Overview
This article defines high flow fans, emphasizing their critical role in cooling applications and the various types available. High flow fans are indispensable for effective heat dissipation in electronics, as they facilitate the movement of large volumes of air at low pressure. This process prevents overheating and enhances the reliability of electronic systems. The article provides a detailed analysis of their specifications, applications, and the latest technological advancements in fan design, thereby underscoring their significance in maintaining optimal performance in electronic devices.
Introduction
High flow fans are essential components of modern cooling solutions, particularly in environments where efficient heat dissipation is critical for maintaining performance and reliability. These powerful ventilators are engineered to move substantial volumes of air with precision, making them indispensable across various applications, from data centers to consumer electronics.
However, as technology advances and electronic components become increasingly compact and powerful, a significant challenge arises: how can engineers effectively select the appropriate type of high flow fan to meet specific cooling requirements while balancing performance, noise, and energy efficiency?
This article explores the definition, importance, and diverse types of high flow fans, offering insights that are vital for professionals engaged in thermal management and electronic design.
Define High Flow Fan: Key Characteristics and Specifications
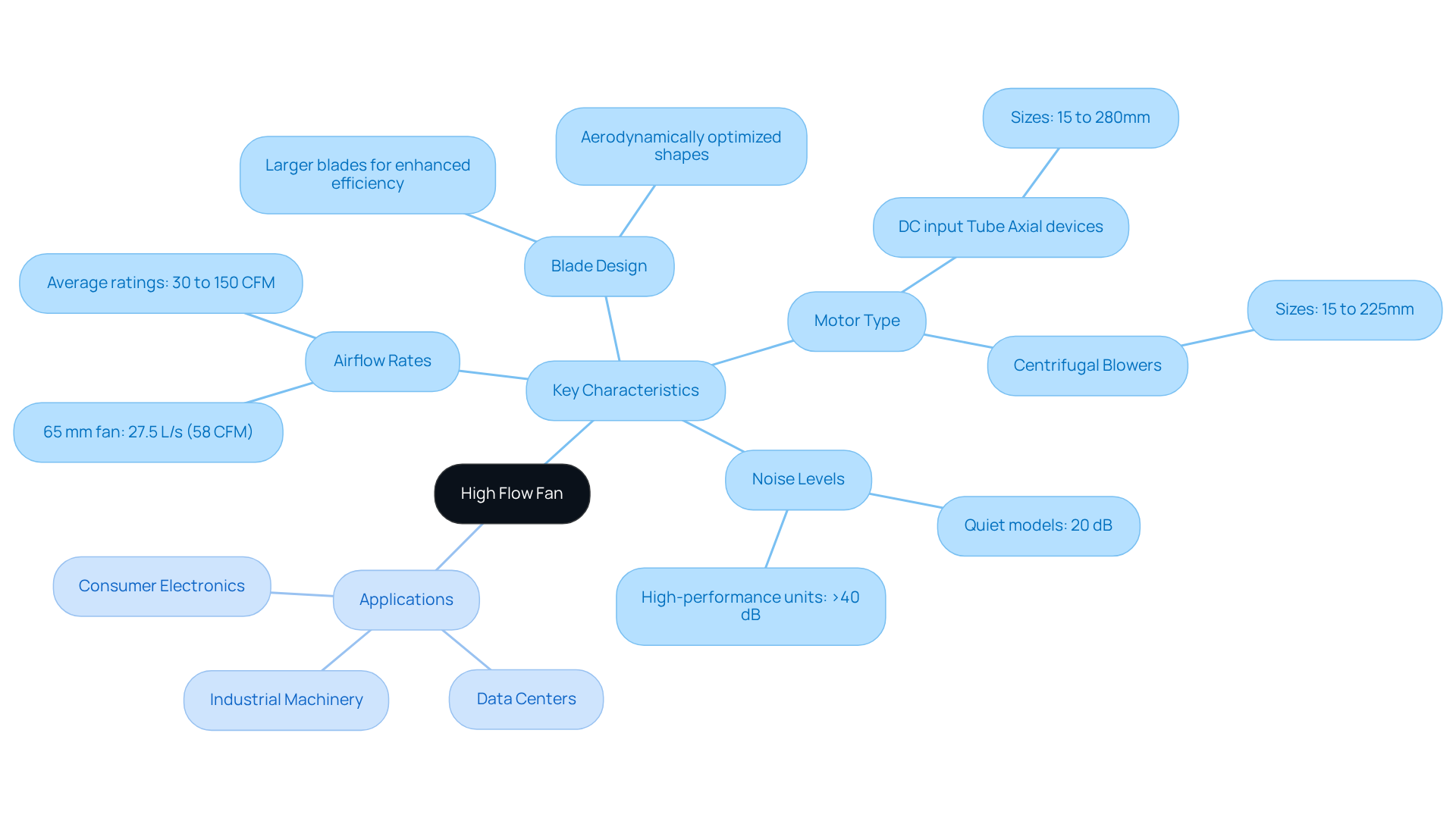
High-capacity ventilators utilize a high flow fan to transfer substantial volumes of air at relatively low pressure, making them indispensable for efficient cooling across various applications. Characterized by elevated airflow rates, typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), the performance of a high flow fan is defined by key specifications such as blade design, motor type, and operational noise levels.
