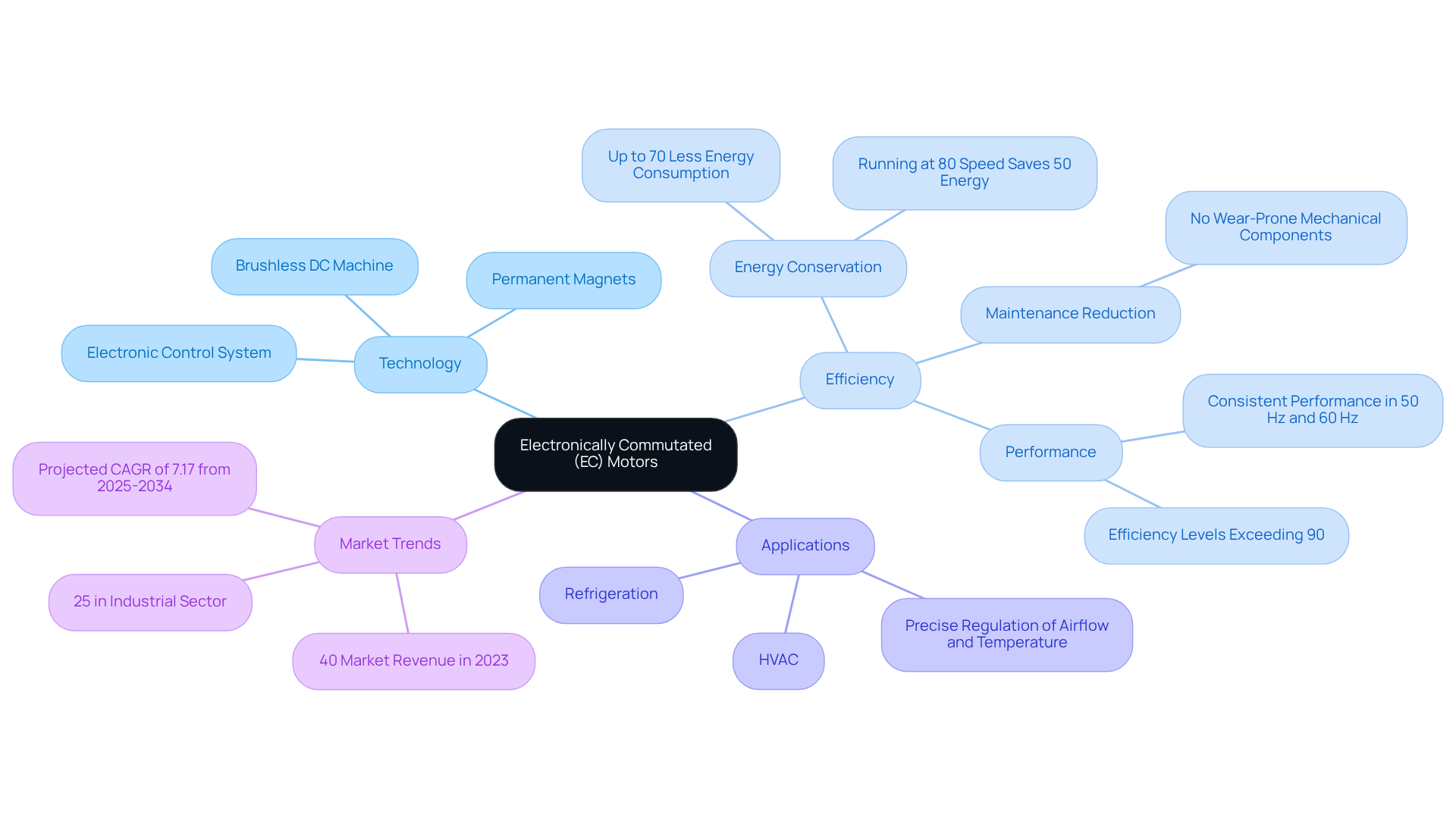
Electronically Commutated (EC) fan motors signify a remarkable technological advancement, functioning as a type of brushless DC machine that employs sophisticated electronic circuitry for commutation. Unlike traditional engines that depend on mechanical brushes and commutators, the EC fan motor utilizes permanent magnets and an integrated electronic control system to precisely manage speed and torque. This innovative design achieves exceptional efficiency levels, often exceeding 90%, in stark contrast to conventional engines that typically operate within an efficiency range of 20-70%. This significant disparity underscores the advantages of using an EC fan motor in terms of and performance, substantially reducing maintenance requirements due to the absence of wear-prone mechanical components.
