Overview
Compact fans represent a critical innovation in efficient ventilation, specifically engineered to circulate air effectively in confined spaces, particularly within electronic systems. There are two primary types: axial and centrifugal fans. The significance of these fans in modern electronics cannot be overstated; they are vital for energy efficiency, noise reduction, and versatility across various applications. Recent advancements in fan technology underscore their indispensable role in maintaining optimal performance and thermal regulation in a wide array of devices. As such, understanding the functionality and benefits of compact fans is essential for professionals aiming to enhance electronic system performance.
Introduction
Compact fans are transforming the realm of electronic cooling solutions, seamlessly merging efficiency with compact design to meet the escalating demands of modern technology. These small yet powerful devices not only fit effortlessly into confined spaces but also deliver remarkable airflow and pressure capabilities tailored for diverse applications. However, with a myriad of options available, engineers and designers face the challenge of navigating the complexities of selecting the right fan to ensure optimal performance and longevity of electronic systems.
Define Compact Fans: Characteristics and Functionality
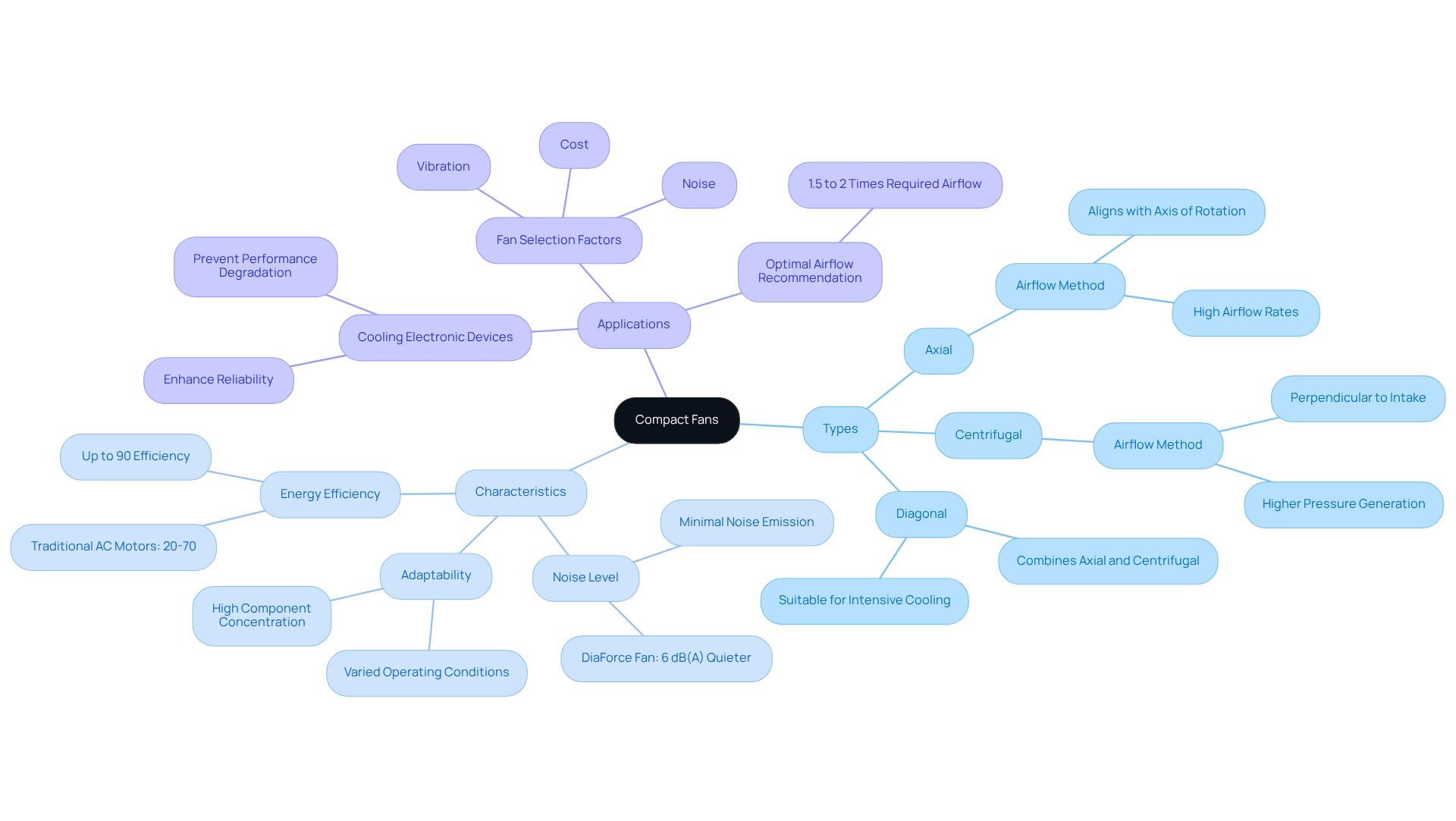
Compact fans are small-sized ventilators that are streamlined yet potent devices designed to effectively circulate air across diverse applications, particularly in electronic systems. The compact fans have dimensions that facilitate installation in tight spaces while delivering efficient cooling solutions. Two primary categories of these compact devices are .
