Overview
Backward curved fans represent a highly efficient solution for managing high static pressures and ensuring consistent airflow. These devices are particularly well-suited for applications in HVAC systems, industrial ventilation, and air pollution control. Their superior energy efficiency, quieter operation, and adaptability to demanding environments highlight their essential role in modern engineering solutions. As industries increasingly prioritize energy conservation and effective ventilation, the significance of backward curved fans becomes even more pronounced. By implementing these advanced fans, organizations can enhance operational efficiency while addressing environmental concerns.
Introduction
Centrifugal fans are integral to a wide range of engineering applications, harnessing centrifugal force to efficiently transport air and gases to critical areas. Among the various types available, backward curved fans are particularly notable for their remarkable energy efficiency and capacity to sustain high static pressures. This makes them essential in diverse environments, from HVAC systems to industrial ventilation.
As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to escalate, engineers face a significant challenge: how to balance performance and cost when selecting the appropriate fan type for specific applications.
This article explores the mechanics, advantages, and optimal uses of backward curved fans, providing insights that can enhance engineering designs and improve operational effectiveness.
Define Centrifugal Fans and Their Role in Engineering
Centrifugal fans are engineered devices that leverage centrifugal force to efficiently move air or gases. They function by drawing air into the center and expelling it outward at a right angle, generating high pressure essential for applications requiring substantial airflow against resistance. This design proves particularly advantageous in , industrial processes, and electronic cooling environments. Gagner-Toomey Associates, the largest producer of standard and custom air-movers globally, offers an extensive selection of DC input centrifugal blowers, optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise, making them ideal for various industrial applications, including electronics and automotive sectors.
