Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison between high output fans and standard fans, underscoring the fact that high output fans are engineered to deliver superior airflow and static pressure. This capability is crucial for applications that demand effective thermal management, particularly in environments such as data centers and high-performance computing.
The analysis presented in the article highlights performance characteristics, demonstrating how high output fans are instrumental in preventing overheating and enhancing reliability in rigorous settings. In contrast, standard fans are more suited for less intensive cooling requirements, making the distinction between the two clear and significant.
Introduction
The distinction between high output fans and standard fans has become increasingly critical as the demand for effective thermal management in electronics rises. High output fans, engineered for superior airflow and static pressure, are indispensable in environments such as data centers, where overheating can jeopardize system reliability. Conversely, standard fans, while cost-effective for simpler applications, may struggle under the intense demands of high-density setups.
As engineers navigate the complexities of fan selection, a pivotal question emerges: how do these two types of fans truly compare in terms of performance, efficiency, and suitability for various electronic applications?
Understanding High Output Fans and Standard Fans
High output fan units are engineered to deliver significantly enhanced air movement compared to standard models, making them indispensable for applications that demand superior temperature regulation. These devices feature more powerful motors and innovative blade designs, enabling them to achieve and increased static pressure. In contrast, standard units suffice for less demanding cooling requirements, providing adequate airflow for conventional electronic components but lacking the performance capabilities of high output devices.