- Axial devices operate by transferring air in alignment with the axis of rotation, making them ideal for scenarios that demand high airflow rates.
- Conversely, centrifugal blowers generate airflow perpendicular to the intake, producing higher pressure, which is advantageous in situations facing greater resistance.
Essential characteristics of small ventilators include minimal noise levels, energy efficiency, and adaptability to varying operating conditions. For instance, axial space-saving blowers are recognized for their ability to deliver high air volume with low power consumption at zero static pressure, making them suitable for exhaust applications. In contrast, centrifugal small blowers excel at producing high pressures, rendering them preferable for situations requiring airflow deflection by 90 degrees.
The efficiency of small fans is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and extending the lifespan of electronic devices, as excessive heat can lead to performance degradation or malfunction. The DiaForce diagonal compact fans exemplify this by merging the benefits of both axial and centrifugal designs to provide enhanced airflow with reduced noise levels, thereby addressing the increasing thermal management demands in electronics due to the growing density of integrated circuits. This innovative fan operates at up to 90% efficiency, significantly surpassing traditional AC motors, which typically operate between 20% and 70% efficiency.
In practical applications, selecting the appropriate fan type is essential. Factors such as vibration, noise, and cost complicate fan selection, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of specific temperature regulation requirements. For optimal performance, it is generally advisable to choose a fan that delivers 1.5 to 2 times the required airflow to accommodate system pressure losses. This approach ensures that electronic systems remain cool and functional, ultimately enhancing their reliability and performance.