Looking ahead to 2025, centrifugal blowers are projected to capture a significant segment of the market, with forecasts indicating they will constitute a considerable portion of industrial applications due to their effectiveness and reliability. For instance, in textile production, centrifugal blowers have demonstrated dependable uptime ranging from 8000 to 10,000 hours before the first maintenance intervention, underscoring their durability. Furthermore, advancements in technology—such as the integration of Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) technology and the use of new high-temperature alloys—have enabled backward curved fan units to achieve effectiveness levels of up to 75% in dry gas applications, significantly enhancing energy savings and operational performance.
Experts emphasize that these devices are vital in HVAC systems, where they not only ensure efficient air circulation but also contribute to noise reduction by 6-10 dB, establishing their role as a fundamental component of modern engineering solutions.
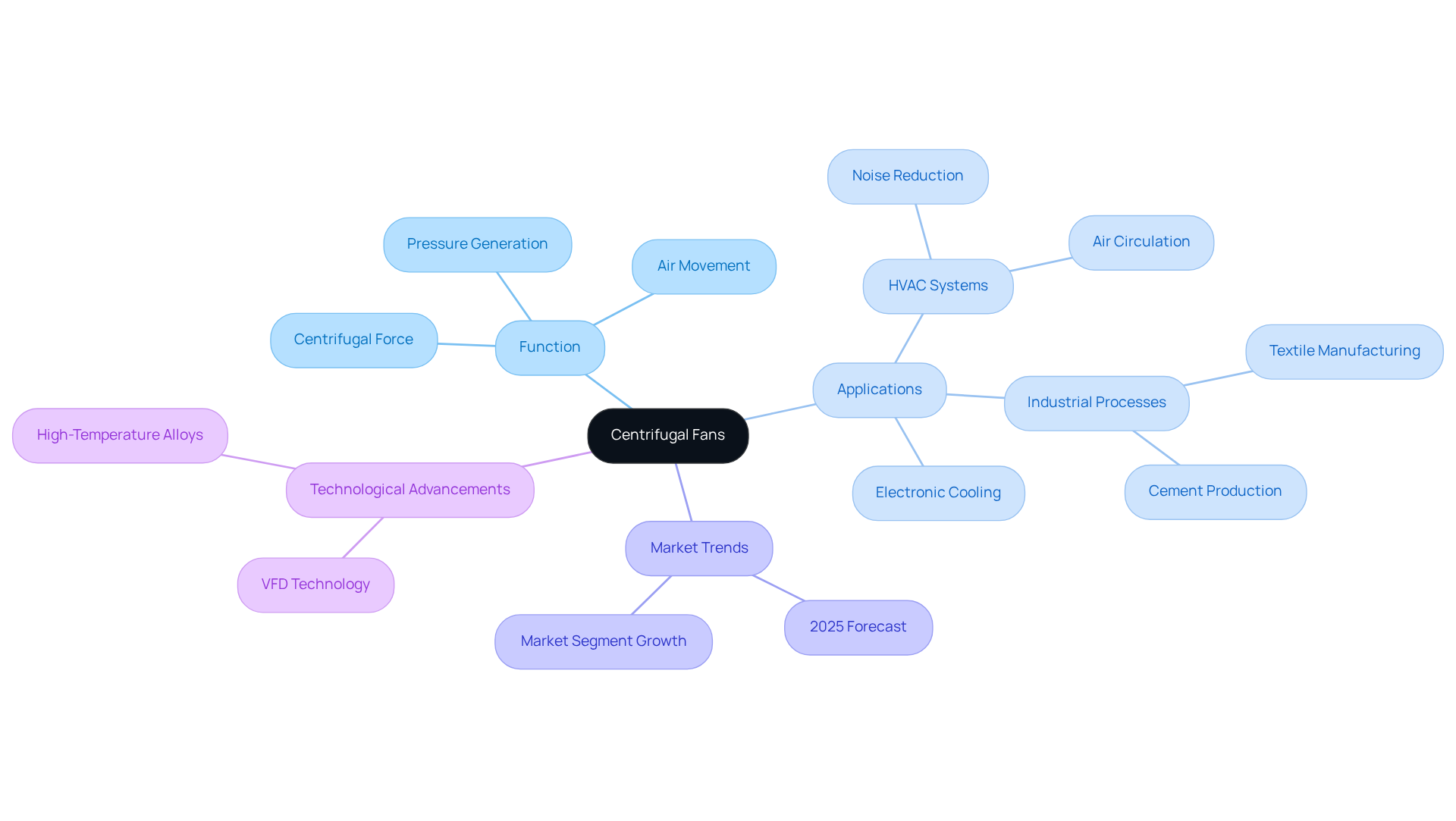
Differentiate Between Forward Curved and Backward Curved Fans
Forward-bent blowers are engineered with blades that bend in the direction of rotation, allowing for the generation of high airflow at low pressure, achieving an efficiency of 60-70%. This design renders them particularly suitable for applications constrained by space and requiring minimal noise levels, such as in household appliances and .
In contrast, backward curved fan blades are designed to curve away from the direction of rotation. This configuration not only enables them to manage higher pressures but also enhances energy efficiency, reaching an efficiency of 80-85%. Such characteristics make backward curved fans ideal for scenarios that necessitate a steady airflow against resistance, including industrial environments and data centers.
As we approach 2025, the trend towards energy-efficient solutions emphasizes the critical need to select the appropriate fan type based on specific application requirements. Engineers must evaluate factors such as airflow demands, static pressure, and energy efficiency when determining the most suitable fan type. Notably, backward curved fans are often preferred in noise-sensitive environments due to their quieter operation and lower maintenance needs, as they are less prone to dust accumulation.
For instance, in the realm of electronics cooling, backward curved fans are utilized to maintain optimal airflow in data centers, whereas forward bending blowers are commonly found in smaller electronic devices. This comprehension of fan mechanics is vital for engineers striving to optimize performance in their designs.
As HVAC engineer John Doe articulates, ‘Selecting the appropriate fan type is essential for ensuring effectiveness and performance in any application.