The ability of the EC fan motor to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) through onboard electronics facilitates its seamless integration into a variety of applications, particularly in HVAC and refrigeration systems. Their compact and lightweight design renders them especially suitable for contemporary engineering solutions, where maximizing space and efficiency is paramount. In practical applications, the use of EC fan motors excels in environments that necessitate precise regulation of airflow and temperature, contributing to energy savings and enhanced operational performance. For example, operating an EC fan motor at 80% speed can result in energy savings of nearly 50%, while running an EC fan motor 80% of the time can conserve 20% of energy, demonstrating their effectiveness in energy conservation.
Data indicates that the brushless segment accounted for over 40% of the Electronically Commutated Machine market revenue in 2023, reflecting the growing preference for these efficient devices. Furthermore, the industrial sector is projected to represent more than 25% of the global market in 2023, highlighting the significance of EC engines across various industries. As Airius notes, “With the arrival of EC technology, clients now possess a choice for a more efficient, quieter-operating solution that performs exceptionally well when utilized at speeds below 100%.” As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to escalate, the adoption of EC fan motors in HVAC systems is expected to rise, driven by their superior performance and reliability.
Explore the Benefits of EC Motors
EC motors present a multitude of significant advantages that enhance their appeal across various applications:
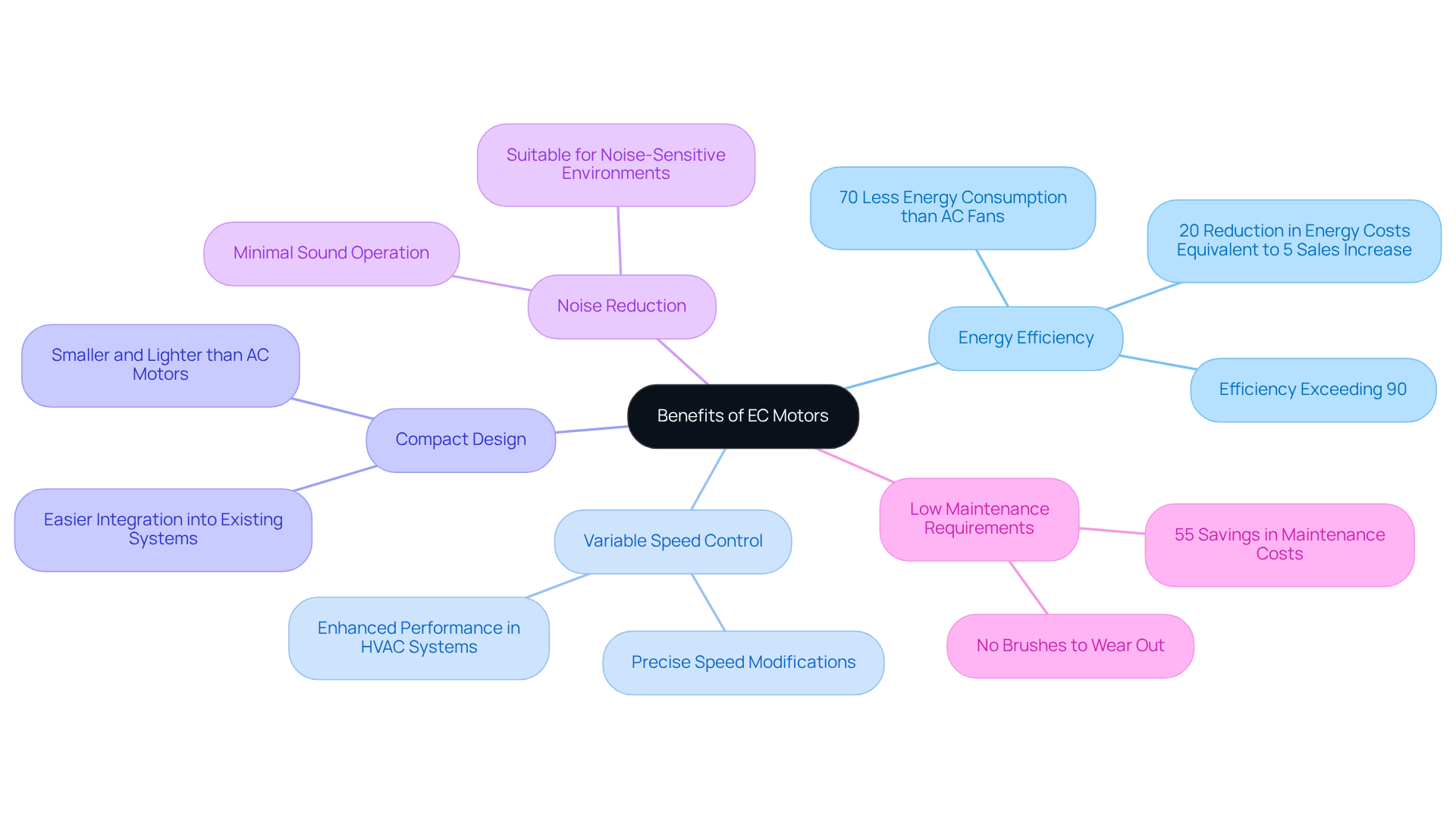
- Energy Efficiency: Achieving efficiencies exceeding 90%, EC motors drastically reduce energy consumption compared to traditional AC motors, which typically operate at 70-88% efficiency. Notably, the EC fan motor utilizes 70% less power than AC fans, leading to substantial cost savings for companies. A 20% reduction in energy costs can equate to the same financial benefit as a 5% increase in sales.