Trace the Evolution of Compact Fans in Electronics
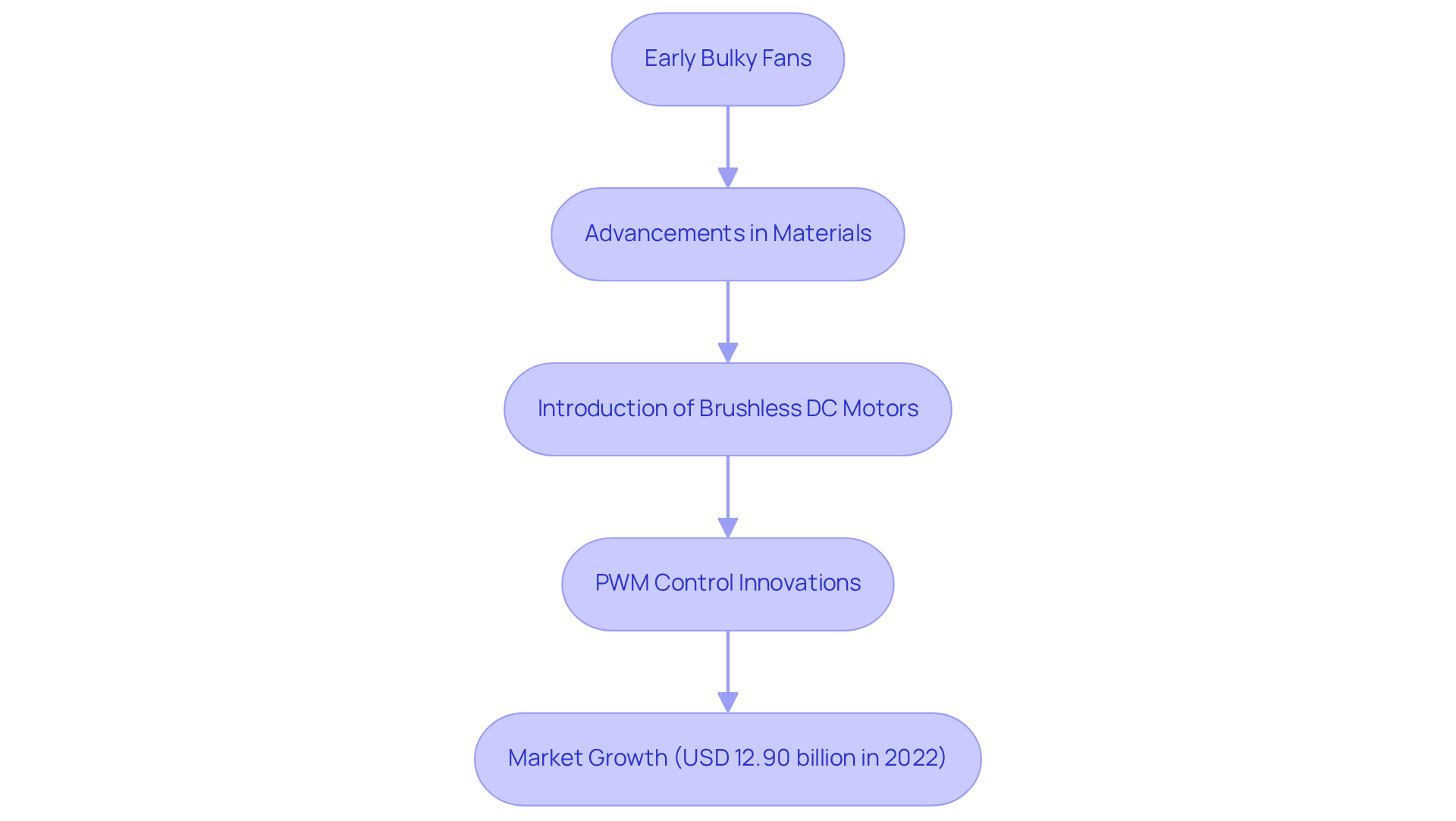
The development of small cooling devices can be traced back to the early days of electrical engineering, where the demand for effective cooling solutions became evident. Initially, these devices were bulky and unwieldy, restricting their use in small electronic applications. However, advancements in materials and motor technology have significantly improved fan design.
The introduction of brushless DC motors in the late 20th century marked a turning point, enabling the creation of smaller, more efficient devices that consume less power and generate less noise. Today, small-sized ventilators are essential to contemporary electronics, with innovations such as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control allowing for precise speed modifications and further enhancing energy efficiency.
Recent market evaluations indicate that the worldwide home ceiling ventilation device market was assessed at USD 12.90 billion in 2022, underscoring the increasing significance of small-scale units in the sector. This evolution reflects the ongoing demand for , which serve as small, high-performance cooling solutions in increasingly miniaturized electronic devices.
As Tim O’Reilly aptly stated, ‘What new technology does is create new opportunities to do a job that customers want done,’ emphasizing the crucial role of technological progress in shaping the future of small appliances.