The market for high output ventilators in the electronics sector is projected to experience substantial growth by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for effective thermal management solutions. Engineers emphasize the importance of selecting the right type of blower for specific applications, highlighting that high output devices can prevent overheating in critical electronic systems. For instance, in data centers, where heat dissipation is vital, high output blowers have demonstrated their effectiveness in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, thereby enhancing system reliability and longevity.
Recent innovations in high output fan technology feature the incorporation of smart capabilities and energy-efficient designs, enhancing performance while aligning with sustainability goals. As the electronics sector continues to evolve, understanding the distinctions between high output and standard cooling devices becomes crucial for engineers and designers aiming to optimize cooling solutions for their applications.
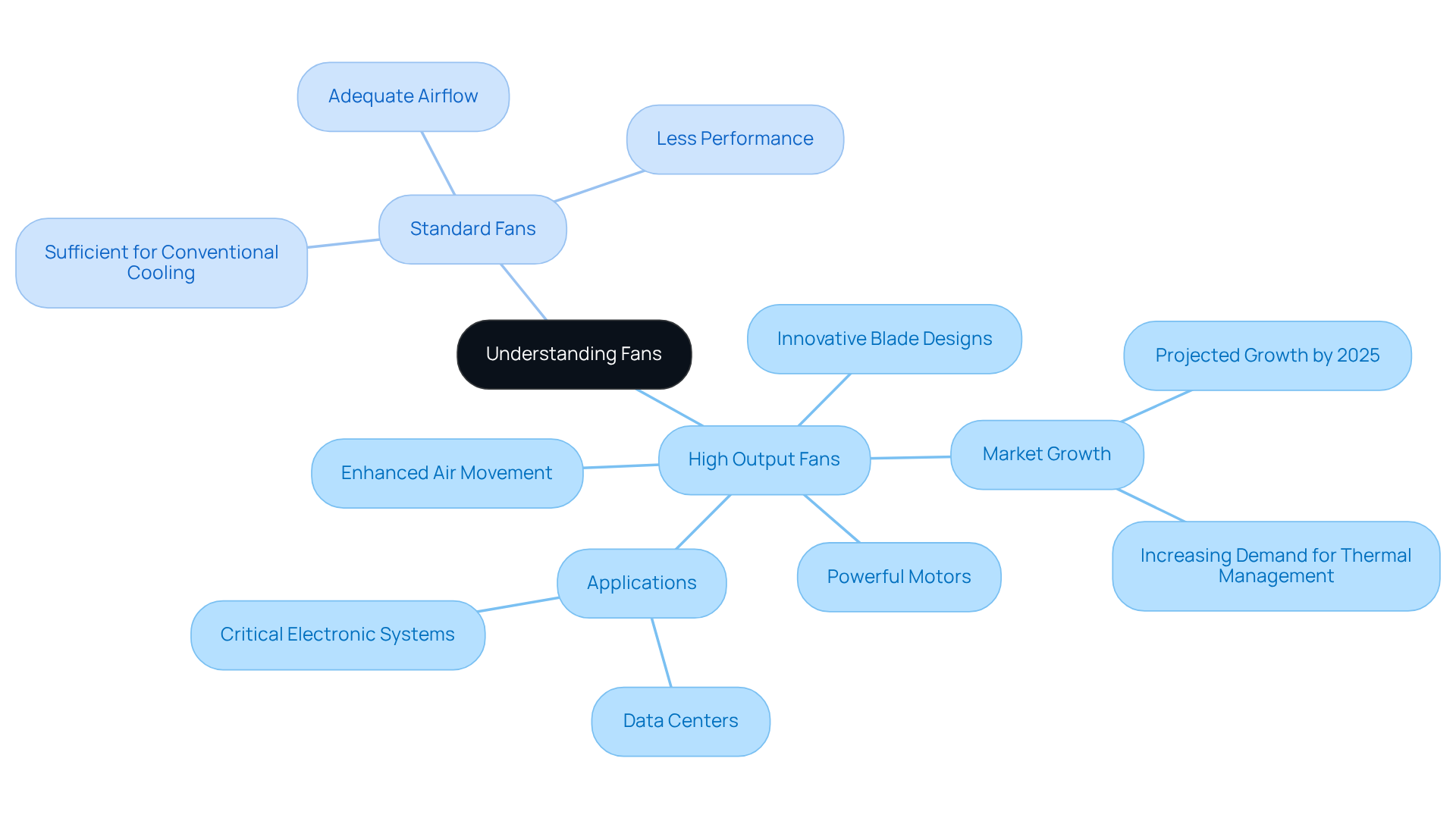
Performance Characteristics of High Output Fans
Elevated output blowers are distinguished by their capacity to deliver airflow rates that often exceed 100 CFM (cubic feet per minute), while maintaining substantial static pressure levels crucial for overcoming resistance in densely packed electronic assemblies. These devices are meticulously engineered to operate at reduced noise levels, with , rendering them ideal for environments where sound control is paramount.
Energy efficiency stands as a pivotal consideration, with many powerful blowers utilizing advanced motor technologies that significantly reduce power consumption without compromising performance. For instance, the Cooler Master Silencio FP 120 boasts a ventilation rating of 44 CFM and a maximum noise level of 14 dBA. This combination of high airflow, low noise, and energy efficiency positions high output fans as essential components in applications such as:
- Server temperature management
- Industrial machinery
- High-performance computing
Recent innovations in fan technology have further improved their efficiency, with certain models featuring fluid dynamic and hydrodynamic bearings that enhance longevity and reduce operational noise. Additionally, factors like installation density play a critical role in fan performance, as a greater number of components can impede airflow, underscoring the importance of meticulous design in ventilation systems.