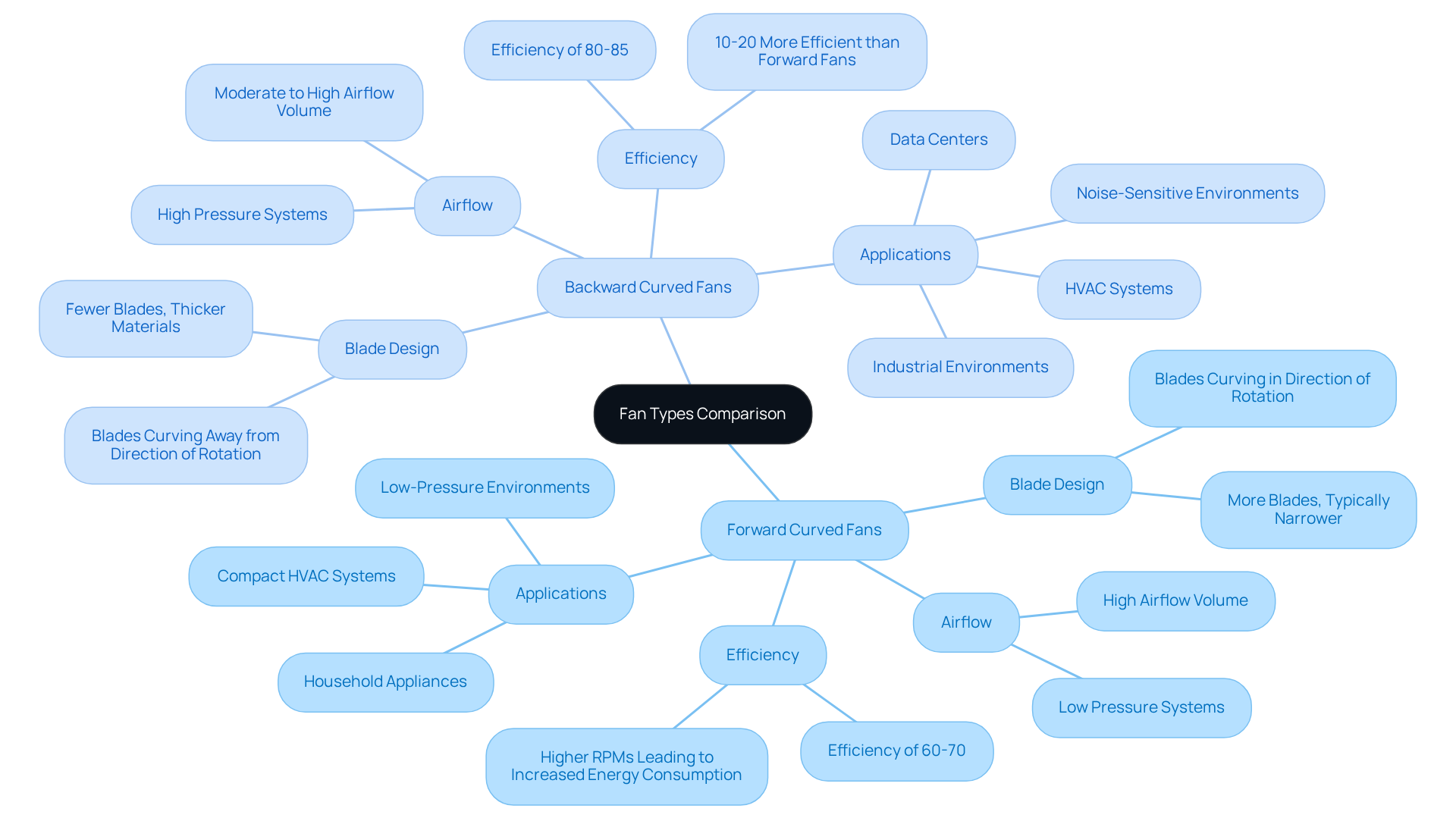
Explain the Mechanics of Backward Curved Fans
Backward curved fans operate on the principle of centrifugal force, where the rotation of the blades establishes a low-pressure zone at the center, effectively drawing air in. The blades’ unique curvature is meticulously designed to minimize turbulence, resulting in streamlined airflow that significantly enhances performance, achieving static efficiencies of up to 85%. As air is expelled, it exits at a higher pressure due to the optimal angle of the blades, which directs the air outward efficiently.