Lower heat generation is a benefit of the efficient design of the EC fan motor, which results in reduced heat production that enhances reliability and prolongs the lifespan of the motor and its associated components. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in environments where heat buildup can lead to operational issues.
A standout feature of the EC fan motor is its minimal maintenance requirements. With no brushes to wear out, these machines demand less upkeep, resulting in over time. This benefit is exemplified by practical applications, such as a project that achieved savings of 55%, where facilities noted considerable decreases in maintenance requirements after transitioning to EC fan motors.
- Variable Speed Control: The electronic regulation mechanisms in the EC fan motor enable precise speed modifications, making it suitable for applications that require varying airflow or cooling capabilities. This flexibility enhances performance and energy savings in HVAC systems, where maintaining optimal conditions is crucial.
- Compact Design: Typically smaller and lighter than their AC counterparts, EC fan motors are well-suited for applications with space limitations. Their compact design facilitates easier integration into existing systems without necessitating extensive modifications.
- Noise Reduction: Operating with minimal sound, EC devices are particularly advantageous in residential and commercial environments where noise levels are a concern. Their quiet operation, facilitated by the EC fan motor, enhances comfort and compliance with noise regulations, making them suitable for sensitive environments such as libraries and hospitals. Importantly, the low sound produced remains consistent throughout the entire speed range, further enhancing their appeal in noise-sensitive applications.
In summary, the transition to EC motors not only promotes energy conservation but also reduces maintenance demands, enhances operational reliability, and contributes to a quieter, more comfortable atmosphere.
Implement EC Motors in Engineering Applications
EC motors are increasingly utilized across a variety of engineering applications, showcasing their versatility and efficiency.