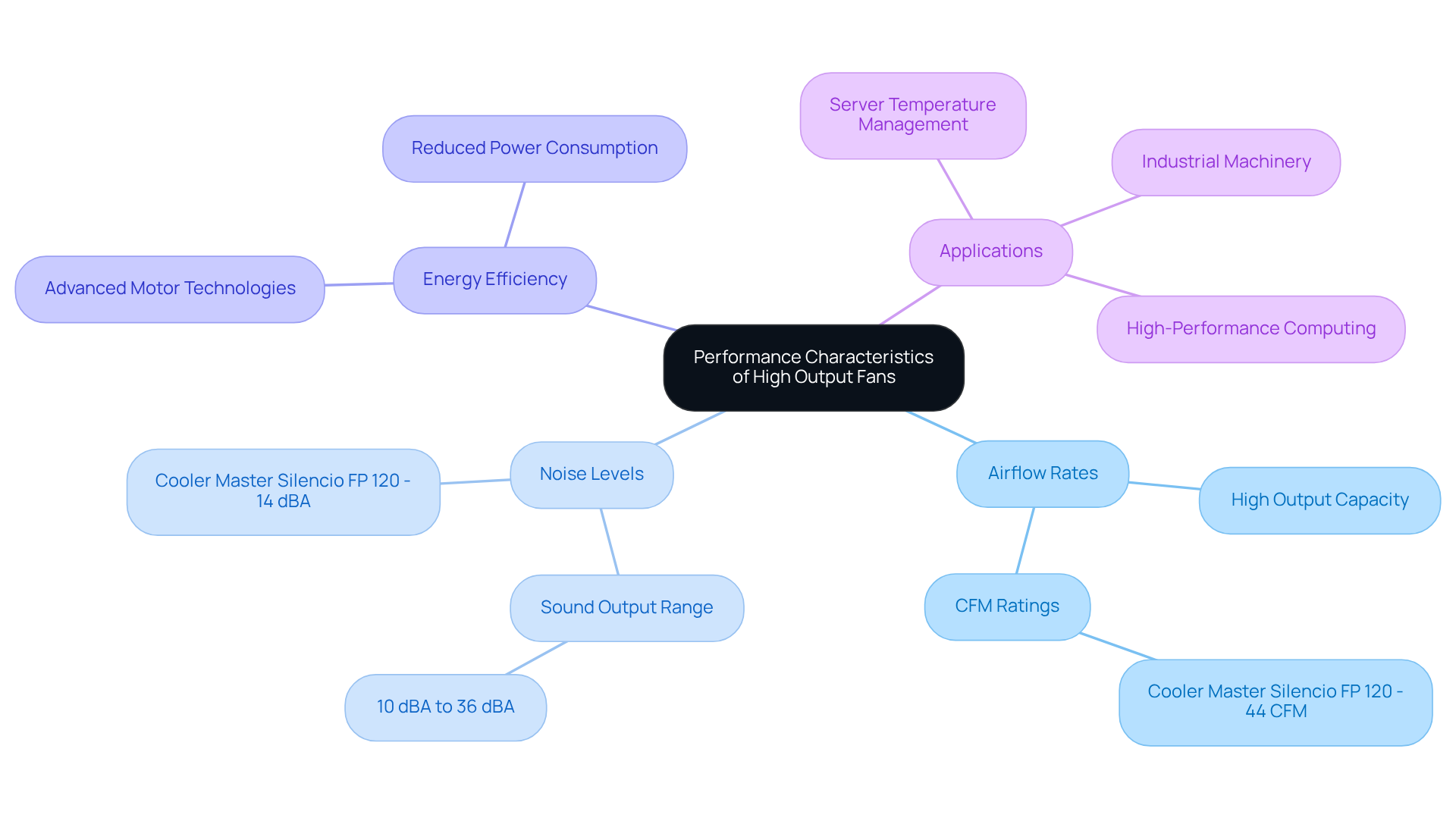
Evaluating Standard Fans: Performance and Limitations
Standard models typically provide circulation rates ranging from 30 to 80 CFM, making them suitable for ventilating simpler electronic systems. However, their limitations become apparent in high-density applications where a high output fan is needed to manage significant air resistance. In such scenarios, typical units may struggle to maintain adequate thermal performance, but those with a can prevent potential overheating and enhance component longevity.
Although standard models are generally quieter than their high output fan counterparts, they may fail to deliver the necessary ventilation in critical situations, necessitating careful consideration when designing thermal management systems for electronics. While their lower cost and simplicity render them appropriate for basic applications, engineers must balance these advantages against their performance limitations.