High-capacity blowers often feature larger blades and optimized shapes, significantly enhancing airflow efficiency. For example, a 65 mm fan can achieve an airflow of 27.5 liters per second (approximately 58 CFM) with a maximum pressure of 0.5 kPa, illustrating the balance between airflow and pressure capabilities. Average airflow ratings for electronic devices generally range from 30 to 150 CFM, providing a broader context for the performance of powerful ventilators.
In scenarios where heat dissipation is critical—such as in data centers, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics—high flow fans are essential. Recent advancements in fan technology have resulted in designs that not only boost airflow but also minimize noise levels, with some models achieving average decibel ratings as low as 20 dB, while others can exceed 40 dB for high-performance units.
Understanding these specifications is crucial for engineers aiming to that meets specific cooling needs while optimizing energy efficiency.
Gagner-Toomey Associates, recognized as the world’s largest manufacturer of standard and custom air movers, offers a comprehensive range of high flow fan solutions tailored for diverse industrial applications, including the electronics and automotive sectors. Their product lineup includes:
- DC input Tube Axial devices ranging from 15 to 280mm
- Centrifugal Blowers from 15 to 225mm
With IP protection available in most models upon request.
Contextualize High Flow Fans: Importance in Electronics Cooling
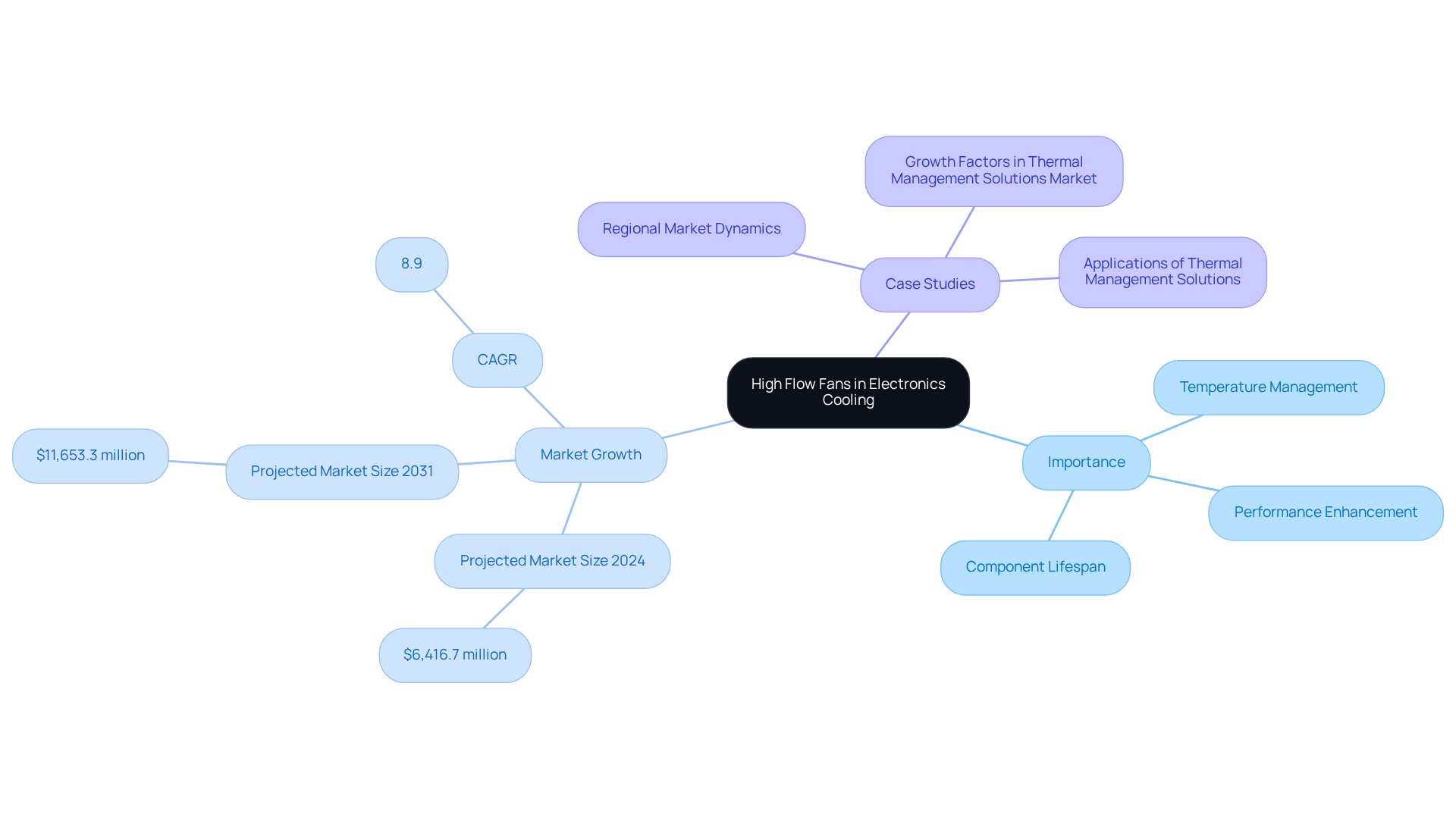
High-capacity ventilators, particularly high flow fans, are critical for effective electronics temperature management, facilitating the dispersion of heat generated by components such as CPUs and GPUs. Excessive heat can result in thermal throttling, which not only reduces performance but can also inflict irreversible damage on sensitive electronics. By maintaining optimal operating temperatures, these powerful ventilation devices significantly enhance the reliability and lifespan of electronic systems. Their capability to move substantial volumes of air with a high flow fan is particularly beneficial in high-density environments, such as server rooms and industrial machinery, where is vital for operational success.
In light of the global electronics thermal management solutions market, projected to reach $6,416.7 million in 2024 and $11,653.3 million by 2031, the utilization of robust circulation devices becomes increasingly crucial. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.9% from 2024 to 2031, highlighting the escalating demand for efficient temperature control solutions. For instance, in scenarios where peak CPU temperatures can reach 392 K, the integration of a high flow fan can prevent overheating and ensure consistent performance.
Case studies demonstrate that adopting advanced temperature regulation solutions, including powerful circulation devices, can extend the lifespan of electronic components, making them indispensable in modern electronic design and thermal management strategies.