This innovative design enables backward curved fans to maintain consistent airflow even under high-resistance conditions, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications such as:
- Ventilation in printing presses
- Laser cutting equipment
- Dust collection systems
Their ability to handle greater static pressures while promoting energy conservation positions them as a preferred choice in modern HVAC systems and other critical environments. Moreover, backward curved fans are recognized for their quieter operation compared to forward-bladed alternatives, and their robust design leads to minimal maintenance requirements, establishing backward curved fans as a reliable option for prolonged use.
Evaluate the Advantages and Disadvantages of Backward Curved Fans
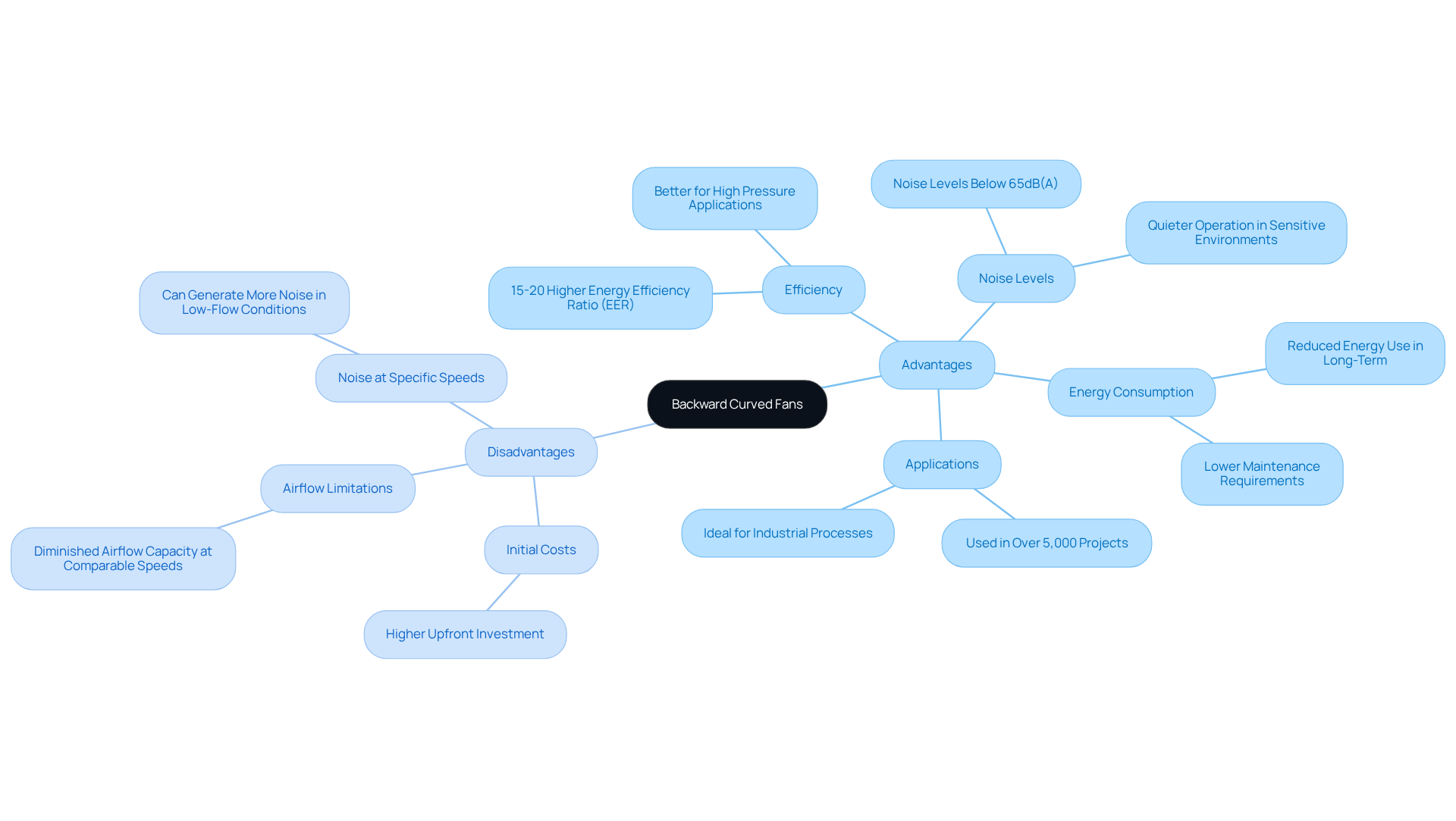
Backward curved fans are recognized for their superior efficiency, reduced energy consumption, and their ability to manage higher static pressures compared to forward bending counterparts. Their design facilitates quieter operation, making them particularly suitable for noise-sensitive environments such as hospitals and schools. Notably, backward bending blowers maintain noise levels below 65dB(A) at 1 meter, significantly quieter than the industry average of 75dB(A). Furthermore, they exhibit greater energy conservation relative to forward-arched devices, achieving a 15-20% higher Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) in numerous applications. Importantly, backward curved fans have been utilized in over 5,000 international projects, underscoring their extensive application and reliability across diverse settings.