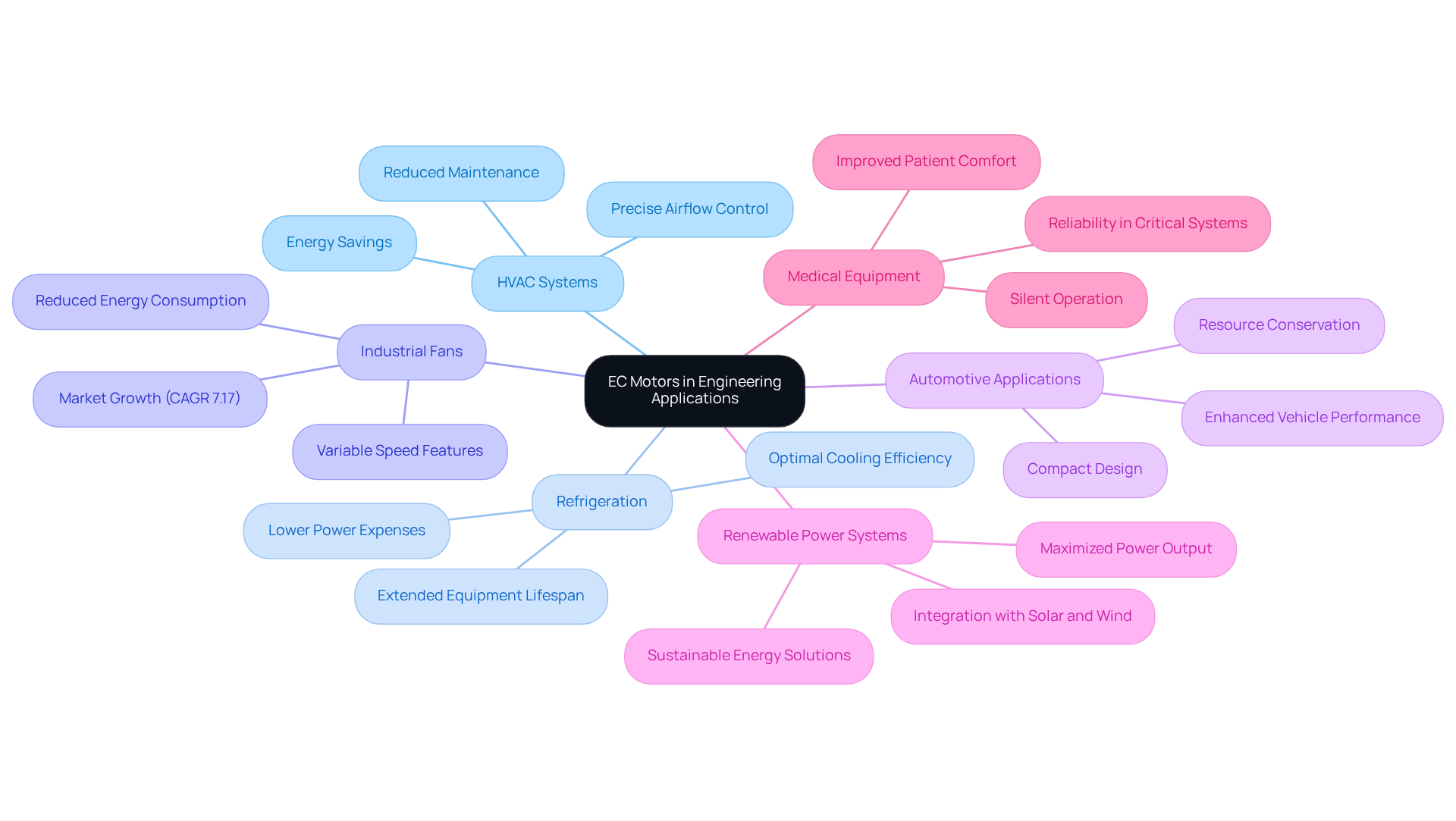
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, EC fan motors significantly enhance energy efficiency and provide precise airflow control. This capability is essential for both residential and commercial structures, where savings can be substantial. For instance, incorporating EC fan motors into HVAC setups can yield savings of 20% to 30% compared to conventional engines, as reported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Refrigeration: Typically found in cooling units, EC devices contribute to lowering power expenses while ensuring optimal cooling efficiency. Their ability to operate effectively under varying loads allows refrigeration units to adapt to changing demands without compromising power consumption. Engineers have noted that utilizing EC devices in refrigeration not only reduces operational costs but also extends the lifespan of the equipment due to decreased heat generation. One engineer remarked, “The efficiency of EC devices in refrigeration systems has transformed our approach to resource management.”
Industrial Fans: Numerous industrial applications employ the EC fan motor for fans, capitalizing on its variable speed features that lead to reduced energy consumption. The electronically commutated drive market is projected to experience significant growth, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.17% from 2025 to 2033, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions in industrial settings.
Automotive Applications: In electric vehicles, EC engines are utilized for cooling mechanisms and other supportive functions, enhancing overall vehicle performance. Their compact design and make them ideal for modern automotive applications, where space and resource conservation are paramount.
Renewable Power Systems: EC devices can be integrated into solar and wind power systems, where their efficiency and reliability are vital for maximizing power output. This integration aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable energy solutions.