For instance, the Noctua NF-A12x15 fan operates at 55 CFM with a noise level of 23.9 dBA, exemplifying a compromise between ventilation efficiency and noise output. Furthermore, observations indicate that in high-density configurations, the demand for enhanced ventilation often outweighs the cost benefits of conventional devices, prompting a shift towards solutions that incorporate a high output fan for more robust temperature regulation.
Accessories such as filters can also impact fan performance, influencing circulation and static pressure, which are critical for ensuring optimal temperature regulation in challenging environments.
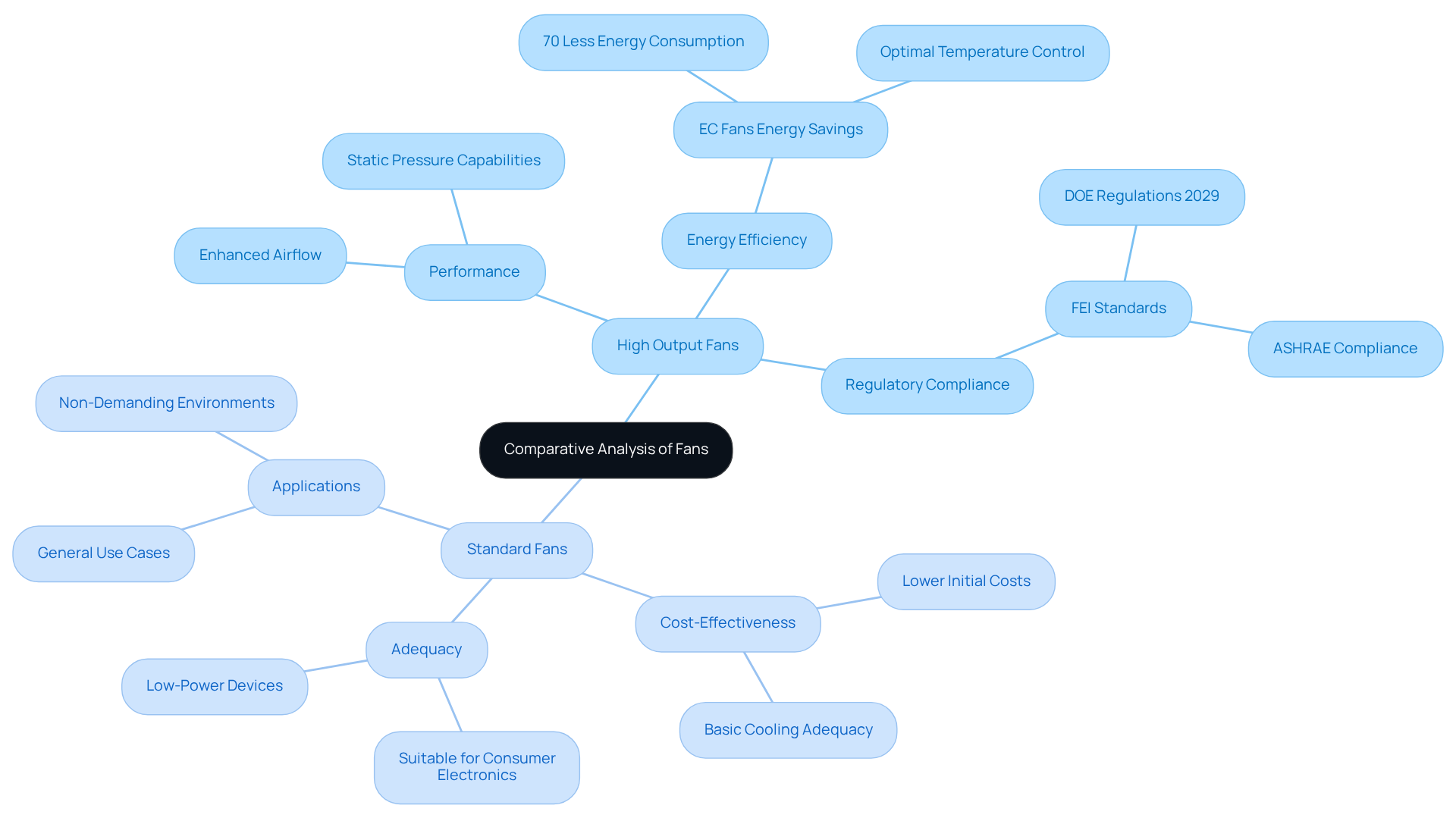
Comparative Analysis: High Output vs. Standard Fans for Electronics Applications
In the realm of electronics applications, the decision between high output fan units and standard units hinges on several critical factors. High output fans prove especially beneficial in demanding environments such as data centers and high-performance computing systems, where enhanced airflow and static pressure capabilities of the high output fan are essential for efficient temperature regulation. The incorporation of EC units in these settings has demonstrated a —up to 70% lower than conventional AC units—while maintaining optimal temperature control.