Examine the Advantages of Compact Fans for Electronics Engineering
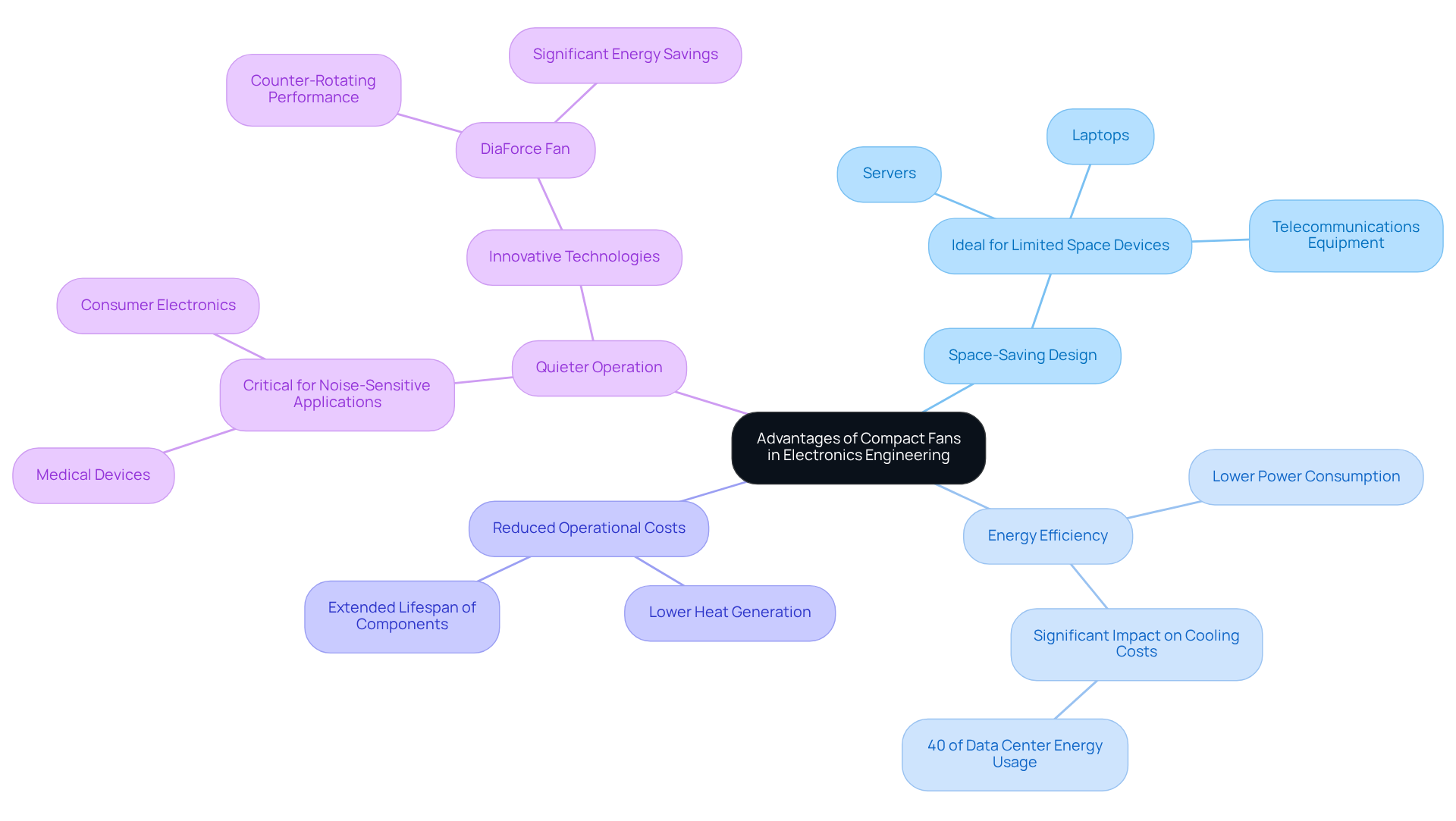
Compact fans are becoming increasingly favored in electronics engineering due to their numerous advantages. Their space-saving design is particularly beneficial for devices with limited real estate, such as laptops, servers, and telecommunications equipment. Remarkably, small ventilators are engineered for energy efficiency, often consuming considerably less power than their larger counterparts while delivering similar airflow. This efficiency translates into reduced operational costs and lower heat generation, which can extend the lifespan of electronic components. For instance, research has indicated that as much as 40% of data center energy consumption in the U.S. is allocated for cooling, underscoring the significance of energy-saving solutions such as small blowers.
Recent advancements in fan technology have also prioritized quieter operation, a critical factor for applications requiring minimal noise, such as medical devices and consumer electronics. As Pete Bartolik notes, “ebm-papst’s revolutionary DiaForce fan delivers the performance of a counter-rotating fan with less noise and significant energy savings.” The DiaForce diagonal space-saving device exemplifies this innovation, merging the performance of counter-rotating units with reduced noise levels and substantial energy savings. This evolution in fan technology not only meets the of modern electronic systems but also addresses the challenges of space and noise constraints. Overall, the incorporation of compact fans into electronic designs provides an appealing blend of size, efficiency, and quiet operation, making them essential for contemporary applications.