Trace the Evolution of High Flow Fans: Historical Development and Innovations
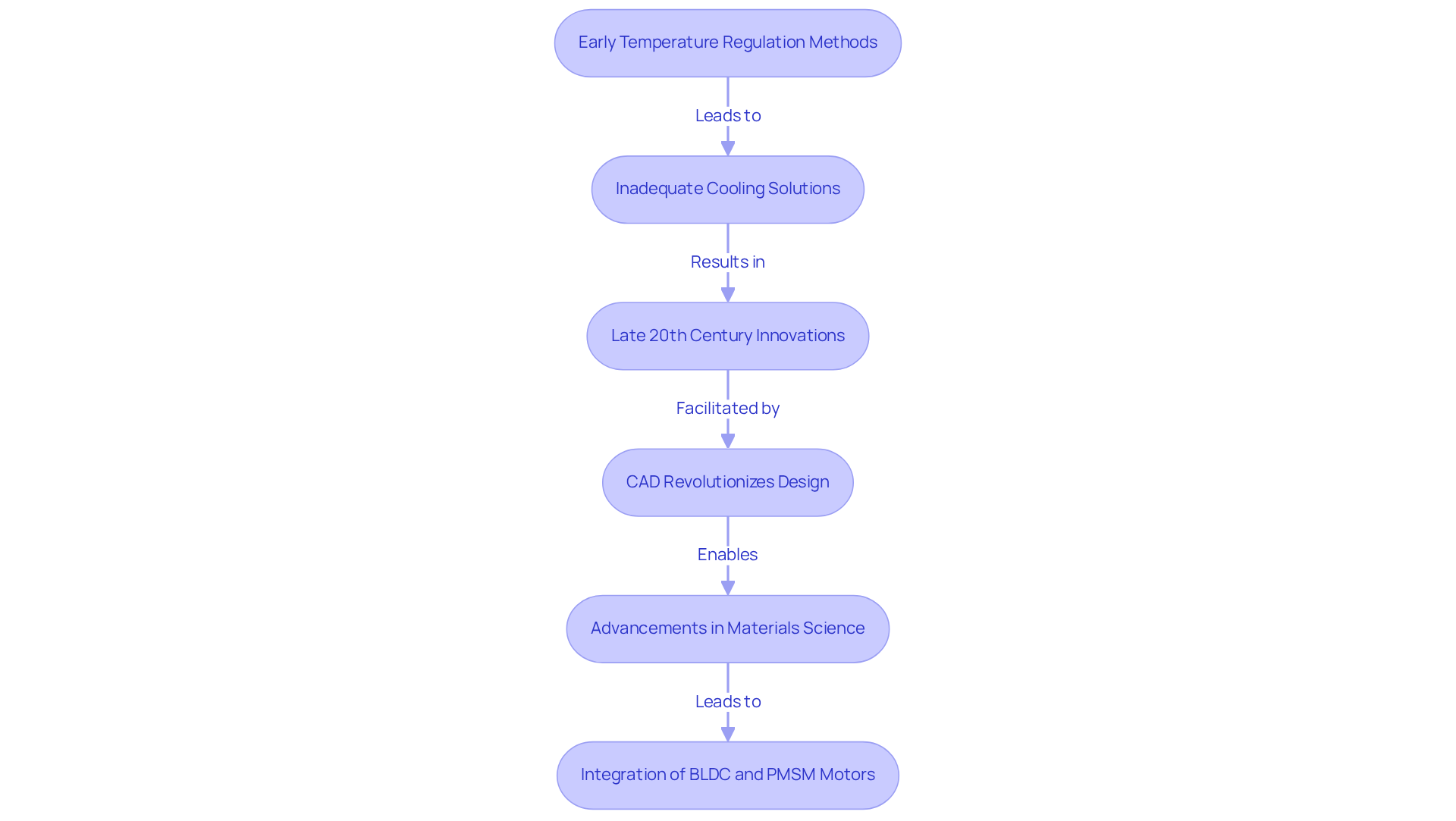
The development of powerful air circulators in the electronics sector began during early periods characterized by simple temperature regulation methods, which often proved inadequate for the increasing thermal demands of electronic components. As technology advanced, fan designs experienced substantial transformations, particularly in the late 20th century, highlighted by innovations in blade geometries and motor efficiencies.
The advent of computer-aided design (CAD) revolutionized the engineering of ventilation components, enabling the creation of powerful airflow devices that not only optimized airflow but also operated at lower noise levels. Today, and aerodynamics play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of powerful ventilators, ensuring they meet the cooling needs of contemporary applications.
Importantly, the integration of brushless direct current motors (BLDC) and permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) has further optimized energy consumption, reflecting a broader trend toward sustainability in fan technology. This ongoing evolution underscores the essential role of high flow fans in maintaining optimal performance in electronic devices.