Medical Equipment: In medical devices, the silent operation and reliability of EC units are essential for maintaining a sterile and controlled environment. Their low noise levels improve patient comfort while ensuring that critical systems function effectively.
The integration of EC devices across these applications not only illustrates their expanding market presence in industrial environments but also underscores their role in fostering energy conservation and sustainability within engineering practices.
Compare EC Motors with AC and DC Alternatives
When comparing EC motors to AC and DC motors, several critical factors emerge that warrant attention:
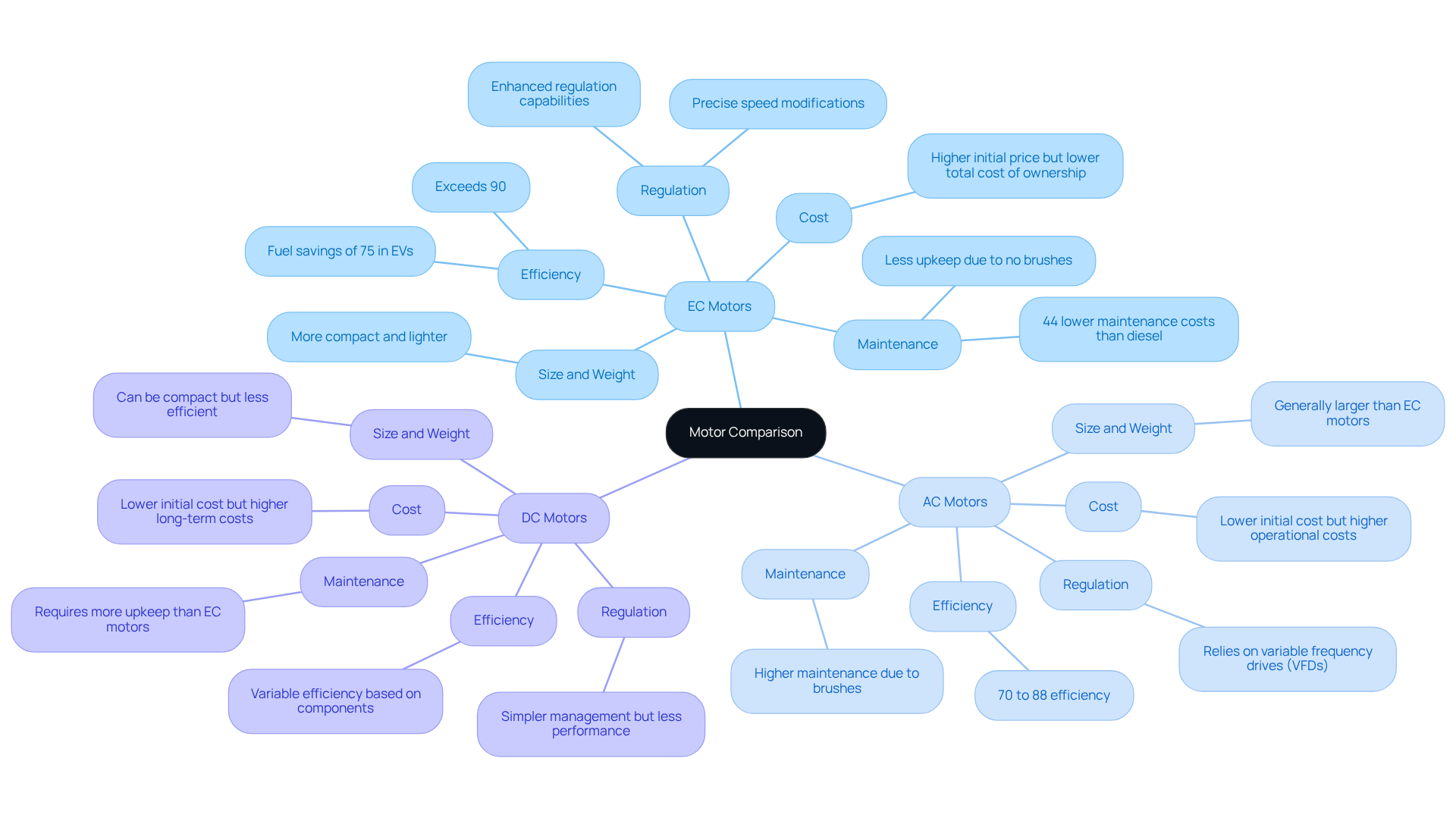
- Efficiency: EC motors typically achieve efficiencies exceeding 90%, significantly outperforming AC motors, which generally range from 70% to 88%. While DC drives can also be efficient, they often require additional components for effective speed control, potentially affecting overall performance. For instance, electric vehicles (EVs) have demonstrated fuel savings of up to 75% compared to conventional vehicles, underscoring the potential of advanced technology.