Despite these advantages, backward bending blowers do present certain challenges. The initial investment is typically higher, which may pose a barrier for some applications. Additionally, while they excel in high-pressure scenarios, backward bending devices may exhibit diminished airflow capacity at comparable speeds when compared to forward bending models. This aspect can be particularly crucial in applications requiring high airflow rates, where forward bent blowers are often preferred.
Real-world applications illustrate these distinctions effectively. In a recent case study, a manufacturing facility transitioned from forward-blade units to backward-blade units, resulting in an increase in static pressure from 1 in. wg to 3 in. wg, while simultaneously from 10.0 kW to 8.5 kW. This shift not only enhanced productivity but also improved the working environment by lowering noise levels.
HVAC experts frequently discuss the cost-versus-performance dynamics associated with backward curved fans. Although the upfront costs may be elevated, the long-term energy savings and reduced maintenance requirements—attributable to their robust construction and lower wear rates—can validate the investment. Moreover, backward curved fans maintain consistent performance even with variations in rotation speed or load, making them reliable in various conditions. Nevertheless, it is essential to consider that their performance can be influenced by ductwork design and filter presence, which may introduce additional resistance and affect overall effectiveness. Furthermore, backward-bent blowers can generate more noise at specific speeds, particularly in low-flow scenarios, which is a vital consideration for noise-sensitive applications.
In conclusion, while backward bent blowers offer considerable advantages in performance and noise reduction, their higher initial costs and potential airflow limitations at certain velocities must be weighed against the specific requirements of the application.