Furthermore, the growing demand for industrial ventilators, driven by energy-saving regulations, highlights the significance of these advancements in addressing modern challenges. As the market for forward-curved centrifugal blowers is projected to expand considerably, understanding these developments becomes imperative for engineers navigating the complexities of contemporary temperature regulation solutions.
Differentiate Types of High Flow Fans: Axial vs. Centrifugal and More
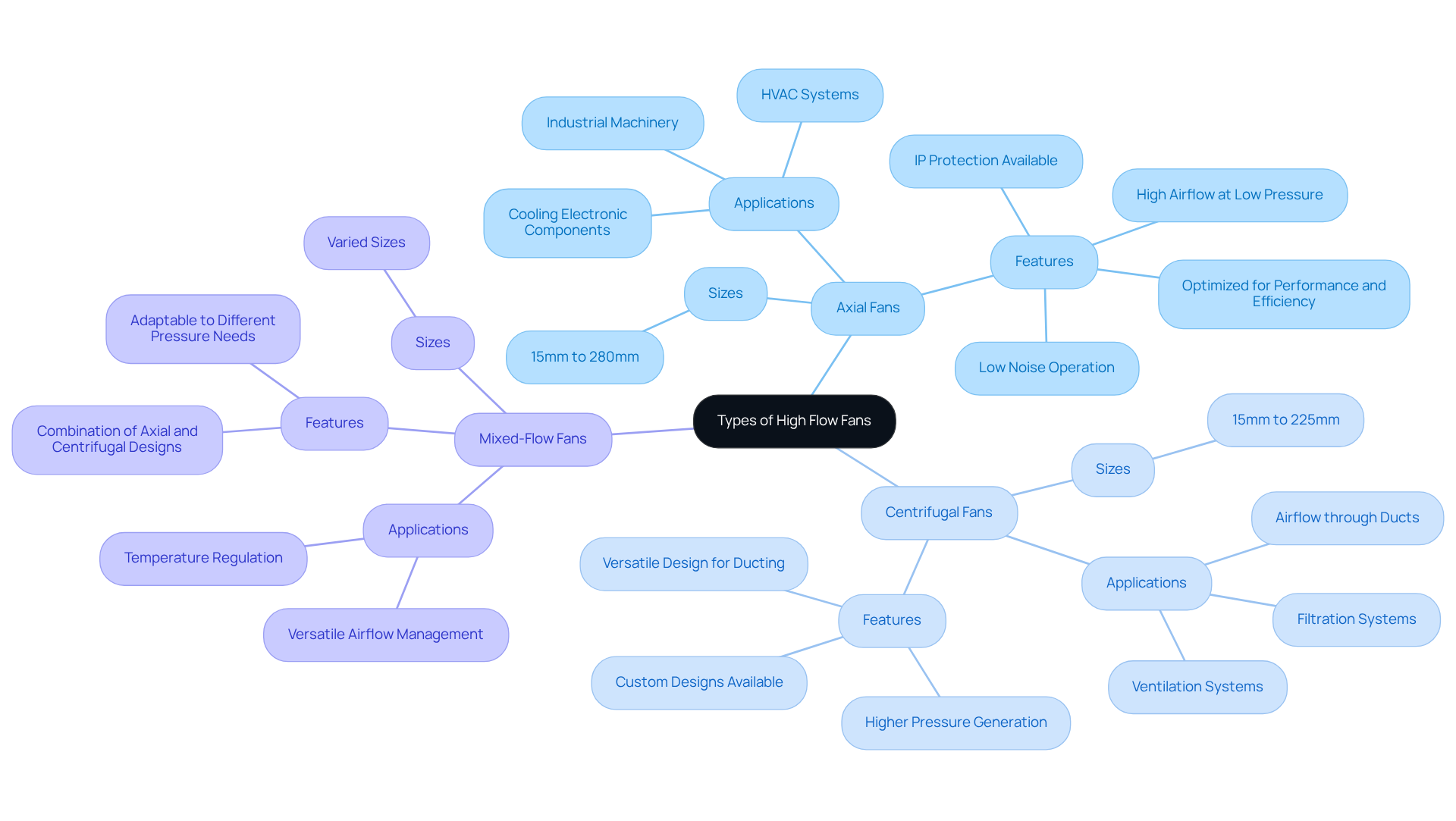
High flow blowers can be categorized primarily into two types: axial and centrifugal models. Axial blowers, which move air parallel to the device’s axis, are commonly utilized in situations requiring high airflow at low pressure, making them ideal for cooling electronic components. Gagner-Toomey Associates, the world’s largest producer of standard and custom air-movers, provides a wide range of DC input tube axial devices varying from 15 to 280mm. These devices are optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise, with IP protection available in most models upon request.