Furthermore, with the upcoming federal regulation by the Department of Energy (DOE), set to take effect in 2029, fan products will be required to comply with FEI standards. This development necessitates that engineers consider these regulations in their designs. Conversely, standard blowers are typically more appropriate for straightforward applications, including consumer electronics and low-power devices, where cost-effectiveness and basic cooling adequacy are paramount.
Ultimately, the choice between these fan types rests on a comprehensive assessment of the project’s thermal management needs, spatial constraints, and budget considerations. Engineers must meticulously evaluate these elements to select the most suitable fan type, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in their designs.
As Ken Kuntz, Director of Strategic Technologies at Greenheck, asserts, ‘FEI is a powerful engineering tool for designing energy-efficient, code-compliant ventilation systems,’ highlighting the significance of informed fan selection in achieving energy efficiency and compliance with evolving standards. Additionally, the sustainability advantages of EC fans, including their extended lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements, further bolster their application in electronics.
Conclusion
High output fans and standard fans fulfill distinct roles in electronics cooling, each offering unique advantages and limitations. The decision between these two types hinges on specific application needs, particularly regarding airflow requirements and efficiency. High output fans excel in high-density environments, delivering superior airflow and static pressure, which are essential for preventing overheating in critical electronic systems. Conversely, standard fans may suffice for simpler applications but often fall short in demanding scenarios where optimal temperature regulation is crucial.
The article highlights key insights into the performance characteristics of high output fans, including their energy efficiency, noise levels, and advanced technologies. This comparative analysis underscores the importance of evaluating thermal management needs, spatial constraints, and compliance with future regulations when selecting the appropriate fan type. As the electronics sector evolves, understanding these distinctions becomes increasingly vital for engineers and designers seeking to optimize cooling solutions.
In conclusion, the significance of selecting the right fan type cannot be overstated. With technology advancing, the demand for effective thermal management solutions will only grow. It is essential to consider the benefits of high output fans over standard models. By prioritizing performance and energy efficiency, stakeholders can ensure the longevity and reliability of their electronic systems, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future in electronics cooling.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are high output fans?
High output fans are engineered to deliver significantly enhanced air movement compared to standard fans, featuring more powerful motors and innovative blade designs for higher flow rates and increased static pressure.
How do high output fans differ from standard fans?
High output fans provide superior temperature regulation and are suitable for applications with demanding cooling requirements, while standard fans suffice for less demanding needs, offering adequate airflow for conventional electronic components.
Why is the market for high output ventilators expected to grow?
The market for high output ventilators in the electronics sector is projected to grow by 2025 due to the increasing demand for effective thermal management solutions.
What role do high output fans play in data centers?
High output fans are crucial in data centers for heat dissipation, helping to maintain optimal operating temperatures and enhancing system reliability and longevity.
What are some recent innovations in high output fan technology?
Recent innovations include the incorporation of smart capabilities and energy-efficient designs, which enhance performance while supporting sustainability goals.
Why is it important for engineers to understand the distinctions between high output and standard fans?
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for engineers and designers to optimize cooling solutions for their applications, ensuring effective thermal management.