- Regulation: The electronic commutation in EC devices provides enhanced regulation capabilities, allowing for precise speed modifications. In contrast, AC machines often rely on variable frequency drives (VFDs) for similar control, whereas DC units, despite their simpler management, may not meet the performance standards of EC devices. Real-world applications, such as those observed in King County Metro’s battery electric buses, illustrate the effectiveness of EC drives in achieving operational efficiency.
- Maintenance: EC machines require less upkeep than both AC and DC variants due to the absence of brushes, which are prone to wear over time. This characteristic leads to , making EC devices a more cost-effective option in the long run. For example, maintenance costs for battery buses have been reported to be 44% lower than those for diesel buses, highlighting the potential savings associated with electric propulsion technologies.
- Size and Weight: Often more compact and lighter than their alternating current counterparts, EC devices are particularly suited for applications with space constraints. While DC devices can also be designed to be compact, they may not deliver the same efficiency benefits as EC alternatives.
- Cost: Although the initial purchase price of an EC fan motor may be higher, their energy savings and reduced maintenance requirements typically result in a lower total cost of ownership compared to both AC and DC motors over time. This positions them as a financially sound investment for various applications, as evidenced by the substantial operational savings reported by municipalities transitioning to electric fleets.
Conclusion
The exploration of Electronically Commutated (EC) fan motors unveils their substantial advantages over traditional motor technologies, establishing them as a pivotal force in energy efficiency and performance. By leveraging advanced electronic circuitry, EC motors not only achieve exceptional efficiency levels but also reduce maintenance requirements, rendering them an attractive option for diverse applications across various industries.
Key points throughout the article underscore the energy savings, variable speed control, compact design, and quiet operation of EC motors. Their integration into HVAC systems, refrigeration, industrial applications, and even medical equipment exemplifies their versatility and effectiveness. Furthermore, a comparative analysis with AC and DC motors accentuates the superior efficiency and reduced operational costs associated with EC technology, reinforcing its increasing market presence.
As the demand for energy-efficient solutions intensifies, the adoption of EC fan motors is set to surge, significantly contributing to sustainability initiatives across engineering practices. Embracing this innovative technology not only fosters considerable cost savings but also bolsters a broader commitment to energy conservation and operational reliability. The transition to EC motors signifies a strategic advancement towards a more efficient and sustainable future across multiple sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Electronically Commutated (EC) motors?
Electronically Commutated (EC) motors are a type of brushless DC machine that use advanced electronic circuitry for commutation, employing permanent magnets and an integrated electronic control system to manage speed and torque without mechanical brushes and commutators.
How efficient are EC fan motors compared to traditional motors?
EC fan motors achieve efficiency levels often exceeding 90%, while traditional motors typically operate within an efficiency range of 20-70%. This significant difference highlights the energy conservation and performance advantages of EC motors.
What applications are suitable for EC fan motors?
EC fan motors are particularly suitable for HVAC and refrigeration systems, as they can seamlessly convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) and are designed for environments that require precise regulation of airflow and temperature.
How do EC fan motors contribute to energy savings?
Operating an EC fan motor at 80% speed can result in energy savings of nearly 50%. Additionally, running an EC fan motor 80% of the time can conserve 20% of energy, demonstrating their effectiveness in energy conservation.
What market trends are associated with EC fan motors?
In 2023, the brushless segment accounted for over 40% of the Electronically Commutated Machine market revenue, with the industrial sector projected to represent more than 25% of the global market, indicating a growing preference for these efficient devices.
What advantages do EC motors offer over traditional motors?
EC motors provide a more efficient, quieter-operating solution that performs exceptionally well at speeds below 100%, leading to reduced maintenance requirements due to the absence of wear-prone mechanical components.