In contrast, centrifugal blowers pull air into the device and discharge it at a right angle, generating higher pressure. This design makes them appropriate for scenarios where airflow must be channeled through ducts or filters. Gagner-Toomey also offers a comprehensive range of DC input centrifugal blowers, with sizes varying from 15 to 225mm, addressing various ventilation requirements, including custom designs.
Additionally, mixed-flow machines combine features of both axial and centrifugal designs, providing versatility in airflow and pressure capabilities. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the for specific temperature regulation needs. As the demand for efficient cooling solutions continues to rise—particularly in high-density environments like data centers and automotive systems—the significance of high flow fans becomes increasingly important.
Conclusion
High flow fans are indispensable in a multitude of industries, particularly in electronics cooling, where they are essential for maintaining optimal temperatures for sensitive components. Their capability to efficiently move substantial volumes of air while minimizing noise levels underscores their critical role in contemporary thermal management strategies. By comprehensively understanding the specifications and types of high flow fans, engineers can make informed decisions that significantly enhance the reliability and lifespan of electronic systems.
Key insights throughout the article have illuminated the characteristics of high flow fans, their vital significance in preventing thermal throttling, and the evolution of fan technology. The article has also explored the distinctions between axial and centrifugal fans, emphasizing how each type caters to different cooling requirements. Moreover, the anticipated growth of the electronics thermal management market signifies an increasing dependence on these powerful ventilation devices.
As technology progresses, the demand for efficient cooling solutions is set to escalate. Embracing innovations in fan design and grasping the specific requirements of various applications will be crucial for maximizing performance and energy efficiency. The role of high flow fans in ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of electronic devices is paramount; thus, investing in the appropriate solutions is essential for future success in any industry that relies on effective thermal management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a high flow fan and what are its key characteristics?
A high flow fan is a type of ventilator that transfers substantial volumes of air at relatively low pressure. Key characteristics include elevated airflow rates measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM), blade design, motor type, and operational noise levels.
How does blade design affect the performance of a high flow fan?
High-capacity blowers often feature larger blades and optimized shapes, which significantly enhance airflow efficiency, allowing for greater air movement at lower pressure.
What is the typical airflow range for electronic devices using high flow fans?
The average airflow ratings for electronic devices generally range from 30 to 150 CFM.
In what scenarios are high flow fans particularly essential?
High flow fans are essential in scenarios where heat dissipation is critical, such as in data centers, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics.
How have recent advancements in fan technology improved high flow fans?
Recent advancements have led to designs that increase airflow while minimizing noise levels, with some models achieving average decibel ratings as low as 20 dB, while others can exceed 40 dB for high-performance units.
Why is it important for engineers to understand high flow fan specifications?
Understanding these specifications is crucial for engineers to select the appropriate high flow fan that meets specific cooling needs while optimizing energy efficiency.
Who is Gagner-Toomey Associates and what do they offer?
Gagner-Toomey Associates is recognized as the world’s largest manufacturer of standard and custom air movers, offering a comprehensive range of high flow fan solutions tailored for diverse industrial applications, including the electronics and automotive sectors.
What types of high flow fans does Gagner-Toomey Associates provide?
They provide DC input Tube Axial devices ranging from 15 to 280mm and Centrifugal Blowers from 15 to 225mm, with IP protection available in most models upon request.