Explore Applications of Compact Fans in Electronic Systems
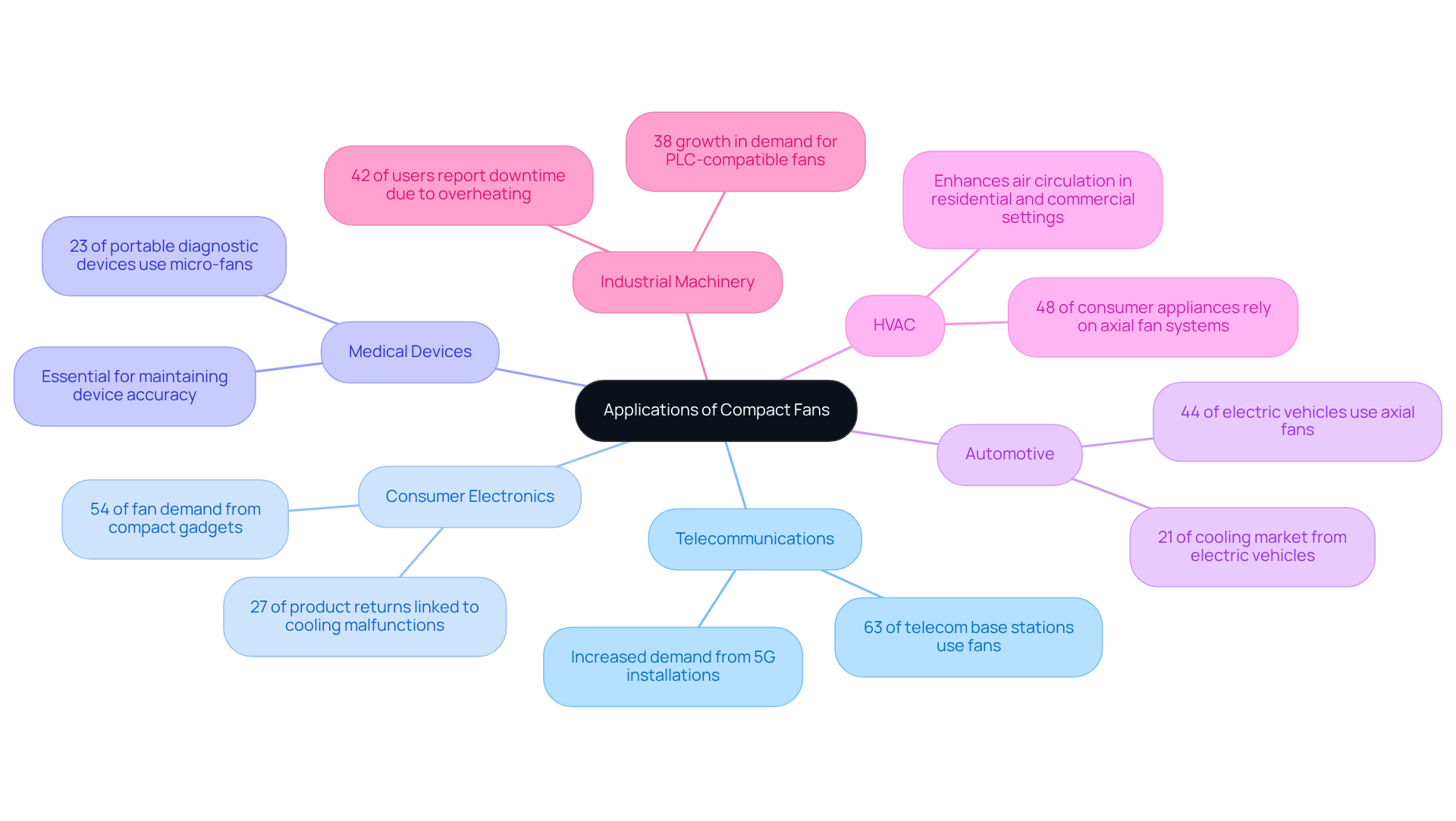
Compact blowers play a critical role across various applications, underscoring their versatility and significance in electronic systems. In the telecommunications sector, these devices are indispensable for cooling apparatus within control cabinets and base stations, ensuring reliable performance in high-density environments. Approximately 63% of telecom base stations and data centers utilize multiple fan systems, emphasizing their crucial role in sustaining optimal performance. In consumer electronics, small fans are prevalent, found in laptops, gaming consoles, and televisions, where they efficiently dissipate heat generated by processors and other components. Notably, consumer electronics account for nearly 54% of fan demand, particularly in compact devices that require effective thermal regulation. Alarmingly, 27% of product returns in this sector are linked to temperature control system malfunctions, highlighting the urgent need for reliable temperature management solutions.