Identify Ideal Applications for Backward Curved Fans
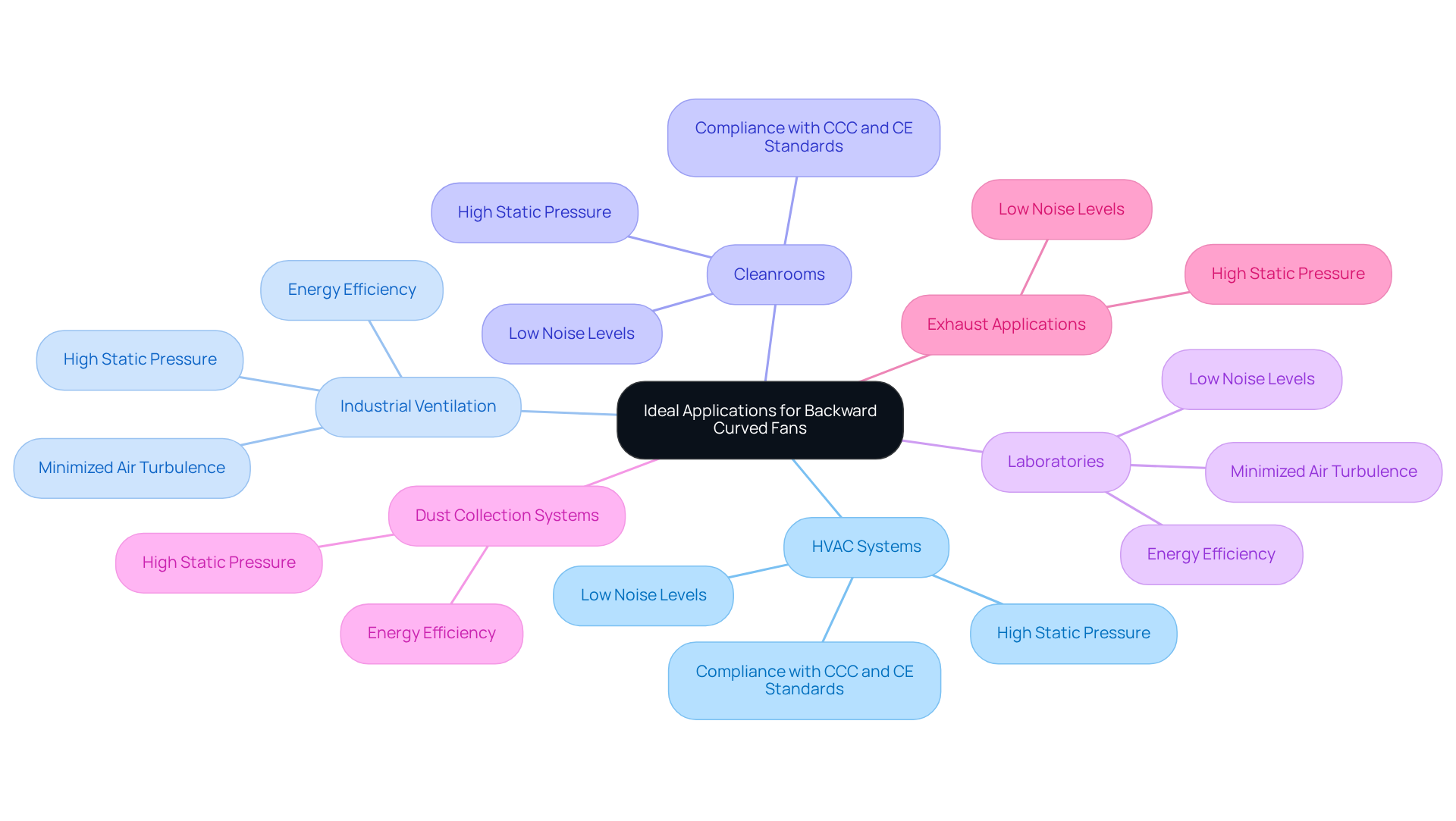
Applications that require high static pressure and consistent airflow, such as HVAC systems, industrial ventilation, and air pollution management, excel with backward curved fans. Their prevalent use in , laboratories, and manufacturing facilities underscores their importance in maintaining air quality and operational efficiency. Moreover, the backward curved fans are adept at handling high resistance, making them ideal for dust collection systems and exhaust applications. Notably, EC backward centrifugal blowers operate quietly, often under 65 dB, which is crucial for fostering a comfortable working environment in sensitive settings like cleanrooms and laboratories.
Additionally, these devices meet CCC and CE standards, ensuring compliance with international safety and environmental regulations—an essential consideration for engineers involved in global projects. The unique blade design of backward bending turbines minimizes air turbulence, thereby enhancing performance while reducing noise levels. By understanding these applications, engineers can effectively leverage the advantages of a backward curved fan, including its compatibility with voltage options of 24V and 48V, which allows for versatile integration solutions.
Conclusion
Backward curved fans signify a monumental leap in centrifugal fan technology, recognized for their efficiency and versatility across a multitude of applications. Their distinctive blade design not only facilitates superior static pressure management but also guarantees quieter operation, rendering them indispensable in environments where noise reduction is paramount. As industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and performance, a comprehensive understanding of the mechanics and advantages of backward curved fans is vital for engineers and decision-makers alike.
This article has illuminated key insights, including the comparative benefits of backward curved fans over their forward curved counterparts, their operational mechanics, and the specific applications where they thrive. The discourse on energy efficiency, noise reduction, and the capacity to manage high resistance highlights their significance in contemporary engineering solutions, particularly within HVAC systems, industrial ventilation, and cleanroom environments. Moreover, real-world examples underscore the tangible advantages these fans offer, reaffirming their status as reliable components across various industrial settings.
In light of these considerations, it is evident that selecting the appropriate fan type is critical for optimizing performance and energy consumption. As industries evolve and the demand for efficient air movement solutions escalates, backward curved fans emerge as a compelling choice. Engineers and industry professionals are urged to assess their specific requirements and harness the benefits of backward curved fans, ensuring they contribute effectively to enhanced operational efficiency and sustainability in their respective applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are centrifugal fans and what is their role in engineering?
Centrifugal fans are devices that use centrifugal force to move air or gases efficiently. They draw air into the center and expel it outward, generating high pressure essential for applications that require substantial airflow against resistance. They are commonly used in HVAC systems, industrial processes, and electronic cooling environments.
What are the advantages of centrifugal blowers offered by Gagner-Toomey Associates?
Gagner-Toomey Associates provides a wide range of DC input centrifugal blowers that are optimized for performance, efficiency, and low noise. These features make them suitable for various industrial applications, including those in the electronics and automotive sectors.
What is the projected market trend for centrifugal blowers by 2025?
By 2025, centrifugal blowers are expected to capture a significant segment of the market, becoming a major component in industrial applications due to their effectiveness and reliability.
How durable are centrifugal blowers in textile production?
In textile production, centrifugal blowers have shown reliable uptime ranging from 8000 to 10,000 hours before the first maintenance intervention, indicating their durability.
What technological advancements are enhancing the performance of centrifugal fans?
Advancements such as Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) technology and the use of new high-temperature alloys have allowed backward curved fan units to achieve effectiveness levels of up to 75% in dry gas applications, leading to improved energy savings and operational performance.
How do centrifugal fans contribute to HVAC systems?
Centrifugal fans ensure efficient air circulation in HVAC systems and help reduce noise levels by 6-10 dB, making them a fundamental component of modern engineering solutions.
What is the difference between forward curved and backward curved fans?
Forward curved fans have blades that bend in the direction of rotation, generating high airflow at low pressure with an efficiency of 60-70%. They are suitable for compact spaces and low noise applications. Backward curved fans have blades that curve away from the direction of rotation, allowing them to manage higher pressures and achieve efficiencies of 80-85%, making them ideal for industrial environments and data centers.
What factors should engineers consider when selecting fan types?
Engineers should evaluate airflow demands, static pressure, and energy efficiency when determining the most suitable fan type for specific applications. The choice between forward and backward curved fans depends on these requirements.
In what applications are forward curved and backward curved fans typically used?
Forward curved fans are commonly found in household appliances and compact HVAC systems, while backward curved fans are used in applications such as electronics cooling in data centers, where steady airflow against resistance is necessary.