Real-world applications further illustrate their significance:
- Portable diagnostic medical devices, such as ultrasound machines, rely on micro-fans to maintain optimal temperatures for both performance and safety.
- In the automotive industry, specialized cooling devices are increasingly integrated into electric vehicles, which represent 21% of the cooling market, where they regulate battery and motor temperatures.
The HVAC sector also benefits from compact blowers, enhancing air circulation and temperature regulation in both residential and commercial settings. Furthermore, industrial machinery relies on these devices for effective thermal management, with approximately 42% of industrial users reporting increased downtime due to motor failures and overheating. The demand for compatible with programmable logic controllers (PLC) in industrial settings is growing at 38%, indicating a rising necessity for efficient thermal management solutions. The compact fans‘ seamless integration into various devices, along with their efficacy in temperature regulation, positions them as essential components in modern electronic design. Additionally, around 34% of new cooling fan models now feature embedded sensors for real-time monitoring and AI-driven performance control, showcasing significant advancements in fan technology.
Conclusion
Compact fans represent a vital innovation in electronic cooling solutions, merging compact design with high efficiency to meet the demands of modern technology. Their ability to fit into tight spaces while providing effective airflow is crucial for maintaining the performance and longevity of electronic devices. As technology continues to advance, the relevance of these small ventilators in various applications becomes increasingly apparent.
The article explores key features of compact fans, including their types—axial and centrifugal—highlighting their operational efficiencies and suitability for different environments. The evolution of these devices, driven by advancements in motor technology and materials, has led to more energy-efficient and quieter solutions that cater to the diverse needs of sectors such as telecommunications, consumer electronics, and HVAC. The significance of selecting the appropriate fan type to ensure optimal performance is emphasized, alongside the growing market demand for these essential components.
In light of the insights presented, the importance of incorporating compact fans into electronic designs cannot be overstated. As industries strive for enhanced performance and energy efficiency, the role of these small yet powerful devices will only grow. Embracing advancements in fan technology not only addresses current cooling challenges but also paves the way for future innovations in electronics, ultimately fostering reliability and sustainability across various applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are compact fans?
Compact fans are small-sized ventilators designed to effectively circulate air across various applications, particularly in electronic systems. They are streamlined devices that can be installed in tight spaces while providing efficient cooling solutions.
What are the two primary categories of compact fans?
The two primary categories of compact fans are axial fans and centrifugal blowers. Axial fans transfer air along the axis of rotation, while centrifugal blowers generate airflow perpendicular to the intake.
What are the advantages of axial fans?
Axial fans are ideal for scenarios that demand high airflow rates and are recognized for their ability to deliver high air volume with low power consumption at zero static pressure, making them suitable for exhaust applications.
What are the advantages of centrifugal blowers?
Centrifugal blowers excel at producing higher pressure, making them preferable for situations that require airflow deflection by 90 degrees and can handle greater resistance.
What are the essential characteristics of compact fans?
Essential characteristics of compact fans include minimal noise levels, energy efficiency, and adaptability to varying operating conditions.
How do compact fans contribute to the functionality of electronic devices?
The efficiency of compact fans is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and extending the lifespan of electronic devices, as excessive heat can lead to performance degradation or malfunction.
What is the efficiency of DiaForce diagonal compact fans?
DiaForce diagonal compact fans operate at up to 90% efficiency, which significantly surpasses traditional AC motors that typically operate between 20% and 70% efficiency.
What factors should be considered when selecting a compact fan?
When selecting a compact fan, factors such as vibration, noise, cost, and specific temperature regulation requirements should be considered to ensure optimal performance.
What is the recommended airflow for compact fans in electronic systems?
It is generally advisable to choose a fan that delivers 1.5 to 2 times the required airflow to accommodate system pressure losses, ensuring that electronic systems remain cool and functional.

